Tech (1156)
- Egypt launched Wa3i.net, a digital awareness platform under the national Digital Citizenship and Online Protection initiative.
- Authorities aim to strengthen cybersecurity awareness among nearly 98 million internet users, representing about 72.2% of the population.
- Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky reported that 27.4% of Egyptian internet users faced online threats in 2024, while phishing and social engineering attacks rose 44% across the Middle East, Turkey and Africa region.
Egypt has chosen to strengthen public awareness of digital safety practices in order to reduce user vulnerability to cyber risks.
The Egyptian Ministry of Communications and Information Technology announced on Friday, March 6, the launch of a national initiative called “Digital Citizenship and Online Protection.” The program places the Wa3i.net platform at its core.
Authorities designed the platform to raise awareness of digital best practices and reduce citizens’ exposure to cyber threats.
The Wa3i.net platform operates as a knowledge hub dedicated to digital security. The platform provides Arabic-language educational content, practical guides and training resources. The platform targets several audiences, including children, teenagers, parents and teachers. Authorities aim to promote best practices in personal data protection, safe internet browsing and responsible technology use. The program follows the principle that awareness represents the first line of defense against cyberattacks.
Authorities believe that stronger digital literacy will reduce citizens’ vulnerability to threats such as phishing attacks, cyberbullying, online fraud and the spread of misinformation. Consequently, the government intends to build a stronger cybersecurity culture across society.
The initiative comes as internet usage expands rapidly in Egypt. Data from DataReportal shows that Egypt had nearly 98 million internet users, representing an internet penetration rate of 72.2% of the population.
However, the growth of digital services, social media platforms and online payment systems has also increased exposure to cybercrime. These risks affect individuals, businesses and public institutions alike.
Industry data confirms the scale of the challenge. Cybersecurity company Kaspersky reported that 27.4% of internet users in Egypt encountered online threats in 2024, including malicious websites or malware distributed through the web.
The company also reported that phishing and social engineering attacks increased by 44% across the Middle East, Turkey and Africa region, highlighting the increasing sophistication of cybercriminal methods.
The Egyptian government plans to address these challenges through a collaborative approach. The program includes partnerships with public institutions, international organizations and private sector companies.
Authorities expect these partnerships to facilitate knowledge sharing, promote best practices and strengthen national cybersecurity capabilities.
Samira Njoya
- The AfCFTA Secretariat, Quest Ghana Limited, and the Seychelles government signed a memorandum of understanding to develop the archipelago as a digital trade hub.
- The initiative aims to integrate Seychellois companies, particularly MSMEs, into Africa’s digital value chains and cross-border e-commerce ecosystem.
- The Seychelles benefits from strong digital readiness, with internet penetration at 87.4%, while its e-commerce market could reach $46.41 million by 2027, according to Statista.
The African Continental Free Trade Area Secretariat formalized a memorandum of understanding on March 5 with Quest Ghana Limited and the Government of Seychelles.
The partners designed the agreement to transform the Indian Ocean archipelago into a competitive hub for digital trade and cross-border commerce across Africa. The initiative focuses on integrating Seychellois businesses into Africa’s digital value chains.
Stakeholders said the project aims to enable local operators to participate more actively in dematerialized trade flows. The program will rely on trade facilitation mechanisms established under the African Continental Free Trade Area. Consequently, authorities expect the initiative to expand the role of Seychelles-based companies in the continent’s growing digital marketplace. The partnership plans to introduce a technical framework that will secure cross-border digital transactions.
The agreement emphasizes system interoperability, which partners consider essential for simplifying payments and commercial exchanges between companies operating under different jurisdictions. This technical alignment aims to reduce friction in cross-border digital trade and accelerate regional integration.
Today, the #AfCFTA Secretariat, Quest Ghana Limited and the government of the Republic of Seychelles signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to advance Seychelles’ digital economy, and digital trade under the AfCFTA.
