Tech (1115)
- Morocco and Cameroon agreed to boost cooperation on digital public administration reforms
- Talks included plans for an African forum on AI-driven governance
- The move supports Cameroon's digital reform efforts and low e-governance ranking
Morocco and Cameroon have pledged to strengthen their cooperation in the digital transformation of public administrations, a move that could significantly advance Cameroon's e-governance initiatives. The agreement emerged from a meeting in Rabat between Joseph Lé, Cameroon's Minister of Public Service and Administrative Reform, and Amal El Fallah Seghrouchni, Morocco's Minister Delegate in charge of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform. The discussion, held on the sidelines of the 60th session of the African Training and Research Centre in Administration for Development (CAFRAD) Board of Directors on Tuesday, July 15, included plans for a future African forum on administrative modernization. This forum would emphasize artificial intelligence (AI) as a key driver for performance, transparency, and efficiency in public governance.
During the meeting, the two officials agreed to boost cooperation between Cameroon and Morocco in digitally transforming public administrations. Discussions included potentially organizing an African forum on administrative modernization. This forum would focus on artificial intelligence (AI) as a tool for improving performance, transparency, and efficiency in public governance.
This meeting aligns with Cameroon's ongoing administrative reforms. Earlier in 2025, Cameroon launched AIGLES (Logical Management Application for Workforce and Payroll) software. This integrated digital tool centralizes the management of public servants' careers and payroll. The system has been lauded for streamlining human resources management within the administration, reflecting the government's push to digitize internal processes.
Morocco, one of Africa's most advanced nations in artificial intelligence and e-government, could significantly support Cameroon. This assistance could involve technical aid, sharing expertise in digitizing public services, developing smart systems, and training civil servants.
Cameroon still faces substantial hurdles in digital governance. The United Nations' 2024 E-Government Development Index report ranks the country 155th out of 193 with a score of 0.4294. This figure is significantly below the global average of 0.6382. Therefore, this partnership with Morocco could be a strategic chance for Cameroon to bridge this gap and firmly establish its administration in the age of smart digital governance.
Samira Njoya
- Gabon’s government launched Missamou, its first virtual assistant chatbot, to modernise state-citizen communication.
- Missamou uses natural language processing to provide round-the-clock official information and public services via Facebook Messenger.
- This move reflects Gabon’s push for digital inclusion and follows similar AI initiatives in African countries like Benin.
Governments worldwide are increasingly turning to chatbots to modernize public communication and improve citizens’ access to information. This growing trend reflects a broader push for more direct, interactive, and continuous engagement between the state and the public.
On July 15, the Gabonese government unveiled Missamou, a virtual assistant available through Facebook Messenger. Described as the country's first government chatbot, Missamou allows users to ask questions, check official news, access public services, and obtain information about administrative procedures—anytime, anywhere.
Built using natural language processing (NLP), Missamou can understand everyday speech and deliver real-time responses from verified government sources. The system is designed to ease the burden on traditional services like call centres and in-person offices.
This initiative is part of Gabon’s broader digital transformation agenda, which promotes transparency, open data, and digital inclusion. By launching Missamou on Facebook Messenger, a widely used platform among the youth, the government hopes to ensure high user engagement and widespread adoption.
With the launch of Missamou, Gabon seeks to enhance the distribution of official information, streamline access to public services, and encourage greater citizen engagement. This effort aligns with a broader regional movement toward digital innovation in governance.
In 2023, Benin introduced GPT-BJ, a sophisticated conversational assistant designed to respond to complex inquiries regarding key legal frameworks such as the General Tax Code, Labour Code, Digital Code, and Penal Code. Created by the Agence des Systèmes d'Information et du Numérique (ASIN), GPT-BJ has been recognized as a pioneering tool for improving legal accessibility and promoting transparent governance.
By adopting similar AI-driven solutions, Gabon is positioning itself alongside regional leaders in leveraging technology for more connected, responsive, and citizen-focused government services.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
- The CNASS has partnered with the State Digital Agency to digitize the national health insurance system
- The agreement targets improved infrastructure, service quality, and digital inclusion for underserved populations
- It supports CNASS’s 2025–2030 strategy to expand coverage, enhance transparency, and better serve vulnerable groups
Mauritania's Caisse Nationale de Solidarité en Santé (CNASS), a voluntary health insurance scheme with a social mission, announced on Tuesday, July 15, the signing of a cooperation agreement with the State Digital Agency (AN-ETAT). This initiative marks the beginning of a partnership aimed at digitally transforming Mauritania's social protection system.
