Tech (1154)
The Algerian government has made digital transformation a key pillar of the country’s socioeconomic development. Beyond investing in infrastructure, authorities are also focused on equipping the population with the digital skills needed to achieve these ambitions.
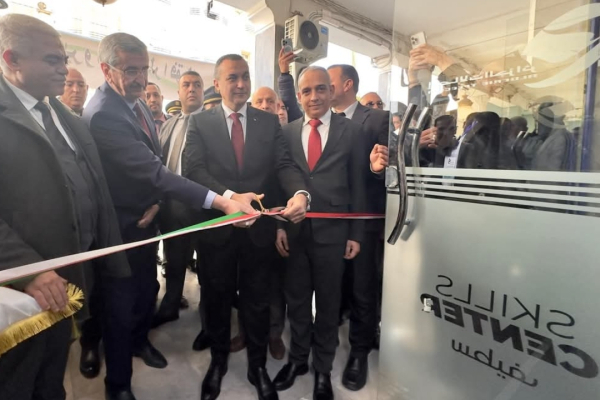
Algeria's Minister of Post and Telecommunications, Sid Ali Zerrouki, inaugurated a Skills Center in Sétif on February 20. The center will provide free training for young people in advanced digital technologies.
Similar infrastructure will be established nationwide to equip Algerian youth with future-ready skills, enabling their integration into the national and global digital economy. They will offer training in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Cloud Computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), Cybersecurity, and other Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) fields.
The initiative aligns with Algeria Digital 2030, the government’s national strategy, which aims to accelerate Algeria’s digital transformation by expanding ICT adoption across all economic sectors and developing a skilled workforce by prioritizing capacity building as one of its five key pillars.
The importance of digital skills is growing across Africa. According to the World Bank, an estimated 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital expertise by 2030. While Algeria is not part of this region, the trend underscores the necessity of digital training for the continent’s economic transformation. A joint study by the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and Google predicts that Africa’s digital economy will be worth at least $712 billion by 2050, representing 8.5% of the continent’s GDP.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
As part of its digital transformation strategy, Senegal is targeting a significant increase in the contribution of its digital sector, aiming for at least 15% of GDP within the next ten years. To achieve this ambitious goal, the government is committed to unifying its digital initiatives and streamlining projects to enhance efficiency and impact.
Senegal will establish a Digital Governance Committee, GouvNum, to coordinate and streamline its digital initiatives, officials said. The project, approved during a Council of Ministers meeting on February 19, aims to create a cohesive framework for state-led digital transformation.
According to the Ministry of Digital Transformation, the past two decades have seen massive investments in modernizing public digital infrastructure and interconnecting government entities. These efforts laid the foundation for a national information system and a government enterprise architecture. However, a fragmented approach to digital projects has led to duplication, inconsistencies, rising inefficiencies, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and misalignment between sectoral strategies and the national digital agenda. These challenges hindered the goals set by the previous digital strategy (SN20-25).
The creation of GouvNum aligns with Senegal’s new digital strategy, the New Deal Technologique, set to launch on February 24. This committee will provide a unified governance framework for digital initiatives, ensuring project coordination, strategic alignment across sectors, improved system security, and more effective monitoring and evaluation.
Additionally, GouvNum will enhance the prioritization of digital programs, laying the groundwork for a more efficient and integrated digital transformation. A key objective of this effort is to boost the digital sector’s contribution to at least 15% of GDP within the next decade. This ambition will be driven by a structured approach under the New Deal Technologique, which includes 12 targeted programs designed to accelerate Senegal’s digital economy.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
The interoperability of digital payments is emerging as a key driver for modernizing financial systems and enhancing banking inclusion. By connecting banks and fintechs, these platforms foster innovation in the financial sector.
Comoros will implement an interoperable digital payment switch, with Moroccan electronic payment solutions company PayLogic executing the project. The company announced the initiative in a statement on Sunday, February 16, marking a step in the country's financial infrastructure modernization.
"This project is a testament to our dedication to delivering innovative solutions that transform financial ecosystems. By implementing an interoperable payment switch, we are helping to create a more inclusive and efficient financial infrastructure in the Union of Comoros. We are excited to partner with local stakeholders to bring this vision to life," said Mohamed Mekouar, Executive Chairman of PayLogic.
The platform, part of the Financial Sector Development Support Project (PADSF), aims to connect financial institutions, banks, and payment service providers, creating a seamless and inclusive digital payment ecosystem. This interoperability will allow users to make instant transfers between mobile operators, between banks, and between mobile operators and bank accounts.