— AfCFTA Secretariat Official (@AfCFTA) March 5, 2026
The collaboration aims to position Seychelles as a… pic.twitter.com/M4xsA9bnZZ
The initiative places particular emphasis on micro, small and medium-sized enterprises. Partners aim to improve MSMEs’ access to digital infrastructure in order to remove barriers that limit participation in intra-African trade. They expect stronger digital access to allow local companies to join Africa’s expanding digital commerce ecosystem.
The Seychelles supports this diversification strategy with a relatively advanced digital environment. Data from DataReportal shows that internet penetration in the country reached 87.4% of the population in early 2025.
At the same time, e-commerce continues to expand. Estimates from Statista indicate that the Seychelles’ online retail market could grow at an average annual rate of 14.35% between 2023 and 2027, reaching $46.41 million by 2027.
At the continental level, the project aligns with the AfCFTA’s ambition to build a single market of 1.3 billion consumers. Policymakers view e-commerce and digital services as key drivers for achieving a combined African GDP of $3.4 trillion. Officials expect digital trade to reduce transaction costs and accelerate the circulation of goods and services across African markets.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
- Orange Business Senegal signed a partnership with Port Autonome de Dakar to transform the port into a Smart Port.
- The agreement includes connectivity upgrades, payment digitalization and critical system security improvements to ensure operational continuity.
- The port generated about 95% of Senegal’s customs revenues, and it ranked first in sub-Saharan Africa in the 2024 Container Port Performance Index.
Orange Business Senegal announced on Thursday, March 5, that it signed a partnership agreement with the Port Autonome de Dakar.
The partners designed the agreement to modernize the port and transform it into a “Smart Port.”
Orange Business Sénégal au cœur de la transformation du Port Autonome de Dakar
— Orange Business Sénégal (@obs_senegal) March 5, 2026
Le Port Autonome de Dakar est bien plus qu’une infrastructure logistique.
C’est un pilier stratégique de l’économie sénégalaise traitant l’essentiel des flux commerciaux du pays.
Ce jeudi 5 mars,… pic.twitter.com/ceBUBpoCLT
Orange said the agreement covers infrastructure modernization through world-class connectivity, improvements in operational performance, digitalization of payment processes, and enhanced security of critical systems to ensure business continuity.
Waly Diouf Bodian, Director General of the Port Authority, said the partnership aims to reshape the port’s value chains around robust digital infrastructure.
“It is no longer just about digitizing what already exists, but about restructuring our value chains around robust and resilient digital infrastructure,” Bodian said during the signing ceremony, according to remarks reported by Seneweb.
The agreement forms part of broader digital transformation efforts underway at the port authority.
The port will launch a pilot phase for the electronic exchange of delivery orders on Jan. 2, 2026, using the electronic single-window port platform, which has operated since February 2024.
Earlier, in October 2024, the port signed a memorandum of understanding with Huawei Technologies to support digitalization of port services.
The agreement includes the implementation of technology solutions designed to improve the management of truck flows and container handling at the port.
Authorities view technological innovation as a key driver of competitiveness for the Port of Dakar at both regional and international levels.
The infrastructure generates nearly 95% of national customs revenues, representing approximately 25% of Senegal’s state budget.
The introduction of the single-window system contributed to performance improvements in 2024, according to the Container Port Performance Index (CPPI) published by the World Bank and S&P Global Market Intelligence.
The port ranked first in sub-Saharan Africa in the 2024 index. Its score improved from –82 in 2023 to +23 in 2024, marking one of the strongest global performance gains during the period.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
- President Abdelmadjid Tebboune validated Algeria’s 2025-2029 national cybersecurity strategy
- Kaspersky recorded more than 70 million cyberattacks targeting Algeria in 2024.
- The International Telecommunication Union ranks Algeria in Tier 3 in its 2024 Global Cybersecurity Index.