According to a CNASS press release, the agreement sets several concrete objectives. These include strengthening and securing CNASS's digital infrastructure, adopting modern solutions to improve service access and quality, and facilitating the sharing of technological expertise between the two institutions. The shared goal is to enhance digital inclusion, particularly for populations with limited exposure to digital tools.
This collaboration occurs amidst a broader national push to accelerate public service transformation. For CNASS, the agreement fully aligns with its upcoming 2025–2030 digitization strategy, which is currently under development. This strategy aims to improve service quality, enhance coordination with healthcare providers, ensure better tracking of benefits, and more effectively address the needs of vulnerable populations.
In Mauritania, CNASS plays a key role in the country’s social protection policy, particularly in expanding health coverage to informal sector workers. By partnering with AN-ETAT, the operational body responsible for implementing the national digital strategy, CNASS is taking a significant step toward more efficient, transparent, and interconnected management.
Ultimately, the partnership is expected to streamline services, improve data reliability, and strengthen transparency in health insurance administration. It also aims to enhance the user experience by facilitating remote access to benefits, while laying the foundation for a more inclusive, modern, and sustainable social protection system for all Mauritanians.
Samira Njoya
• Ivory Coast and French group Ynov Campus signed an agreement to open the first Ynov Campus in sub-Saharan Africa.
• A second deal with the Magic System Foundation will launch a Digital Academy to train youth in digital skills.
• These projects aim to create 40,000 jobs and attract $1.6 billion in investment by 2028.
Ivory Coast has taken two bold steps to tackle the digital skills gap and fuel its economic growth.
Authorities signed two major agreements to train local youth in tech and prepare the country for a digital future. The Village of Information Technologies and Biotechnology (VITIB), based in Grand-Bassam, signed a deal with French training powerhouse Ynov Campus.
This agreement will establish the first Ynov campus in sub-Saharan Africa. Ynov will offer hands-on training in digital fields like web development, data science, digital design, audiovisual production, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence.
Officials sealed the deal during the inaugural Ivoire Tech Forum held in Abidjan from July 9 to July 11.
A second agreement between VITIB and the Magic System Foundation will launch the VITIB Digital Academy. This academy will boost local digital skills, help youth integrate into the job market, and improve employability in high-demand tech sectors.
Both projects form part of VITIB’s larger expansion strategy. The site already hosts 96 companies, five data centers, and a one-stop-shop for business setup. VITIB's 2023–2028 plan, budgeted at CFA180 billion ($320 million), seeks to transform Grand-Bassam into a fully integrated smart city.
VITIB wants to create 40,000 jobs and attract $1.6 billion in investment over the next three years.
As digital transformation accelerates, Ivory Coast is under pressure to build a tech-savvy workforce that meets international standards. The Ministry of Digital Transition plans to train thousands in cybersecurity, cloud computing, data management, advanced programming, and AI.
Authorities have made digital upskilling a national priority. They want to support startup growth, ensure digital sovereignty, and fully integrate into West Africa’s digital economy.
Samira Njoya
-
Côte d’Ivoire signed two MoUs with UAE’s G42 Presight to support digital governance and strategy renewal
-
The deal comes as the current digital plan nears its 2025 end, after major infrastructure gains
-
Partnership aims to enhance AI use and public service efficiency, leveraging G42’s regional expertise
The Ivorian government has signed two non-binding memoranda of understanding with G42 Presight, an Emirati tech firm specializing in big data analytics and artificial intelligence. The agreements were signed on the sidelines of the inaugural Ivoire Tech Forum, held in Abidjan from July 9 to July 11.
One agreement establishes a collaborative framework for public administration reform and digitalization, signed with the Ministry of State in charge of Civil Service and Administrative Modernization. The second involves developing a national digital strategy, in partnership with the Ministry of Digital Transition and Digitalization.