The initiative aligns with the Central Bank of Comoros’ policy to promote financial inclusion. The institution has encouraged local banks to offer free bank account openings for individuals and fee-free money transfers for the diaspora. Since early August, this measure has led to the opening of hundreds of new accounts, with a goal of reaching a 50% banking penetration rate by the end of 2025.
PayLogic's interoperable switch could strengthen these efforts by improving access to digital financial services, especially for rural populations and the diaspora. Reducing reliance on cash and enhancing transaction efficiency will drive broader adoption of banking and online payment services across the country.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
By working closely with the Nigerian government and its partners, Microsoft is playing a pivotal role in building a digitally skilled workforce and positioning Nigeria as a leader in AI and emerging technologies.
Microsoft has unveiled a $1 million investment in its AI Skilling Initiative, aimed at training one million Nigerians in artificial intelligence (AI) over the next two years. The announcement was made on February 19 during the Microsoft AI Tour in Lagos, a gathering of business leaders, IT professionals, and developers focused on exploring the latest advancements in AI.
Managing Director of Microsoft Nigeria and Ghana, Ola Williams emphasized the company’s dedication to AI’s transformative potential. She also highlighted that Microsoft's commitment to advancing AI skills in Nigeria underscores its dedication to empowering individuals and organizations to achieve greater success.
Microsoft reinforces its commitment to Nigeria’s digital transformation with this latest investment. The initiative is poised to drive economic growth, industrialization, social inclusion, and technological innovation, ultimately shaping a future where AI-powered opportunities are accessible to all Nigerians.
This initiative is set to accelerate AI adoption in Nigeria, reinforcing the country's status as a leading force in Africa’s digital economy. It aligns with the strategic goals outlined in Nigeria’s National Artificial Intelligence Strategy (NAIS), which envisions the nation as a global leader in leveraging AI for responsible, ethical, and inclusive innovation. The NAIS highlights Nigeria’s rapidly expanding AI market, which is projected to reach $434.4 million by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 44.2%.
Hikmatu Bilali
Mobile money is emerging as a crucial tool for financial inclusion in Africa, with growing adoption driven by innovative solutions. In this dynamic landscape, Orange Money continues to expand, offering increasingly tailored services to meet user needs.
Orange Money, the mobile money transfer and payment service of French group Orange, officially opened its headquarters in Abidjan on Tuesday, February 18. This move marks a new step in the company's commitment to expanding mobile financial services across Africa and the Middle East.
According to Aminata Kane, CEO of Orange Money Group, establishing the headquarters is a key step in Orange's mission to digitize transactions and support its growing customer base. Jérôme Hénique, Executive Director of Orange Africa and the Middle East (OMEA), emphasized that the initiative reflects the company's drive to strengthen its presence in key markets and continue its 15-year history in mobile financial services.
Since its launch in Ivory Coast in 2008, Orange Money has seen rapid growth, reaching 40 million active monthly users as of February 2025. This growth aligns with a regional trend where mobile financial services play a key role in financial inclusion. In 2023, mobile money transactions in the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA) reached 171,959.1 billion FCFA (approximately $275 billion), a 146.3% increase from the previous year. Ivory Coast, with over 23 million mobile financial service users in 2023, is a major player in this transformation.
The establishment of Orange Money Group’s headquarters in Abidjan creates new opportunities for the Ivorian market and the region. It will allow for closer engagement with users and more responsive service development. West Africa is becoming a leading hub for mobile money, gradually surpassing East Africa in adoption and growth of digital financial services.
Orange Money continues to innovate, introducing QR code payments for merchants and end users. Through a partnership with Mastercard, the company launched a virtual card in 2024. Available in seven countries, the service is set for further expansion in 2025, reinforcing Orange Money’s role in shaping the future of mobile finance in Africa.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
AI is transforming various sectors and enhancing productivity. African nations are increasingly recognizing its potential and seeking to invest in this field to harness its economic benefits, foster innovation, and strengthen their position on the international stage.
Algeria aims for artificial intelligence (AI) to contribute 7% of its gross domestic product (GDP) by 2027, Minister of Post and Telecommunications Sid Ali Zerrouki said at the third edition of the CTO Forum Algeria on Monday, February 17. The initiative seeks to diversify the national economy and position the country among global AI leaders.