The Information Systems Security Agency of the Ministry of National Defence unveiled Algeria’s 2025-2029 National Strategy for Information Systems Security on March 3. President Abdelmadjid Tebboune approved the document, which aims to structure the state’s response to rising cyber threats and strengthen the country’s digital resilience.
The plan is based on several priorities. Authorities plan to strengthen technical capabilities, improve inter-agency coordination and reinforce prevention and cyber-incident response. The strategy also places particular emphasis on improving cybersecurity awareness among public institutions and citizens.
According to the Ministry of National Defence, the strategy pursues three main objectives: protecting critical infrastructure, securing sensitive state data and ensuring the continuity of public services amid rapid digital transformation. More broadly, it aims to safeguard Algeria’s digital sovereignty and strengthen trust in the national digital ecosystem.
The initiative comes amid sustained cybercrime activity. Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky reported that Algeria faced more than 70 million cyberattacks in 2024. Over the same period, systems blocked more than 13 million phishing attempts and nearly 750,000 malicious email attachments, highlighting the scale of the threat.
Institutionally, Algeria remains at the “establishing” stage, or Tier 3, in cybersecurity according to the 2024 Global Cybersecurity Index published by the International Telecommunication Union. The ranking reflects structured government engagement that remains in a consolidation phase.
Beyond security concerns, authorities view stronger cyber capabilities as an economic priority. Globally, cybercrime generates annual losses estimated in the trillions of dollars. In this context, the 2025–2029 strategy aims to secure the expansion of Algeria’s digital economy and protect digital investments.
Samira Njoya
-
Generative AI enables the creation of synthetic sexual abuse images and deepfakes targeting minors.
-
Around 40% of Africans aged 15–24 currently have internet access, increasing both opportunity and exposure to risk.
-
African regulatory frameworks remain fragmented and largely unprepared to address AI-generated harms.
As submarine cables multiply and 4G and 5G networks expand across the continent, an entire generation integrates into the digital world. Governments and businesses leverage this connectivity to drive economic, educational and social development. However, millions of minors face new, more sophisticated and harder-to-detect threats.
According to joint estimates from the International Telecommunication Union and the African Union, about 40% of Africans aged 15 to 24 currently access the internet. This steadily rising figure creates a dual imperative: authorities must accelerate digital inclusion while strengthening child protection mechanisms.
Generative AI, a New Frontier for Online Abuse
Generative AI is transforming the nature of online harm targeting children. Cyberbullying no longer relies solely on insults or the circulation of authentic images. Individuals now use widely accessible applications to fabricate intimate images, clone voices or manipulate videos from a single photograph.
In 2023, the Internet Watch Foundation reported for the first time the circulation of entirely AI-generated child sexual abuse images online. The organization warned that these technologies significantly lower technical barriers and complicate perpetrator identification. INTERPOL also acknowledged that increasingly sophisticated deepfakes hinder investigations and make it harder to distinguish authentic material from manipulated images. Criminals also use these tools to conduct “sextortion,” in which individuals blackmail teenagers and their families using fabricated content.
Child rights organizations report that predators also use AI to analyze online behavior, emotional states and personal interests in order to refine manipulation strategies.
Legal Frameworks Remain Inadequate
Regulatory responses remain uneven across the continent. The Malabo Convention, adopted by the African Union, establishes a foundation for cybersecurity and personal data protection. However, policymakers drafted the convention before the emergence of generative AI, and the text does not explicitly address synthetic content targeting minors.
Several African countries have enacted data protection laws that regulate the collection and processing of personal information. However, most frameworks do not include specific provisions regarding platform liability in cases involving deepfakes of children.
In South Africa, the Protection of Personal Information Act imposes strict obligations regarding data processing, including data relating to minors. Nevertheless, lawmakers designed the framework primarily to protect privacy rather than to proactively prevent AI-generated harmful content.
In Cameroon, authorities adopted a charter on online child protection in 2023 that establishes shared responsibility among telecom operators, regulators and families. However, the law protects only children under 18, while the legal age of majority in Cameroon stands at 21, which leaves a segment of minors without full legal coverage.