This initiative comes as Côte d’Ivoire’s National Digital Development Strategy (SNDN) is set to expire this year. Launched five years ago, the SNDN aimed to strengthen digital inclusion, cybersecurity, and digital infrastructure development. Its achievements include deploying over 5,207 kilometers of fiber-optic cable, creating several online public service portals, and operationalizing the National Cybersecurity Agency.
In artificial intelligence, the country also adopted a dedicated data management strategy. This strategy aims to build a more efficient, accessible, and resilient administration capable of addressing the challenges of 21st-century digital governance.
While non-binding, these agreements lay the groundwork for stronger technological cooperation between Abidjan and Abu Dhabi. Through this partnership, Côte d’Ivoire seeks to leverage the expertise of G42 Presight, which has previously supported projects in Egypt and Rwanda in big data, AI, and smart governance. The goal is to improve the quality of public services, increase transparency in public action, and enhance state decision-making.
Samira Njoya
African governments push digital transformation to modernize healthcare. Computerized patient records (CPRs) emerge as a key tool in this effort. Although adoption remains uneven, countries make steady progress amid growing digital public services.
Consulting firm McKinsey & Company reported in 2023 that digital health tools including teleconsultations, CPRs, and chronic disease apps could reduce African health expenditures by up to 15%. This cost-saving potential, combined with the need to upgrade healthcare, drives government interest in CPRs. These systems now form the backbone of many national e-health strategies.
CPRs centralize and secure medical data. They improve patient follow-up, coordinate care, and reduce medical errors. By replacing paper records, which often cause information loss and delays, CPRs address urgent modernization needs.
Beyond care quality, CPRs supply health authorities with real-time data. This data helps anticipate, monitor, and manage epidemics. It also supports public health policy decisions.
Pilot Projects Underway in Several Countries
Several countries run pilot CPR projects. Côte d’Ivoire’s health facilities with CPRs generated over CFA1.25 billion ($2.2 million) in tracked medical revenue in 2024, according to the Directorate of IT and Digital Health. More than 268 facilities connect to the Hospital Information System (HIS) and CPR.
Senegal, Rwanda, Ghana, and Kenya have launched similar systems. Nigeria currently tests interoperability between CPRs and its national health insurance database.
A Rapidly Growing Global Market
The global electronic medical records market grows rapidly. Market intelligence firm Mordor Intelligence projects it will reach $42.1 billion by 2029, up from $32.8 billion in 2024, with a 5.11% annual growth rate. The Covid-19 pandemic accelerated this trend by highlighting the need for fast, reliable, and secure clinical data access.
Technological advances, political will, and wider accessibility drive this growth—even in low- and middle-income countries.
Persistent Challenges to Overcome
Despite potential, Africa faces major hurdles. Limited internet access, especially in rural areas, remains a top barrier. The International Telecommunication Union reported only 38% of Africans had internet access in 2024. Training healthcare workers in digital skills also lags. Without it, CPR reliability and adoption suffer. Data protection poses another challenge. Only 40 African countries have personal data protection laws, and cybersecurity remains weak. Patient and professional trust depends on securing medical information.
Towards Pan-African Governance of Digital Health
Experts call for pan-African coordination to overcome these challenges. Harmonizing standards, ensuring system interoperability, and setting common data security rules would create a strong foundation for sustainable e-health.
Widespread CPR adoption could transform African healthcare—if governments invest in digital infrastructure, train professionals, and protect data. CPRs must become more than technology tools; they should form the backbone of modern, resilient, and inclusive public health policies.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
Algeria is turning to its growing start-up ecosystem to help modernize its infrastructure and strengthen national innovation.
On July 9, the government created a joint commission linking the Ministry of Public Works and Basic Infrastructure with the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Start-ups, and Micro-enterprises. The goal: involve start-ups in designing and executing large-scale infrastructure projects.
The collaboration aims to build a structured framework for start-ups to contribute to projects in railways, guided transport systems, and smart construction site management. At the center of the strategy lies digital innovation, applied research, and knowledge management.
To operationalize this, the government plans to launch exchange platforms and co-development workshops. These will connect start-ups with infrastructure stakeholders early in the process—from planning and monitoring through to project execution. Authorities want to embed local, agile, and cost-effective solutions into the fabric of national infrastructure.
This initiative forms part of the knowledge economy strategy introduced in 2020. Since then, Algeria has created a dedicated Ministry for Start-ups, a "Start-up" label, the Algerian Start-up Fund (ASF), and several incubators and support programs.