To achieve this objective, Algeria has invested in top-tier universities specializing in AI, robotics, and mathematics. Additionally, incubators have been deployed nationwide to foster innovation and support the emergence of technology startups.
State-owned telecom operator Algérie Télécom has committed to establishing a 1.5 billion dinar ($11.1 million) investment fund to support startups specializing in AI, cybersecurity, and robotics. This initiative aligns with a presidential strategy to create 20,000 startups as quickly as possible.
In parallel, the government is betting on training programs such as Scale Centers to enhance skills in AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing, particularly targeting young people without a university education. The National AI Commission has also launched an ambitious strategy to structure and energize this key sector.
Strengthening Digital Infrastructure
To support this growing AI ecosystem, Algeria has made significant investments in digital infrastructure. The government has installed 265,000 kilometers of fiber optic cable and connected 1,400 sites with 4G technology, aiming to improve coverage in remote areas. Additionally, it plans to deploy 7,000 new 4G stations by 2025 to boost connectivity and increase internet speeds.
If successful, this strategy could profoundly transform Algeria’s economy by enhancing productivity in key sectors such as industry, agriculture, and services. AI is expected to play a central role in this transformation by optimizing resource management, automating processes, and facilitating data-driven decision-making.
By fostering the emergence of local startups capable of developing advanced technological solutions, Algeria could not only enhance its economic efficiency but also position itself as an exporter of technology. In this regard, Olumide Balogun, Google’s director for West Africa, highlights that AI could add up to $1.5 trillion to Africa’s GDP by 2030. This projection underscores the importance of Algeria’s full commitment to AI development to capture a significant share of this rapidly expanding market.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
In response to the growing challenges of digital transformation, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, many African countries are seeking to strengthen their technological capabilities. In this context, international cooperation is creating new opportunities for development.
Congolese Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and the Digital Economy, Léon-Juste Ibombo (photo, left), met with Russian Federation Ambassador to the Republic of Congo, Ilias Iskandarov (photo, right), on Monday, February 17, to discuss bilateral cooperation in digitization, artificial intelligence (AI), and cybersecurity.
During the meeting, Ibombo confirmed ongoing negotiations to establish mutually beneficial cooperation with Russian institutions, particularly for the creation of a Russian-African Studies Center, which would include IT training for Congolese citizens.
Iskandarov proposed expanding this cooperation by introducing educational programs dedicated to digital transformation in Congo. These initiatives, planned for administrative and industrial centers, aim to provide advanced training for government officials and private-sector IT specialists on digital regulation, data protection, and AI applications.
This meeting is part of the Congolese government’s efforts to accelerate digital transformation through strategic partnerships. Russia, recognized as an emerging power in technology and cybersecurity, has played a key role in enhancing global digital security.
Since 1998, Russia has been a pioneer in addressing information security at the United Nations, demonstrating early awareness of digital age risks. After years of investment and innovation, Russia has strengthened its expertise, positioning itself among global leaders in the sector. According to the International Telecommunication Union, Russia ranks among the top countries in ICT development, with a score of 90.6 out of 100. In cybersecurity, Russia is classified as Tier 2, a category including advanced nations with scores between 85 and 95.
This partnership is expected to bring significant benefits to Congo, including strengthening local digital skills, improving IT infrastructure security, and facilitating access to advanced technologies. Furthermore, this collaboration could serve as a springboard for new international partnerships in the digital sector, positioning Congo as a key player in the African and global tech ecosystem.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Tingo AI Radio places Africa at the forefront of artificial intelligence innovation, proving that the continent can create and implement cutting-edge AI solutions. By showcasing the practical application of AI in media, it sets the stage for broader AI adoption in industries such as healthcare, agriculture, finance, and governance.
Nigerian businessman and tech entrepreneur Dozy Mmobuosi has launched Tingo AI Radio 102.5 FM in Lagos, Nigeria. The radio station, unveiled on February 14, received full authorization from the Nigerian Broadcasting Corporation (NBC) and operates from a cutting-edge facility on Victoria Island, Lagos.
“Our AI-generated content will be authentically Nigerian, featuring AI agents that understand local languages and accents,” said Dozy Mmobuosi, emphasizing the station’s commitment to responsible AI use and regulatory compliance.
The station merges advanced artificial intelligence with Afro-centric content to deliver a distinctive, immersive audio experience tailored for African listeners.