Toward More Structured AI Governance
Policymakers are advancing discussions at both continental and global levels. The African Union is developing a strategy to regulate AI development and use, with a focus on ethics, data governance and digital sovereignty. Policymakers are increasingly recognizing child protection as a cross-cutting issue, particularly in a continent with the world’s youngest population.
At the global level, UNICEF advocates a “Safety by Design” approach that integrates child protection into the design phase of digital products. The organization argues that stakeholders must anticipate risks rather than intervene only after harmful content spreads. UNICEF also warns that children face heightened exposure to online threats in environments where regulation, local-language moderation and reporting mechanisms remain underdeveloped.
Samira Njoya
-
Morocco’s CNDP and Portugal’s CNPD signed a memorandum of understanding in Lisbon on Feb. 25 to formalize institutional cooperation.
-
The agreement prioritizes artificial intelligence, deepfakes and digital violence amid rising cross-border data risks.
-
Morocco’s internet penetration exceeded 92% at end-2025, while Portugal reported high generative AI adoption and advanced GDPR enforcement.
Morocco and Portugal have stepped up coordination to tackle emerging digital challenges. The national authorities responsible for personal data protection in both countries signed a memorandum of understanding in Lisbon on Wednesday, Feb. 25, to structure their institutional cooperation.
Paula Meira Lourenço, president of the Comissão Nacional de Proteção de Dados (CNPD), and Omar Seghrouchni, president of Morocco’s Commission nationale de contrôle de la protection des données à caractère personnel (CNDP), signed the agreement at the CNPD headquarters. The text established an operational framework to intensify technical expertise exchanges and information sharing.
AI and Digital Violence at the Core of Priorities
The cooperation will primarily target issues related to artificial intelligence, image manipulation technologies such as deepfakes and digital violence. These phenomena have raised growing concerns regarding privacy protection, legal certainty and regulation of digital practices. The memorandum also provides for training programs, educational projects and the exchange of best practices in oversight and enforcement of regulatory frameworks, as technology continues to evolve rapidly.
This initiative comes as both countries experience strong digital momentum. In Morocco, internet penetration exceeded 92% at the end of 2025, according to DataReportal, placing the country among the most connected markets in Africa. Meanwhile, Portugal has recorded high adoption rates of generative artificial intelligence, according to a recent study by Bain & Company. Portugal has also built advanced experience in enforcing the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Anchoring Cooperation in Regional Networks
The agreement provides for annual bilateral meetings to ensure structured follow-up. Each institution will also leverage its international networks. The CNPD will rely on the Ibero-American Data Protection Network (RIPD) and the Lusophone Data Protection Network (RLPD). Meanwhile, Morocco’s CNDP will activate the Network of African Data Protection Authorities (NADPA-RAPDP) and the Francophone Association of Data Protection Authorities (AFAPDP).
Samira Njoya
-
The Gabonese government approved a draft ordinance amending the Criminal Procedure Code to regulate the admissibility of digital evidence.
-
Authorities now require digital evidence to prove reliability, authenticity and traceability through verification by authorized public entities.
-
An international Cellebrite study shows that 60% of investigators consider digital evidence more decisive than DNA in some cases, while 74% say it improves case resolution rates.
The Gabonese government approved a draft ordinance on February 26, during a cabinet meeting. Justice Minister Augustin Emane presented the text, which amends the Criminal Procedure Code to regulate the admissibility of digital evidence before courts. The reform introduces formal requirements that aim to adapt the judicial system to the rise in digital-related offenses.
The reform establishes a technical framework for the use of electronic data in criminal proceedings. Authorities will admit digital evidence only if it demonstrates reliability, authenticity and traceability. Authorized public entities, including cybersecurity services and competent state bodies, will verify the data before courts accept it. Authorities aim to secure the judicial use of digital data and to limit manipulation and falsification risks.