Currently, Algeria counts between 5,000 and 8,000 start-ups, with more than 1,200 having received the official “Start-up” label from the National Labeling Commission.
By involving these companies in strategic infrastructure development, the government aims to boost homegrown innovation, reduce technological dependence, and build national capacity. The wider ambition is to create skilled jobs and anchor entrepreneurship around the real needs of the domestic market.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
McKinsey estimates that artificial intelligence (AI) could contribute as much as $1.2 trillion to Africa's economy by 2030. Unlocking this potential will largely depend on strategic talent development, a path Cameroon is now strongly pursuing.
Cameroon aims to train 60,000 artificial intelligence (AI) specialists by 2040, including 40% women, as part of its National AI Strategy (SNIA). Minister of Posts and Telecommunications Minette Libom Li Likeng recently unveiled this initiative, which is part of a broader vision to position the country as an African hub for artificial intelligence.
The strategy's key objectives include creating 12,000 direct jobs, developing 12 sovereign solutions with significant socioeconomic impact, and anticipating an AI contribution to national GDP of between 0.8% and 1.2%. Special attention is being given to linguistic diversity, with efforts to develop AI models that incorporate national languages. This is seen as a crucial way to boost digital inclusion and promote local cultural heritage.
To achieve these ambitions, however, Cameroon must address several critical gaps. The country still lags significantly in digital infrastructure, particularly in deploying modern data centers, developing secure cloud platforms, and ensuring consistent broadband connectivity, especially in rural areas.
This reality is reflected at the continental level in the latest ranking by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Cameroon scored 46.3 out of 100, placing 30th out of 42 African countries. This result falls below the continental average of 56, underscoring the need for the country to accelerate its efforts.
Addressing Talent Shortages and Promoting Inclusion
Training qualified talent remains one of the main challenges. A shortage of engineers, researchers, and AI specialists is holding back sectoral growth. To address this, Cameroon will need to invest heavily in creating centers of excellence, establish schools and institutes focused on advanced technologies, and integrate AI training programs into secondary and university curricula. Structuring partnerships between universities, tech companies, and public institutions will be essential to align educational content with market needs.
In addition, it will be crucial to implement continuing education and professional retraining programs to equip a broad segment of the population with the digital skills needed for tomorrow’s economy. Expanding access to high-speed internet, especially in remote areas, must accompany this momentum, as should the stimulation of an innovative entrepreneurial ecosystem capable of attracting investors and fostering the emergence of local solutions.
The goal of training 40% women is ambitious and commendable. Achieving it calls for proactive measures such as awareness campaigns, mentoring, support for women’s careers in tech, and efforts to combat gender stereotypes in science-related fields.
Despite these challenges, encouraging signs are emerging. The recent adoption of a data protection law and the first national consultations on AI reflect a clear political will to establish a robust regulatory framework. This is an essential condition for structuring the sector and building trust among stakeholders.
Samira Njoya
Personalization, Data, Planning: How AI Is Transforming African Education
Africa faces a deep education crisis. Student numbers surge, teachers are scarce, and infrastructure lags behind. In 2024, UNESCO reported that 58% of adolescents aged 15 to 17 in sub-Saharan Africa do not attend school. The continent counts 98 million children outside the education system. Many schools lack electricity, internet, and basic resources.
AI Offers a Lifeline for Overworked Teachers
Teacher shortages cripple African classrooms. UNESCO says Africa needs to recruit more than 16.5 million teachers by 2030 to keep up with population growth. AI cannot replace teachers, but it can help them. Automated grading, custom teaching materials, and lesson planning tools lighten the load. In Kenya, teachers use the Kalasik assistant—a chatbot that generates lesson plans and automates repetitive tasks.
AI Delivers Personalized and Inclusive Learning
AI adapts learning to each student’s needs. Overcrowded classrooms make individual attention impossible, but smart systems change that. Students access interactive exercises, tutorials, and tailored feedback—even after school hours. Personalized learning keeps students engaged and cuts dropout rates, especially in rural and marginalized communities.
In West Africa, the Kwame for Science assistant tutors science students in 11 countries. It boasts an 87% accuracy rate for its top-three answers and serves 750 users over several months.