Tingo AI Radio’s infrastructure eliminates traditional human roles in broadcasting, relying entirely on AI for news direction, sound engineering, and DJing. Listeners can request songs and enjoy curated playlists through a virtual DJ, enhancing interactivity.
The launch event also introduced TingoGPT, an AI model designed for African users, further cementing Tingo’s role in Africa’s technological evolution.
Chief Technology Officer Abraham Samuel highlighted how AI voice cloning streamlines broadcasting, allowing interviews to be pre-recorded with AI-generated voices. AI-driven news, weather forecasts, and interactive features redefine traditional radio operations while cutting operational costs.
“With just a voice sample, we can clone it into our AI system, enabling AI agents to conduct interviews and read scripts, saving time and resources,” Samuel explained.
According to a 2018 McKinsey Global Institute study, the automation trends could boost productivity by up to 2% annually.
However, the launch of Tingo AI Radio 102.5 FM also presents a challenge for the multimedia sector. It raises concerns about the potential impact on jobs within the sector.
Hikmatu Bilali
Thanks to financial support from partners like the World Bank, Burkina Faso is rapidly advancing its digital transformation. In 2024, these efforts have significantly improved government efficiency.
Burkina Faso's Ministry of Digital Transition, Posts, and Electronic Communications unveiled its 2025 digital sector priorities during a 2024 objectives review ceremony on Friday, February 14, chaired by Prime Minister Rimtalba Jean Emmanuel Ouédraogo.
Key 2025 projects include completing data center construction, currently 70% finished, and expanding network coverage to at least 500 underserved localities. The ministry also plans to enhance the digitization of administrative services, conduct large-scale population enrollment for the WURI electronic unique identification project, and launch the Digital Transformation Acceleration Project (PACT DIGITAL), with an estimated budget of $150 million.
In 2024, the ministry launched a project to provide network coverage to over 130 localities in "white zones," rehabilitated the National IT Network for Administration (RÉSINA), began construction on two data centers, and deployed strategic digital platforms to accelerate digital transformation. Other initiatives included developing electronic signatures and legislative reforms to improve the country's digital environment. The ministry reported a 90.4% achievement rate for its 2024 objectives.
These initiatives aim to further Burkina Faso's digital transformation, with the government seeking to position the country as an African leader in integrating ICT into public administration, education, healthcare, commerce, and agriculture. However, Burkina Faso ranks 175th out of 193 countries in the United Nations E-Government Development Index (EGDI), with a score of 0.2895 out of 1, below the West African subregional average (0.3957), the continental average (0.4247), and the global average (0.6382).
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) assigned Burkina Faso a score of 30.1 out of 100 in its 2024 ICT Development Index, placing it 43rd out of 47 African economies analyzed. According to the ITU, internet penetration in Burkina Faso is 19.9%, and mobile phone penetration is 21%. 3G network coverage reaches 53.2% of the population, while 4G coverage is 36.6%. In cybersecurity, Burkina Faso is classified at Tier 3 out of 5, indicating a need for stronger technical measures and skill development.
The ministry did not specify challenges preventing full achievement of its 2024 objectives, though the 90.4% completion rate was deemed "satisfactory." However, in its mid-year 2024 review, the government acknowledged that efforts to rehabilitate infrastructure and expand digital services in rural areas were hindered by security challenges, exacerbated by political instability.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Cybercrime is rapidly increasing across Africa, with a surge in attacks that exploit security vulnerabilities. Weak infrastructure protection, a lack of public awareness, and outdated software are leaving countries vulnerable to cyber threats, endangering businesses and institutions.
Cyberattacks exploiting security vulnerabilities, or "exploits," nearly doubled in Cameroon over the past year, rising from 174,472 in 2023 to 333,930 in 2024, a 91% increase. These vulnerabilities allow hackers to infiltrate systems through outdated or poorly secured software, threatening critical digital infrastructures. Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky revealed the figures at the KNext forum, held in Douala and Yaoundé on February 12 and 13.
"Faced with a growing cyber threat, Cameroonian businesses and institutions must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity. The commitment of the Ministry of Posts and Telecommunications to KNext Yaoundé 2025 sends a strong signal on the need for collective mobilization against cyberattacks," said Gladys Salmouth, Corporate Communications Manager for Central and West Africa at Kaspersky.
The surge in attacks is largely driven by Cameroon’s ongoing digital transformation. With over 10 million internet users and an estimated internet penetration rate of 45% in 2024, the rapid adoption of online services, cloud computing, and remote work, along with the rise in digital transactions, has significantly expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals.