Through this amendment, authorities seek to strengthen the reliability of investigations and to enhance the protection of litigants. The formal recognition of technical validation standards also aims to regulate prosecutions related to digital offenses, which have increased alongside the rapid expansion of digital usage in the country. Internet penetration now covers more than half of Gabon’s population, which increases the volume of digital interactions that may generate disputes.
The ordinance forms part of a broader regional movement to modernize African legal frameworks in response to digital transformation. Governments across the continent face a growing number of disputes related to electronic content, online transactions and information systems. At the international level, digital evidence continues to gain importance in criminal investigations. A study conducted by Israeli digital forensics specialist Cellebrite among more than 2,000 investigators, prosecutors and experts shows that 60% of respondents consider digital evidence more decisive than DNA in certain cases, while 74% state that its use improves investigation resolution rates.
According to Gabonese authorities, the ordinance will enter into force after publication in the Official Gazette, in line with legislative promulgation procedures. Authorities consider the reform a first step toward modernizing the judicial handling of digital offenses and strengthening legal certainty in criminal matters in line with the country’s technological evolution.
Samira Njoya
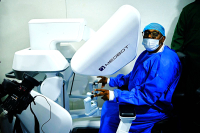
Medical robotics is reshaping healthcare in Africa, creating new opportunities to improve care quality and streamline costs. But the continent faces significant hurdles, from workforce training to financing, if these technologies are to deliver tangible benefits for patients.
Medical robotics, covering robot-assisted surgery, diagnostics and hospital logistics, is emerging as a lever for healthcare modernization in parts of Africa.
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the medical robotics market in the Middle East and Africa is forecast to grow at a compound annual rate of 13.5% between 2022 and 2029. The market is projected to expand from $451.26 million in 2021 to $1.14 billion by 2029.
Despite this growth, adoption across Africa remains limited compared with other regions and is largely confined to higher-income countries or those with advanced hospital infrastructure.
Flagship initiatives across the continent
South Africa is among the most advanced markets. Several public hospitals have performed more than 600 robot-assisted procedures, mainly in urology and gynecology. Hospitals report shorter recovery times and fewer post-operative complications.
In Nigeria, authorities recently approved a robotic surgery platform, enabling such procedures in a public hospital for the first time.
In Luanda, Angola, medical teams have conducted telesurgery trials using robotic systems. These tests suggest robotic surgery could be deployed even in settings with limited network capacity.
Morocco has also positioned itself as a regional pioneer. A radical prostatectomy was performed remotely between Casablanca and Shanghai, demonstrating the feasibility of long-distance telesurgery. Additional procedures between Moroccan cities point to growing domestic expertise and institutional interest in robotic surgery.
Beyond surgery, robotics is being deployed in Kenya and other countries for hospital logistics and assistance tasks. This improves operational efficiency and allows nursing staff to focus on clinical care.
Barriers to wider adoption
Cost remains the primary constraint. Robotic systems often cost several million dollars, limiting access for public hospitals. A platform such as the da Vinci 5 typically ranges between $1.5 million and $2.5 million, excluding maintenance and consumables.
Training is another major hurdle. Robot-assisted procedures require specialized surgical and technical skills, as well as ongoing certification.
Institutions such as Ircad Africa in Rwanda are addressing this gap by training African surgeons in minimally invasive and robotic techniques. At the same time, the rise of startups and innovation hubs focused on artificial intelligence, robotics and e-health could support longer-term ecosystem development.
Medical robotics also presents regulatory and ethical challenges, including liability in case of system failure, data protection standards and the role of automation in patient care.
Growth trajectory despite constraints
Globally, the surgical robotics market is expected to exceed $22.89 billion by 2030, according to Spherical Insights. Emerging economies investing in healthcare digitization could capture part of this expansion.
For African countries, scaling medical robotics will depend on coordinated public policy, targeted investment, workforce training and international partnerships. If these conditions are met, robotics could become a practical tool for strengthening healthcare systems and improving the quality of care.