Data-Driven Decisions Shape Education Policy
AI gives education leaders real-time data. Ministries of Education spot low-enrollment regions, forecast teacher demand, and allocate resources where they matter most. Predictive analytics shifts planning from reactive to proactive, using demographic and school data.
Governments Put AI at the Heart of Education Strategy
Several African nations now weave AI into their education plans. Kenya launched a national AI strategy for 2025–2030 with UNESCO, focusing on digital skills in schools. Zambia and Côte d’Ivoire have also prioritized education in their AI strategies, promoting data analysis and personalized learning. Nigeria develops AI skills and integrates AI in education through partnerships with universities and private companies. Senegal, Burkina Faso, and Congo have added AI in education to their digital roadmaps.
Major Hurdles Remain
Despite these advances, African education systems face steep challenges in scaling AI. To begin with, poor digital infrastructure slows down deployment in many regions. Moreover, Teacher training on digital tools remains insufficient. Finally, data privacy and ethics are often under-regulated and sustainable funding models for EdTech remain elusive.
AI solutions need heavy investment and a solid business model. Protecting student data requires strict ethical rules. Tools must fit local languages and cultures. Above all, governments, partners, investors, and the private sector must commit long-term support to move beyond pilot projects and build a sustainable education system.
Samira Njoya
The rapid rise of remote work has fueled the phenomenon of digital nomads, creating new opportunities for African countries. With growing appeal, developing infrastructure, and policies still taking shape, the continent could very well become a major player in this new global work landscape.
Since 2020, the way people work has been changing in deep but often unnoticed ways. In only a few years, digital nomadism has evolved from a niche concept into a global trend. This rise has been fueled by the digital shift in many jobs, the growth of remote work, and a growing demand for more flexible living. While it first took hold in large Western cities, the movement is now spreading across Africa, a region with the potential to unlock billions of dollars in economic value if it takes the right steps.
A Global Movement with Local Impact
Digital nomads are workers who use a laptop and an internet connection to work from anywhere in the world. It could be a freelance marketer living in Nairobi for six months, a Senegalese developer dividing her time between Dakar and Bali, or an American designer spending the summer in Zanzibar.
According to 2025 data from Nomads.com, a global digital nomad community platform, there are now more than 80 million digital nomads worldwide—and the number keeps rising. Their financial footprint is significant. On average, a digital nomad earns $124,000 annually and spends between $1,000 and $3,000 per month in their host country on housing, food, entertainment, coworking spaces, and transport. This provides a steady stream of income for local economies, without the strain of mass tourism. Americans make up the largest share, with 46 million nomads. About 88% of global digital nomads come from countries outside Africa.
|
Category |
Subcategory |
Value |
|
Age |
53% are between 31 and 39 years old |
|
|
|
Men |
91% |
|
Gender |
Women |
7% |
|
Other genders |
2% |
|
|
Education |
90% have higher education |
|
|
|
Per city |
63 days |
|
Average length of stay |
||
|
Per country |
167 days |
|
|
Average annual income |
$124,304 |
|
|
|
Full-time employees |
38% |
|
Work Status |
Startup founders |
18% |
|
Freelancers |
18% |
|
|
Top Sectors (Men) |
Software development |
35% |
|
Web development |
28% |
|
|
Startup founders |
28% |
|
|
Marketing |
16% |
|
|
Top Sectors (Women) |
Marketing |
16% |
|
Creative industry |
15% |
|
|
Startups |
12% |
|
|
Software development |
10% |
|
|
Motivations |
Work setting + getaways in Africa |
Africa Steps Into the Spotlight
Africa is starting to gain recognition as an appealing destination for remote workers. Cities like Cape Town, Johannesburg, Marrakech, Accra, Dakar, Abuja, Luanda, Libreville, and Cotonou are seeing growing interest. These places attract a new wave of remote workers seeking authentic experiences, lower living costs, and meaningful social connections. Many of these cities offer reliable high-speed internet, electricity, modern accommodation and workspaces, and access to food, transport, and healthcare—making it possible to balance productive workdays with tourist exploration.
This trend is not limited to foreign visitors. A growing number of young Africans in digital fields—web development, design, content creation, community management—are also embracing a mobile lifestyle, often within the continent. This intra-African nomadism is supported by countries offering full or partial visa exemptions, such as Senegal, Benin, Kenya, Ghana, and Rwanda. These policies are reshaping how professionals move and work in Africa’s digital age.