Beyond exploits, other threats are also gaining ground. Intrusions via the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) reached 163,298 cases in 2024, while backdoor attacks accounted for 139,395 incidents. These methods enable cybercriminals to stealthily access systems, steal sensitive data, or deploy ransomware, disrupting businesses and government operations.
The economic consequences of these attacks are substantial. In 2024, cyberattacks cost Cameroon millions of dollars due to data breaches, service disruptions, and ransom payments. Beyond financial losses, companies and institutions also suffer reputational damage and an erosion of trust, key elements for the growth of the country's digital economy.
The threat extends beyond Cameroon. Across Africa, cyberattacks pose a major challenge to local economies. According to the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa, inadequate cybersecurity preparedness costs African nations an average of 10% of their GDP, amounting to nearly $4 billion annually.
To counter these growing threats, Kaspersky urges businesses and institutions to strengthen their cybersecurity posture. Key recommendations include adopting advanced security solutions capable of detecting and blocking threats in real time, securing remote access by restricting unprotected RDP connections, and implementing strict access and data management policies.
Raising employee awareness and providing training on cyber risks, particularly phishing and social engineering attacks, are also essential. Finally, enhanced collaboration between the private sector and government authorities remains a priority. Sharing best practices and reinforcing cooperation among key stakeholders can improve threat detection and response, contributing to a more secure digital environment.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
More...
Blockchain technology is increasingly transforming African economies by providing innovative solutions in finance, energy, and agriculture. Its adoption boosts transparency, streamlines transactions, and accelerates digital transformation.
On Monday, February 17, cryptocurrency company Tether announced it signed a memorandum of understanding with the government of the Republic of Guinea. The strategic collaboration aims to establish a framework for the adoption of blockchain and peer-to-peer technologies to drive economic growth and position Guinea as a key player in Africa’s digital transformation.
"We are thrilled to collaborate with the Republic of Guinea to potentially unlock the immense potential of blockchain and digital technologies across Africa. This MoU reflects our commitment to helping countries build resilient digital economies. Together, we aim to implement efficient blockchain solutions that benefit both public and private sectors, paving the way for economic growth and establishing Guinea as a leader in technological innovation,” said Paolo Ardoino, CEO of Tether.
The agreement focuses on education, innovation, and sustainable technological practices. It includes the introduction of educational programs in both the public and private sectors to raise awareness, enhance skills, and develop local talent in digital technologies. This framework is expected to facilitate blockchain adoption in Guinea and create an environment conducive to innovation.
Tether has undertaken several similar initiatives internationally. The company has been involved in the Lugano Plan in Switzerland, aimed at promoting blockchain adoption, as well as educational projects on digital assets in Turkey and the Middle East.
This initiative is part of the Simandou 2040 project, launched by President Mamadi Doumbouya, which places technology at the core of the country’s development strategy. The agreement follows a recent meeting between the Minister of Posts, Telecommunications, and the Digital Economy, Rose Pola Pricemou, and a Tether delegation. The meeting aimed to establish a favorable framework for implementing the collaboration.
In Guinea, where digital transformation is underway, blockchain adoption could play a crucial role in financial inclusion. This technology offers solutions tailored to local realities, such as facilitating cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs, and securing financial exchanges. With a low banking penetration rate, digital assets and blockchain present a significant opportunity to modernize financial systems and promote more inclusive growth.
Beyond finance, blockchain can also contribute to sustainable development in Africa. In agriculture, it enables tracking product value chains, ensuring compliance with sustainable practices and certification. Farmers can thus prove that their products are organic and fair trade, gaining access to new markets and increasing their incomes.
In the energy sector, blockchain facilitates the management of decentralized power grids and promotes the adoption of renewable energy. Blockchain-based microgrids make it possible to monitor energy production and consumption in real time, improving electricity access in rural areas while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Africa's growing digital economy and technological advancements are driving demand for specialized skills, but training opportunities remain limited.
The digital training platform Code 213 has announced the opening of its third coding school in Algeria, further strengthening its presence in the country. This initiative is part of a broader strategy to expand into other North and Sub-Saharan African countries, where demand for digital skills is rising rapidly.
"Our mission is to create a pipeline of highly skilled digital professionals who can compete in the global job market. Expanding into new regions allows us to reach more young talents, empowering them with the skills they need to succeed," said Amina Bergui, Code 213’s marketing manager.