Samira Njoya
-
Plan includes artisan ID card, national registry
-
Sector employs 22%, contributes 7% to GDP
Morocco will invest 36 million dirhams ($3.9 million) to fast-track the digital transformation of its handicrafts sector, under agreements signed on Wednesday between the State Secretariat for Handicrafts, the Chambers of Handicrafts and their Federation, and the Digital Development Agency. Two additional agreements covering international promotion and institutional support were signed at the same ceremony.
The digitalization agreement provides for the rollout of a professional artisan ID card and the launch of a National Artisan Registry. It also includes the digitalization of services offered by the Chambers and their affiliated bodies. Authorities say the system will streamline administrative processes, improve efficiency, and establish core digital infrastructure for the sector.
The initiative is part of the national development program for handicrafts. The sector is a key contributor to Morocco’s economy, supporting employment, exports, and regional development.
Official figures show the sector employs 22% of the national workforce and contributes 7% to GDP. Exports have grown by 7.6%, while handicraft sales account for 10% of tourism-related foreign exchange earnings. The digital upgrade is expected to boost productivity, formalize activities, and expand access to domestic and international markets.
International promotion and institutional support
The two additional agreements focus on promoting Moroccan craftsmanship abroad, in partnership with SMAP EVENTS, and on a 2026 sector development plan. That plan targets professional structuring, training, and technical support for artisans.
Together, these measures aim to strengthen the sector’s competitiveness and improve market access for artisans, while fostering a more structured and productive ecosystem alongside the digital reforms led by the Digital Development Agency.
Samira Njoya
-
Tunisia CDC launches MAIR for greentech scale-up
-
Program targets commercialization-stage startups, SMEs
-
Tunisia startups raised $6.6 million in 2025
Tunisia’s Caisse des Dépôts et Consignations (CDC) on Tuesday announced the launch of the first cohort of the MAIR program, Market Access for Impact and Resilience. The financing mechanism targets greentech startups and small and medium-sized enterprises in the commercialization phase.
The program aims to support industrial scale-up, facilitate initial market entry, and strengthen revenues for selected companies.
MAIR prioritizes sectors linked to the green transition, including renewable energy, sustainable mobility, eco-construction, waste management, sustainable agriculture, water technologies, energy efficiency and biodiversity. By providing financing at a stage when funding needs increase for industrialization and commercialization, MAIR seeks to bridge the gap between seed funding and full commercial rollout.
MAIR is deployed under the GreenTECH initiative led by Smart Capital and integrated into the Greenov'i project. The project is funded by the European Union through the Tunisie Verte et Durable program and implemented by Expertise France in collaboration with the International Center for Environmental Technologies of Tunis, the Ministry of Environment, and the Ministry of Economy and Planning.
Financing architecture
The mechanism forms part of a broader financing framework that also includes VAIR, Venture Acceleration for Impact and Resilience, which supports startups in the ideation phase as they develop proofs of concept. The overall program plans to fund 32 early-stage startups and support 10 startups and SMEs in accessing markets, with a target of roughly 300 direct jobs in green transition sectors.
The launch comes amid limited funding for Tunisia’s entrepreneurial ecosystem. According to Wamda’s annual report, Tunisian startups raised $6.6 million across 13 deals in 2025, below levels recorded in several other Middle East and North Africa markets. In that context, public instruments dedicated to impact-driven innovation are positioned as key support mechanisms for early-growth companies.
By targeting industrial segments linked to the green transition and focusing on companies at a later stage of development, MAIR aims to strengthen the ability of Tunisian startups to turn innovations into marketable products and secure a sustainable position in their markets.
Samira Njoya
More...
- Algeria launched four new digital platforms, bringing total integrated university digital services to 73.
- The platforms target academic management, entrepreneurship, student welfare, and service modernization.
- The initiative aligns with Algeria’s national digital transformation strategy through 2030.