Billions in Economic Opportunity
According to global immigration firm Newland Chase, the 35 million digital nomads counted in 2021 contributed $787 billion to the global economy. Although detailed data for Africa is lacking, a modest projection suggests the continent could earn $6 billion per year if it hosted 500,000 foreign digital nomads spending $1,000 monthly. If Africa attracted just 2% of the world’s estimated 80 million nomads in 2025—that is 1.6 million individuals—the continent could bring in close to $20 billion annually through direct local spending.
Beyond daily spending, digital nomadism can fuel growth in sectors such as short-term housing, food and hospitality, internet services, local transport, and leisure activities like hiking and tourism. Thousands of small businesses—especially in urban areas—stand to benefit from this expanding market.

Early but Promising Initiatives
Some African countries have already started tailoring offers to digital nomads. In 2020, Mauritius introduced its Premium Visa. It is free, valid for one year (renewable), and available to citizens of 114 countries. Applicants must prove that their main income is earned outside Mauritius and show a minimum monthly income of $1,500.
Cape Verde launched a similar visa in 2020, targeting both tech and tourism. The visa lasts six months (renewable) and requires payment. Digital nomads in Cape Verde are exempt from income tax and local taxes. While there is no official income threshold, applicants must show an average bank balance of at least €1,500 over the previous six months.
In 2024, South Africa joined in with its digital nomad visa, allowing stays from three months to three years. Applicants must provide three months of bank statements showing a gross annual salary of at least 650,796 rand (about $36,782).
Other countries like Namibia and Kenya also launched digital nomad visas in 2024 to attract skilled professionals and boost their economies. However, Africa still lags behind Latin America and Southeast Asia, which already offer nomad visas, tech hubs, tax incentives, and tailored services.
Challenges That Remain
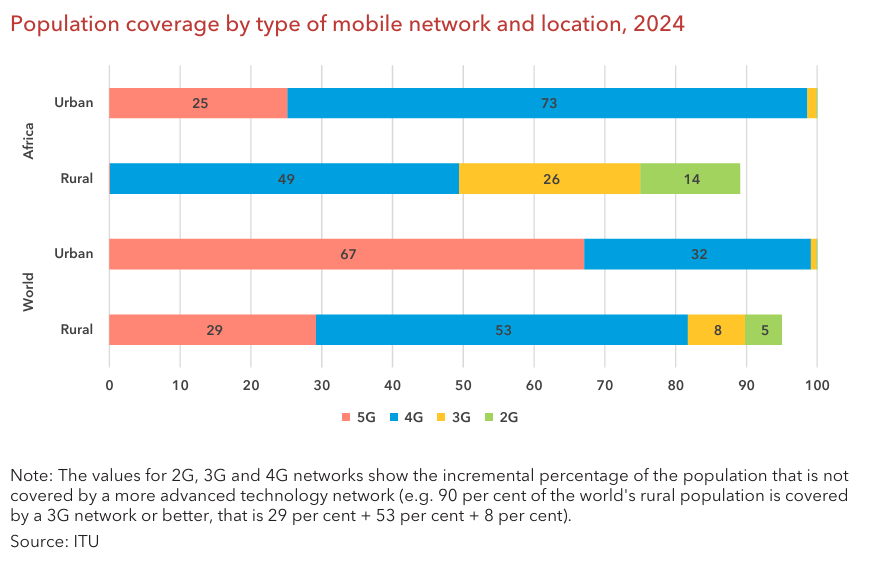
Africa has clear potential to benefit from digital nomadism. Internet coverage is improving across the continent. According to the International Telecommunication Union, 4G now covers 71% of the population, while 3G covers 86%. However, 5G still only reaches 11%. In urban areas, 4G covers 73% and 5G reaches 25%. Countries like South Africa, Senegal, Mauritius, Nigeria, Botswana, Ethiopia, Seychelles, Tunisia, and Lesotho already offer 5G access in their capitals. In rural areas, coverage is lower—49% for 4G, 26% for 3G, and 14% for 2G. While major cities usually offer stable internet, many secondary regions do not.