Since its launch in July 2023, Code 213 has offered training programs in software development, cybersecurity, data science, artificial intelligence, and digital marketing. The platform combines online courses with in-person mentoring and provides internationally recognized certifications, including CompTIA, Microsoft, and Google. Additionally, the use of Noor AI enables personalized tracking of learners’ progress.
The expansion comes at a time when Africa is facing a severe shortage of skilled labor in the tech sector. According to the "Foresight Africa 2025-2030" report by the Brookings Institution, an estimated 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. The report also predicts up to 650 million digital training opportunities, representing a potential $130 billion market. However, access to specialized training remains limited, largely due to high costs and inadequate infrastructure.
With its growing presence and ambitious expansion plans, Code 213 aims to contribute to the development of a competent digital workforce, a crucial factor for Africa’s economic future. By offering training in high-growth industries, this initiative could also help reduce youth unemployment, a persistent challenge across the continent.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Information and communication technologies (ICT) enhance creativity and learning from preschool and primary levels. However, in Africa, digital integration in education remains limited due to a lack of preparedness for its adoption in early learning.
The Nigerien government has launched an ambitious program to equip over 7,000 teachers with educational tablets, aiming to improve teaching skills and student monitoring, particularly in remote areas. On Friday, February 14, Elisabeth Sherif, Minister of National Education, Literacy, Vocational Training, and Promotion of National Languages, visited the Niger-LIRE project headquarters to assess progress on the "One Teacher, One Tablet" initiative, which seeks to digitize education.
"These tablets contain dynamic content tailored to all regions, including the most isolated ones," explained Aboubacar Mamadou Diakité, Director of Statistics and New Technologies at the Ministry of National Education. "They have long battery life and come with 21,000 mAh power banks, allowing up to a week of use without recharging." He also announced the arrival of an additional 3,400 tablets under the project.
"One Teacher, One Tablet" is part of LIRE (Learning Improvement for Results in Education), a $140 million World Bank-funded government program. It aims to modernize education through digital tools to improve student outcomes, addressing Niger's historically low integration of technology in classrooms.
The initiative seeks to enhance teaching conditions and make learning more interactive through resources such as video lessons, interactive materials, teaching guides, practical exercises, and digital assessment tools. The tablets will also help teachers diversify their teaching methods and provide structured support, especially in regions with limited access to textbooks and specialized training.
This initiative aligns with the African Union’s Digital Education Strategy (2023-2028), which encourages member states to develop national policies for digital transformation in education. By 2027, the strategy aims to ensure that at least 50% of schools across the continent have reliable and affordable high-speed internet (less than $25 per Mbps per month). It also targets providing digital devices to 20% of students and 50% of teachers by 2027, expanding to one-third of students and all teachers by 2030.
Samira Njoya
Many regions in Africa still struggle with limited and expensive internet access. By providing a direct undersea connection between South Africa and Brazil, Project Waterworth will improve bandwidth, lower latency, and reduce reliance on existing routes, making internet services faster and more affordable.
Meta, the parent company of Facebook, has unveiled an ambitious new undersea internet cable project, dubbed Project Waterworth, it announced on February 14. The initiative spans over 50,000 km and aims to connect North and South America, Africa, Asia, and Australia, making it the longest undersea cable ever deployed.
The cable will link major regions, including the U.S. East Coast, Brazil, South Africa, India, Australia, and the U.S. West Coast. Meta asserts that the project will promote economic collaboration, enhance digital inclusion, and accelerate technological advancements in these regions.
Furthermore, Meta has announced the deployment of advanced cabling technology to enhance resilience against natural wear and potential threats. The cables will be laid in deep waters, reaching depths of approximately 7,000 meters, making them more difficult to access and sabotage. Additionally, enhanced burial techniques will be used in high-risk fault areas, such as coastal waters, to protect against ship anchors and other hazards.
With Project Waterworth, Meta is not only securing its infrastructure but also positioning itself as a leader in global internet connectivity. This investment could transform digital access and economic opportunities in the connected regions while setting new standards for undersea cable security and resilience.
Project Waterworth could significantly boost African development by improving connectivity and driving economic growth. As of January 2024, internet access in Africa varies, with Morocco at 90.7% while Central Africa lags at 10.6%, according to Statista. By providing a direct undersea link between South America and Africa, Project Waterworth aims to enhance bandwidth, reduce latency, and make internet access more affordable and widespread.
Hikmatu Bilali