Kamel Baddari, Minister of Higher Education and Scientific Research, officially launched the platforms on February 24, in Algiers. The launch increased the total number of digital services integrated into the sector’s information system to 73.
During the ceremony, Kamel Baddari stated that universities, data centers, and research laboratories across the country jointly drove the expansion of the digital ecosystem.
He emphasized that the platforms “illustrate the high level of digitalization achieved by the sector in its teaching, research, governance, and services to the university community.”
The four new platforms cover strategic and social priorities.
The Digital Registry of University Programs aims to improve the management of university economic programs and enhance the conversion of scientific research results into projects with high economic and social added value.
The University Network of Incubators and Entrepreneurship Development Centers (AUNEI) seeks to consolidate the innovation ecosystem and support students and researchers in launching start-ups.
An online psychological consultation platform promotes mental health within universities. In addition, an integrated meal reservation platform within the student mobile application modernizes campus catering services.
The launch builds on a broader digitalization process within the higher education sector. Authorities have already deployed electronic diploma management systems, scientific research monitoring portals, and dematerialized administrative management modules in recent years.
These services aim to reduce bureaucratic delays, improve governance efficiency, and strengthen collaboration between universities and socio-economic partners.
The initiative aligns with Algeria’s national digital transformation strategy through 2030.
Two cross-cutting pillars support this strategy. First, authorities are establishing an adapted legal and regulatory framework, including a draft law on digitalization currently under development. Second, authorities are strengthening cybersecurity measures to protect data and information systems against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
-
Uganda signed a public-private partnership to establish an ICT innovation hub in Mbale focused on skills and jobs.
-
The project includes blockchain-based digital certification to reduce credential fraud.
-
Authorities aim to align youth training with global digital labor demand.
The Ministry of ICT and National Guidance announced on February 19, the signing of a partnership with Spotlight on Africa and Algorithmic Partners.
The agreement provides for the creation of an ICT innovation hub in Mbale. The hub aims to strengthen digital skills among Ugandan youth and support local technology entrepreneurship.
According to authorities, the initiative marks a shift from policy intent to implementation in Uganda’s digital development agenda. The project relies on public-private collaboration to expand access to in-demand skills, stimulate local innovation, and promote economic empowerment, particularly for women.
The future center will offer training ranging from basic digital literacy to advanced competencies, including coding, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technologies.
The program also integrates a blockchain-based digital certification system. The system aims to secure qualification verification and reduce document fraud.
By strengthening trust between training institutions, employers, and graduates, the tool should improve transparency in the digital labor market and support the emergence of a structured, skills-driven innovation ecosystem.
Beyond training, the project seeks to expand access to digital public services in underserved areas and energize local innovation ecosystems.
The initiative aligns with Uganda’s national digital roadmap, which prioritizes digital infrastructure, skills development, cybersecurity, and data protection. The roadmap aims to build an inclusive, job-creating digital economy.
Programs such as the DigiTrack mobile computer lab have already trained more than 11,000 people nationwide over the past two quarters. These programs have included young people with special needs by delivering digital skills directly to communities.
The initiative also complements Uganda’s national business process outsourcing strategy, which aims to connect English-speaking young professionals to global markets.
The initiative also reflects broader continental trends. According to the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation, sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills for approximately 230 million jobs by 2030.
The fourth industrial revolution accelerates the digital transformation of labor markets and creates large-scale demand for qualified talent. As a result, centers such as the Mbale hub provide practical responses by training youth for future jobs and supporting economic and social inclusion at scale.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
- Madagascar converted CNTEMAD into a Public Virtual University backed by $3 million in financing.
- The university aims to enroll up to 49,000 students annually by 2029 and produce 10,000 additional graduates each year.
- The World Bank estimates that 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030.
The National Center for Tele-Education and Distance Learning (CNTEMAD) has transitioned into a Public Virtual University. Authorities officially launched the project on February 20 in Antananarivo. The World Bank is supporting the initiative through its DECIM program to expand access to higher education via digital tools and strengthen Madagascar’s human capital.