Another barrier is cost. The cheapest mobile data plan (2GB) costs 3.9% of the average monthly gross national income (GNI) per person, while fixed internet (5GB) costs 13.4% of GNI. These rates are considered high, exceeding the United Nations target of 2% of GNI for affordable access. Globally, the average cost is closer to 1% of GNI for mobile and 2.3% for fixed internet.
Other obstacles include political and security concerns, especially in areas affected by instability—although these are a minority. The lack of a clear legal status for digital nomads also makes many destinations less appealing. Tourist visas are not designed for extended stays and lack tailored benefits. To change this, digital nomadism needs to be integrated into national policies on tourism, entrepreneurship, and youth employment.
Digital nomadism is not just a trend or a lifestyle for Western elites. It reflects a deep shift in how the world works. Africa has a real chance to play a leading role—if it invests, plans, and innovates wisely.
More...
• Cameroon launched its AI strategy to become Africa’s leading hub by 2040, with goals for jobs, training, and GDP growth.
• It focuses on governance, infrastructure, local language models, edge computing, talent, and regional cooperation.
• The IMF ranks Cameroon low in AI readiness (0.34/1), citing gaps the strategy aims to close.
On Monday, July 7, Minister of Posts and Telecommunications Minette Libom Li Likeng unveiled Cameroon’s National Artificial Intelligence Strategy (SNIA) during the second edition of the National Consultations on AI. This strategy, anchored in a vision for 2040, aims to position the country as a continental AI hub by focusing on sovereign, inclusive, and sustainable solutions rooted in African cultural realities.
The SNIA seeks to make Cameroon "the leading AI hub in Africa" by promoting solutions based on African values. Its key targets include training 60,000 individuals, with 40 percent being women. The strategy also aims to create 12,000 direct jobs, generate a GDP contribution from AI of between 0.8 percent and 1.2 percent, and develop 12 sovereign, high-impact AI solutions. Special attention is given to linguistic diversity through the development of multilingual models that incorporate national languages.
Seven Structural Pillars to Deliver the Strategy
The strategic document is built around seven interdependent pillars. The first pillar focuses on governance and digital sovereignty. This includes establishing a Cameroonian AI Authority, a Presidential Council on AI, and drafting a framework law that addresses ethical considerations and inter-ministerial coordination mechanisms. The second pillar addresses data and digital infrastructure, calling for the creation of a government Data Lake, mass digitization of public services, interoperability standards, and a targeted Open Data policy.
The third pillar promotes multilingual and inclusive AI through the development of a local language model, referred to as "GPT Cameroon." It also emphasizes enhancing national languages via linguistic research and voice data collection. The fourth pillar targets sovereign technological infrastructure, including the deployment of 15 regional Edge Computing nodes powered by solar microgrids to strengthen energy resilience.
The fifth pillar is dedicated to training, research, and human capital. Plans include establishing five AI centers of excellence, training 4,000 people annually, implementing a diaspora talent return program, and providing greater support for local research. The sixth pillar centers on innovation and sector-specific use cases. This aims to support startups through accelerators and encourage AI adoption in key areas such as health, agriculture, justice, and education.
Lastly, the seventh pillar emphasizes cooperation and regional outreach. This involves creating an AI network for Central Africa, strengthening international partnerships, and exporting "Made in Cameroon" digital solutions.
According to the 2024 AI Preparedness Index published by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Cameroon scores 0.34 out of 1. This places it in the lower half of the global ranking. The country lags in digital infrastructure and innovation but shows promising potential in human capital. The national strategy specifically aims to address these gaps by accelerating regulatory alignment and encouraging AI adoption across public services.
With this roadmap, Cameroon aims to align with the continent’s broader digital transformation momentum and fully harness emerging technologies to support its socio-economic development.
Samira Njoya
Morocco is stepping up efforts to make digital technology a key driver of development and technological independence. The country plans to open an engineering school focused on digital transition and artificial intelligence.
On July 4, Minister of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform Amal El Fallah Seghrouchni signed a partnership deal with Minister of Higher Education Azzedine El Midaoui and André Azoulay, president of the Foundation for Research, Development and Innovation in Science and Engineering (FRDISI). The agreement sets up the Higher School of Engineers in Digital Transition and Artificial Intelligence and launches specialized training programs.
The Ministry of Digital Affairs said the initiative aims to align academic programs with real-world needs. The goal is to match training to the demands of local regions, the economy, and national technology priorities.
This project supports Morocco’s “Digital Morocco 2030” strategy, which targets training 100,000 young people annually by 2030 and creating 240,000 digital sector jobs. The plan follows the National AI Forum held last week in Salé, where nine agreements were signed with public and private partners. The forum stressed the importance of building human capital and developing a national roadmap for ethical and responsible AI use.
The new school will train engineers who can create and implement innovative digital solutions across sectors like public services, healthcare, industry, and education. Morocco aims to solve internal challenges while preparing young people for the jobs of the future.
Beyond education, the project will boost Morocco’s digital sovereignty, drive innovation, and help position the country as a magnet for tech startups and regional R&D centers.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
- “Siraj” service covers 1.2 million students with tools for attendance tracking and records access.
- Part of a broader push to digitise education, including e-textbooks and diploma authentication.
- Low internet penetration and device access remain key implementation challenges.
Mauritania has launched a new digital service enabling parents to monitor their children’s school attendance, academic records and learning materials, authorities said on Tuesday, July 1, as the country accelerates efforts to modernise its education system.
The platform, called “Siraj,” is accessible via the government’s digital portal “Khidmati” and serves about 1.2 million students nationwide. Parents can view required textbooks, track absences, check annual grade averages, request school transfers, and locate schools on an interactive map.
The initiative is part of a national digital education transformation strategy under development. Earlier this year, officials began designing a roadmap to digitise the sector, including plans to introduce digital diplomas and an online training platform for primary school teachers. In October 2024, the government announced the rollout of e-textbooks.
Authorities said Siraj is intended to strengthen family engagement in education, a factor linked to improved academic performance. A 2023 UNESCO report, Edtech And Parental Engagement, cited strong potential for educational technologies to help parents better support their children’s learning.
However, implementation faces hurdles. UNESCO’s research on similar initiatives in Kenya highlighted obstacles such as limited parental involvement, lack of digital skills, and inadequate infrastructure.
In Mauritania, internet access remains uneven: only 37.4% of the population was online in 2023, according to the International Telecommunication Union. Ensuring that parents have internet-capable devices and affordable connectivity will be critical to the programme’s success, officials said.
- MPs propose a West African pact for responsible AI and multilingual digital content.
- Initiative aligns with ECOWAS Digital Strategy 2024–2029 and $10.5 mln World Bank project.
- Region aims to equip 63% youth population with 21st-century digital skills.
Integrating digital technologies into African education systems is often presented as a panacea for the structural weaknesses of the sector. The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) wants to make it a strategic lever for its youth.
As part of efforts to modernise schools and train young people for the digital economy, West African lawmakers recommend drawing a regional pact for ethical and sovereign use of artificial intelligence in education.
Meeting since June 30 in Dakar, members of the ECOWAS Parliament’s joint committee on Education, Health, Culture, Telecommunications, and IT discussed accelerating the integration of technology into education systems across the region.
The proposed West African Pact would promote responsible AI, develop inclusive multilingual digital content, and strengthen teacher training through a regional EdTech lab network, officials said.
Lawmakers also called for expanded electricity and internet access in schools, a comprehensive mapping of digital platforms, support for homegrown innovation in universities, and deeper regional cooperation to share educational resources.
The discussions align with the ECOWAS Digital Strategy 2024–2029, adopted last October, which positions ICT and digital education as pillars for growth, inclusion, and regional autonomy.
Funding will partly come from the West Africa Regional Digital Integration Project (WARDIP), a $10.5 million World Bank programme aiming to improve connectivity and promote an integrated digital market.
Some member states, including Senegal and Nigeria, have already deployed online learning platforms and distributed tablets in rural communities. ECOWAS now plans to expand these efforts through transnational e-learning initiatives and a regional fund to narrow the educational digital divide.
With about 63% of the region’s population under 25, ECOWAS faces a demographic imperative to equip youth with relevant digital skills. The African Union estimates that $60 million will be needed over the next five years to finance large-scale digital education programmes across the continent.
Officials said the investments should not only improve employability and foster EdTech innovation but also reduce inequalities, enhance academic mobility, and bolster the region’s technological sovereignty.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ola Schad Akinocho