The new digital university operates on a platform developed in partnership with SAYNA. The platform manages the entire student journey remotely, from enrollment to examinations and thesis defenses. The project seeks to address growing demand for university education, particularly in remote areas, while reducing logistical costs and modernizing teaching methods.
The government allocated $3 million in financing to the project. The Public Virtual University plans to enroll up to 49,000 learners annually by 2029 and to generate 10,000 additional graduates each year.
The reform aligns with Madagascar’s national strategy for human capital development and digital transformation. Afrobarometer reported that more than 40% of young people aged 18 to 35 were unemployed in 2024. Policymakers view access to market-relevant training as a strategic lever to improve employability.
Survey data identified lack of training or preparation as the main barrier to employment at 30%, followed by lack of experience at 27% and mismatch between academic qualifications and employer needs at 16%. These constraints highlight the need for innovative and inclusive education solutions.
In parallel, the Public Virtual University project includes modernization of technical infrastructure and expansion to 16 regional centers equipped with autonomous solar solutions. The infrastructure will ensure operational continuity in areas with limited electricity access.
The initiative complements national digital training programs such as ASAN’AI and Skills4Job, which aim to equip young people with in-demand competencies, particularly in digital professions and customer relations.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
-
Authorities launched an online platform to process VAT, banking tax and customs duty exemptions for renewable energy equipment.
-
Importers can now submit and track applications digitally through a system developed with the Single Window for Foreign Trade.
-
Ivory Coast targets 42% to 45% renewable energy in its power mix by 2030.
The Ivorian administration has intensified its transition toward e-government. Authorities have expanded digital public services, including recently launched sectoral platforms, as part of a strategy to modernize public action and facilitate user access to administrative procedures.
#Économie | Modernisation de l'administration énergétique: la plateforme digitalisée de demande d'Attestation d'Exonération de la TVA officiellement lancée
— Gouvernement de Côte d'Ivoire (@Gouvciofficiel) February 21, 2026
Abidjan, le 20 février 2026- Le directeur général de l'Énergie, Narcisse Kalifa Éhouman, a lancé officiellement, le… pic.twitter.com/WkzpBQLmz4
The Directorate General of Energy launched on February 20 in Abidjan an online platform dedicated to applications for exemptions from value-added tax (VAT), the banking operations tax (TOB) and customs duties on renewable energy equipment. Officials designed the initiative to simplify administrative procedures, reduce processing times and secure the review of files linked to clean energy investments.
Director General of Energy Narcisse Kalifa Éhouman stated that the platform represents a major step forward in the digital transformation of the energy administration. “Thanks to this platform, developed in close collaboration with the Single Window for Foreign Trade, importers will now be able to submit their applications online, track the progress of their files in real time, and interact with the administration in a more fluid, efficient, and transparent manner.” he explained.
Authorities expect the digitalization of these procedures to shorten review times, improve traceability of administrative decisions and strengthen the reliability of file assessments. By centralizing exemption requests, the government aims to lower investment costs for solar, wind and hybrid projects while providing a clearer operational framework for industry players.
The launch forms part of Ivory Coast’s broader strategy to modernize public administration through the dematerialization of services. In recent years, authorities have accelerated digitalization by automating foreign trade formalities, expanding online tax services and gradually integrating digital tools into the management of economic public services.
The initiative coincides with the acceleration of the national energy transition. Ivory Coast aims to raise the share of renewable energy in its electricity mix to between 42% and 45% by 2030. Authorities are developing several solar and energy infrastructure projects to support growing electricity demand.
The digitalization of exemptions for renewable energy equipment aligns with a wider e-government drive to enhance administrative transparency, improve the business climate and facilitate private investment. The Ivorian state plans to progressively extend dematerialization to other sectoral procedures, enabling centralized and online monitoring of applications.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum