Tech (1163)
Senegal, with backing from the United Arab Emirates, plans to digitize its daaras, the traditional Quranic schools that educate thousands of children nationwide. A meeting held in Dakar on Monday, April 7, between Senegal’s Minister of National Education, Moustapha Mamba Guirassy, and a delegation from Abu Dhabi-based digital education firm Alef Education, advanced this initiative.
"Fruitful discussions laid the groundwork for a strong partnership, with a pilot phase set to begin in October 2025. The objective is clear: to build a digital education model rooted in our cultural and spiritual values, and capable of equipping daaras with 21st-century teaching tools," the Ministry of National Education said in a press release.
This initiative follows President Bassirou Diomaye Faye’s visit to Alef Education’s headquarters in the United Arab Emirates, where he established the foundation for the collaboration. It falls under the government’s "Senegal Daara Digital Transformation" project, which in its initial phase aims to deploy an artificial intelligence-powered personalized learning platform targeting over 10,000 students. The curriculum will include Arabic, mathematics, and Islamic studies.
Daaras are an important component of Senegal’s education system. According to a 2018 survey by the NGO Global Solidarity Initiative (GSI), there are more than 2,000 such schools across the country. This partnership is expected to create new educational opportunities. Alef Education, known for its expertise in educational technologies, is poised to play a central role in this transformation, providing students with modern digital tools while respecting the cultural and spiritual distinctiveness of the daaras.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Platform offers details on academic programs, admission, application tracking, and student life
- Includes resources for embassies, cooperation bodies, and enrolled foreign students
Algeria's Minister of Higher Education and Scientific Research, Kamel Baddari, officially launched the "Study in Algeria" digital platform on Tuesday, April 8, in Algiers. Designed for international students looking to pursue their studies in Algeria, the platform is part of a broader effort to modernize the university system and boost its international appeal.
"Today, we are entering a new phase in the modernization of higher education and its opening to the world," said Baddari. "Algeria is increasingly seen as an attractive destination for international students, thanks to the global outreach we’ve initiated and the reforms undertaken to modernize our education system and improve its quality."
The platform offers a comprehensive overview of academic programs across Algeria, details on admission requirements, an online application portal, and real-time tracking of applications. It also includes practical guidance on administrative procedures, living conditions, and profiles of universities and research centers. Dedicated sections are available for embassies, cooperation services, and international students already enrolled in Algerian institutions.
This initiative follows the presidential decree issued in February, which lays out the framework for admitting foreign students to Algerian institutions, and forms part of the Higher Education Ministry’s five-year action plan (2024–2029). That roadmap prioritizes digital transformation and the expansion of academic cooperation at both regional and international levels.
The launch of "Study in Algeria" is a significant milestone in Algeria’s push to digitize higher education. The platform aims to enhance the country’s academic appeal, facilitate institutional exchanges, and position Algeria as a reputable study destination. By centralizing and streamlining access to university services, the initiative is expected to boost the global visibility of Algerian universities.
Samira Njoya
- Mauritania launches digitized road traffic management system via “Khadamaty” app
- System enables online tracking of violations, fine payments, and complaint submissions
- Initiative aims to reduce bureaucracy, prevent injustices, and streamline citizen access to services
Mauritania launched a digitized road traffic management system on Monday, integrating it into the government's "Khadamaty" application. The system, overseen by the Interior Minister and his counterparts from the Ministries of Digital Transformation and Transport, aims to streamline traffic violation tracking, fine payments, and complaint submissions.
According to the Minister of Digital Transformation and Administrative Modernization, the system aims to reduce administrative burdens, eliminate unfair practices, and enhance citizen convenience. Users will be able to easily view vehicle offenses and pay fines online, eliminating lengthy delays and vehicle immobilization.
Developed through a collaboration between the General Directorate of National Security and the Ministry of Digital Transformation, the system aligns with President Mohamed Ould Cheikh El Ghazouani's "My Ambition for the Nation" initiative. This initiative prioritizes a modern, transparent, and citizen-centric administration driven by digital technologies. The recent launch of online criminal record payments exemplifies this approach.
This reform comes at a time when global indicators show that Mauritania lags significantly behind in e-government development. In 2024, the country ranked 165th in the United Nations E-Government Development Index with a score of 0.3491, significantly below the African average (0.4247) and global average (0.6382). Mauritania's online services score was notably low at 0.1688, lagging behind both African (0.3862) and global (0.5754) averages.
Beyond administrative efficiency, the system is expected to improve road safety by enhancing driver accountability and streamlining traffic management. An advanced digital platform, coupled with surveillance cameras, will bolster traffic control and promote greater road discipline.
By Samira Njoya
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Cameroon has set up an interministerial working group on e-government to coordinate digital transition
- Group includes around 30 administrations and experts, led by the Ministry of Culture
- Tasks include conducting surveys, setting digital archiving standards, and ensuring system interoperability
Cameroon is advancing its multi-year program to digitize public archives, aiming to modernize document management and enhance information accessibility. To expedite this effort, an interministerial working group on e-government has been established to coordinate digitization across the public administration. The announcement came during a meeting held April 2 in Yaounde.
According to Minette Libom Li Likeng, Minister of Posts and Telecommunications, the initiative reflects "the government’s strong commitment to achieving a secure, structured, and strategic digital transition of public administration." She underscored the significance of digital archiving as a tool to bolster national data sovereignty and improve public service efficiency.
The newly formed interministerial working group on e-government comprises approximately 30 administrations and experts tasked with overseeing the national archives' digitization. Coordinated by the Ministry of Culture, the group will conduct field surveys, establish digital archiving guidelines, and structure an accessible and secure database. The group is also responsible for ensuring system interoperability and guaranteeing archive management adheres to international electronic governance standards.
This initiative is part of a broader reform effort to transform public administration, making it more responsive, transparent, and better equipped to serve citizens' needs. It aligns with efforts to optimize information management and enhance data security, critical components of good governance and national development.
The digital archiving of state records is projected to yield numerous benefits, including increased transparency within Cameroon's public administrations, reduced data loss risks, and streamlined citizen access to public information. Furthermore, effective archive management is expected to enhance the traceability of administrative decisions, reinforcing state accountability while lowering costs associated with physical archives.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Artificial intelligence is rapidly reshaping sports worldwide, and in Africa, it offers significant potential to modernize the sector, improve performance, and drive economic growth, especially ahead of major continental sporting events.
Africa is poised to host a series of major sporting events, including the 2025 Africa Cup of Nations (AFCON) in Morocco, the 2026 Youth Olympic Games in Senegal, and the 2030 World Cup, co-hosted by Morocco. These events present significant opportunities for economic and technological advancement, beyond their sporting significance.
A March 2025 report by multinational management and technology consultancy BearingPoint, titled "Intelligence artificielle et sport en Afrique," highlights the growing role of AI in organizing and enhancing sports events across the continent. The report identifies AI as a tool for large-scale optimization, modernization, and value creation.
AI for Optimized Organization
BearingPoint's report indicates that AI can revolutionize sports event management in Africa by optimizing key areas. This includes logistical planning, crowd control, security, ticketing, and visitor flow forecasting. For athletes, AI enhances performance through game data analysis, injury prevention, personalized training programs, and fitness monitoring. Spectators benefit from personalized offerings, optimized content delivery, and improved accessibility solutions.
The integration of these technologies throughout event organization could stimulate local economies, optimize resource management, and enhance Africa’s international appeal.
Measurable Economic Impact
The economic impact of major sporting events is substantial. The 2010 World Cup in South Africa generated approximately 130,000 jobs and $385 million in revenue, while the 2019 AFCON in Egypt yielded $83 million. AI can maximize these returns by refining demand forecasts and optimizing service efficiency.
This trend aligns with global momentum. A Mordor Intelligence study projects the AI market in the sports industry to grow from $5.93 billion in 2024 to $20.94 billion by 2029, with an average annual growth rate of 28.69%. This growth reflects increasing interest in AI within the sports sector.
A dynamic SportsTech ecosystem is emerging in Africa, blending sports and innovation. In 2023, investments in this sector reached $5.3 million. AI is being utilized for talent identification, performance enhancement, injury prevention, and infrastructure management. This movement, driven by startups, incubators, and sports institutions, has the potential to drive sustainable growth.
Addressing Key Challenges
However, significant challenges remain. These include a lack of robust digital infrastructure, insufficient investment, a shortage of specialized skills, and the absence of a clear regulatory framework for personal data management. Stronger public-private sector collaboration is essential to overcome these obstacles. This includes implementing appropriate infrastructure, developing local skills, and establishing suitable regulatory policies.
By integrating AI throughout event preparation and organization, African sports events can become catalysts for digital transformation. AI is positioning itself as a strategic lever for modernization and enhancing the continent's attractiveness.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Smart Africa alliance announces creation of African Artificial Intelligence Council
- Council to coordinate AI development across 40 African nations
- Focus areas include computing infrastructure, data governance, skills development, and industrial applications
Smart Africa, an alliance of 40 African nations driving the continent's digital agenda, announced the formation of the African Artificial Intelligence Council on April 3. The decision, made during the organization's 20th steering committee session in Kigali, seeks to structure AI development through governance frameworks and increased investment.
"In a historic decision, the steering committee approved the creation of the African Artificial Intelligence Council, a dedicated body to lead continental coordination on key AI pillars, including computing infrastructure, data management, skills development, industrial applications, and governance," the meeting's final communiqué stated.
The council will support African states by defining common AI frameworks, fostering public-private partnerships, and ensuring ethical and inclusive adoption. It will also accelerate digital infrastructure deployment and local talent training to maximize AI's economic and social benefits. AI has the potential to transform sectors such as agriculture, health, and education, where machine learning and data processing solutions are emerging.
This initiative aligns with African countries' efforts to leverage AI for growth. The Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) estimates AI could add $2.9 trillion to the continent's GDP by 2030, representing a 3% annual increase. However, AI development in Africa is hindered by coordination gaps, inadequate infrastructure, and nascent regulations.
The African AI Council aims to address these challenges by establishing a shared framework to attract investment and promote locally tailored solutions. It will also assist countries in tackling issues such as insufficient computing infrastructure, specialized skills shortages, and ethical considerations surrounding AI use.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Face aux défis de la modernisation, de nombreux pays misent sur la transformation numérique pour améliorer l’accès aux services publics. La numérisation des documents officiels, notamment les diplômes, devient une priorité pour renforcer l’efficacité administrative.
Mauritania's government is developing a digital diploma system to modernize issuance and enhance authenticity.
The project's framework was discussed at an April 2 meeting at the Ministry of National Education and Education System Reform, chaired by Minister Houda Mint Babah, and attended by Digital Transformation Minister Ahmed Salem Bede. The system aims to directly link diplomas to the civil registry, ensuring traceability and simplifying citizen access.
Graduates will be able to retrieve certified diplomas via the "Houwiyeti" (My Identity) app, a digital platform for public services already used for birth certificates and passports. The app will streamline access to diplomas, particularly baccalaureate and preparatory education certificates, reducing administrative burdens.
This initiative is part of a broader government digital transformation program. Last year, Mauritania announced a $30 million investment to modernize digital infrastructure and develop public service solutions. However, Mauritania lags in digital administration. In 2024, it ranked 165th globally on the United Nations e-Government Development Index, with a score of 0.3491 out of 1, below the African average of 0.4247 and the global average of 0.6382.
By integrating diplomas into its digital registry, the government aims to simplify access to official documents, combat forgery, and enhance certification reliability. This digital shift is crucial for improving transparency, increasing administrative efficiency, and facilitating graduate integration into the national and international labor markets.
- TikTok removed 8 million videos in Sub-Saharan Africa in Q4 2024
- In North Africa, 7 million videos were taken down in the second half of 2024
TikTok removed eight million videos in Sub-Saharan Africa during the fourth quarter of 2024 for violating community guidelines, up from 7.5 million in the previous quarter, the company announced. In North Africa, seven million videos were taken down in the second half of 2024.
The increased removals reflect heightened moderation efforts across the continent, where several countries have criticized the platform for inadequate content control.
The figures were disclosed at the second annual African Summit for a Safer Internet, held last week in Cape Town, South Africa, which convened government officials, regulators, and industry stakeholders from South Africa, Nigeria, Ethiopia, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, and Kenya. Discussions centered on online safety, content moderation, and the development of Africa-specific digital policies.
"Billions of people come to TikTok every day to create, share and connect and we're continually evolving our policies and practices to safeguard our platform so our community can discover and do what they love," said Helena Lersch, TikTok's Vice President of Public Policy.
Several African nations have recently taken action against TikTok. Senegal blocked the platform in August 2023, citing its role in disseminating hateful and subversive messages that threatened national stability. Before service restoration in February 2024, the government demanded assurances on moderating content deemed contrary to national values and public morals.
Somalia suspended TikTok in August 2023, alleging its use for distributing violent content and disinformation. South Sudan suspended the platform for a week in January 2025 following the circulation of graphic videos showing violence against South Sudanese nationals in Sudan. "The rise in violence linked to social media content in South Sudan underscores the need for a balanced approach that addresses the root causes of online incitement while protecting the rights of the population," said Napoleon Adok Gai, Director General of the South Sudanese Communications Authority.
In Kenya, during April 2024 parliamentary debates over a proposal to suspend TikTok for alleged propaganda, fraud, and sexually explicit content, the government opted for a co-regulation model. Similar regulatory discussions have occurred in Morocco, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), and Burkina Faso.
Despite the increased moderation and video removals, concerns persist about the effectiveness of TikTok's measures. A BBC investigation published March 3, 2024, revealed serious abuses, including young users' exposure to explicit sexual content, from which the platform allegedly indirectly profits. A July 2024 report by the Mozilla Foundation and AI Forensics highlighted security flaws in TikTok Lite, used in developing countries, that facilitate the spread of inappropriate content.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
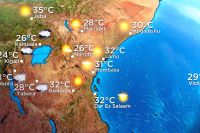
- Google integrates short-term precipitation forecasts for all of Africa into its search engine
- Forecasts use Google Research’s MetNet AI model, updated every 15 minutes, covering 12-hour periods at 5-km resolution
- System combines satellite and limited ground data, addressing Africa’s sparse weather radar coverage (approx. 40 stations vs. 300+ in North America)
Google recently announced the integration of new short-term precipitation forecasts for the entire African continent into its search engine. This initiative aims to improve access to accurate, near-instant weather information, particularly in areas with limited monitoring infrastructure.
The forecasts, enabled by advances in Google Research's MetNet nowcasting model, combine satellite data with ground-based observations to deliver precipitation forecasts at a 5-kilometer resolution, updated every 15 minutes for the next 12 hours, according to a Google press release. The direct integration into Google Search results allows African users to easily access real-time information.
The deployment comes as Africa remains one of the least-covered continents by weather radar, with approximately 40 radar stations compared to nearly 300 in North America. This infrastructure gap renders traditional forecasting models less reliable on the continent. MetNet, an artificial intelligence-based system, provides accurate forecasts without the need for ground-based radar. The project was partially developed by Google Research Africa, with input from local experts in Accra and Nairobi, to tailor it to on-the-ground conditions.
For smallholder farmers, this innovation represents a significant advancement. Agriculture, a cornerstone of African economies, employs about 60% of the labor force and contributes between 30% and 60% of GDP in some countries. Smallholders, who account for nearly 60% of farms in sub-Saharan Africa, are especially vulnerable to weather-related risks.
With more accurate weather forecasts, these farmers can better plan planting, harvesting, and other agricultural activities, mitigating climate risks and improving yields. The technology will also strengthen the resilience of rural communities to climate change impacts by providing tools to adapt to shifting weather patterns.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Kaspersky report warns of rising online risks tied to social validation
- The report highlights tension between digital validation and authentic connections
Social media, while a vital digital exchange space, exposes users to significant risks, a Kaspersky research recently released found. The research reveals a drive for online validation leaves many vulnerable to harassment, scams, and manipulation.
Nearly 45% of millennials, those born between the early 1980s and mid-1990s, report sharing major life events – promotions, moves, breakups – online before informing close friends or family, according to Kaspersky.
Despite this digital reliance, 55% of respondents believe in-person relationships remain more authentic, the study said. This heavy digital exposure carries consequences. More than 70% of millennials do not consistently verify the identity of their online contacts, and 64% have interacted with malicious individuals. Furthermore, 14% admit to using false names or profiles, indicating a normalization of online anonymity.
Accordion to Ruth Guest, a digital behavior specialist, there's a deep need for social validation among this generation, which grew up with digital technology. However, the pursuit of online recognition can distort perceptions. When a carefully crafted post generates a surge of positive reactions, it becomes tempting to prioritize this instant gratification over genuine, meaningful exchanges.
The study indicates these trends are amplified in Africa, where social media adoption is surging, driven by smartphone proliferation, improved internet connectivity, and a growing youth demographic. A 2024 study by Meltwater and We Are Social reported Africa had nearly 276.2 million social media users.
Kaspersky’s report arrives amid a sharp rise in African cyberthreats. INTERPOL cites online scams, identity theft, and social engineering as major concerns. Cybercriminals exploit personal social media information to enhance social engineering attacks and gain system access for ransomware deployment.
A lack of awareness and inadequate regulation in many African nations further exposes internet users to cybercriminal attacks, INTERPOL said. Social media is increasingly used for fraud, romance scams, and disinformation campaigns targeting vulnerable populations.
To mitigate social media risks, the report recommends verifying contact identities and avoiding friend requests or interactions without confirming authenticity. Protecting personal information involves limiting the sharing of sensitive data on public platforms. The use of strong, unique passwords for each account is also advised. Users should be wary of suspicious links and messages from strangers, which may be phishing attempts.
“The ease of online communication can lead to neglecting essential precautions. Verifying identities, limiting access to personal information, and learning to recognize warning signs are now crucial habits for safe internet navigation,” said Marc Rivero, a Kaspersky cybersecurity researcher.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
More...
- Senegal launches "Tabax Sénégal" digital platform to boost employment and investment
- Platform matches users with job opportunities, funding sources, and strategic partnerships
- Features include personalized profiles, CV database, and project tracking tools to enhance transparency, skills certification, and streamlined recruitment processes
Senegalese President Bassirou Diomaye Faye on Tuesday launched "Tabax Sénégal," a digital platform designed to connect job seekers, entrepreneurs, and investors, addressing the country's employment, entrepreneurship, and project financing challenges.
The platform matches job seekers with relevant professional opportunities, supports project developers by facilitating access to funding and strategic partnerships, and showcases high-growth-potential initiatives to investors, aiming to stimulate Senegal's economic development.
Tabax Sénégal offers personalized user profiles, simplified stakeholder matching, business opportunities, interactive project and application tracking, and skills certification. The platform allows Senegalese citizens to upload their resumes to a database of job offers and applications, ensuring fairness and transparency.
The initiative is part of the National Strategy for Employment, Entrepreneurship, and Investment, and comes as Senegal faces a slight increase in unemployment. Data from the National Agency for Statistics and Demography (ANSD) shows the country's unemployment rate reached 20.3% in the third quarter of 2024, up from 19.5% in the same period in 2023, an increase of 0.8 percentage points.
With 200,000 to 300,000 young people entering the job market annually, securing stable employment is a critical issue. The digitization of employment services is expected to streamline recruitment and improve the match between labor supply and demand. The platform also aims to mobilize local and international financing to support entrepreneurship.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Guinea's Digital Economy Minister met VINCI Energies to discuss tech collaboration
- Talks focused on key projects including Technopole creation, second data center, and telecom upgrades
- Future discussions will define partnership terms and select pilot projects for rollout
The Guinean Minister of Posts, Telecommunications and the Digital Economy Rose Pola Pricemou (photo, center) met with a delegation from VINCI Energies Guinea on Wednesday to explore collaboration opportunities to accelerate the country's digital transformation.
VINCI Energies, a global player in energy and digital infrastructure, has been active in Guinea since 2016, primarily focusing on energy infrastructure development. The company is now expanding its focus to include digital infrastructure projects.
The meeting focused on several key initiatives of the Ministry, including the establishment of a technology park, the expansion of metropolitan networks nationwide, the development of a second data center, and the improvement of overall telecom infrastructure.
Minister Pricemou emphasized the crucial role of private sector partnerships in achieving Guinea's digital ambitions. "Collaborating with experienced players like VINCI Energies will be instrumental in accelerating our digital transformation journey," she stated.
Guinea has made significant progress in improving connectivity in recent years through substantial investments. However, challenges remain, such as expanding internet access to rural areas and enhancing the security of digital infrastructure.
The meeting comes at a key moment for Guinea, as the country seeks to modernize its digital infrastructure to support economic growth. The government's "Simandou 2040" vision aims to transform Guinea into a regional technology hub by developing robust digital infrastructure and fostering an environment conducive to innovation and economic growth.
A partnership with VINCI Energies could significantly contribute to this vision by facilitating the deployment of innovative solutions, strengthening local technical expertise, and improving access to digital services for both citizens and businesses.
The parties are expected to finalize the specific terms of their collaboration and identify pilot projects for implementation in the coming months. This partnership marks a significant step forward for Guinea in its digital transformation journey, leveraging the expertise of an international leader in energy and digital infrastructure.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Morocco launched the program on March 25, expanding a 2024 pilot to integrate digital tech into education.
- The program will train 1,800 teachers in AI, robotics, and augmented reality.
Morocco's Ministry of National Education, Preschool and Sports, in collaboration with Huawei Morocco, launched the "DigiSchool 2025" program on Tuesday, March 25. Building on the success of its initial phase in 2024, this initiative aims to further integrate digital technologies into the country's education system.
Speaking about the project, Mohamed Saad Berrada, Minister of National Education, stated: “This program develops the digital skills of teachers and students, fosters their spirit of innovation, and broadens their openness to modern technologies. We are working toward a resilient and connected future, with quality public education accessible to all.”
The DigiSchool 2025 program plans to train 1,800 teachers in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and augmented reality. Simultaneously, 36,000 students will participate in DigiSchool clubs across 248 schools located in Morocco’s 12 regions. These clubs will offer an introduction to future technologies and transversal skills, thereby encouraging innovation among younger generations.
This initiative is part of Morocco’s 2022–2026 roadmap aimed at modernizing its education system, with the objective of preparing a generation of students and teachers to succeed in a digital environment. Through the utilization of public-private partnerships, the program represents a significant step towards a more inclusive and innovative education system.
DigiSchool 2025 also aligns with the national strategy "Morocco Digital 2030," which seeks to position the country as a major technology hub in Africa. Among the key objectives are training 100,000 young people annually in digital professions and creating 240,000 jobs within the digital sector by the year 2030. This initiative thus addresses the growing demand for digital skills while contributing to the development of a qualified workforce prepared to meet the challenges of the digital age.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
With its young population, Africa could emerge as a major player in the global workforce over the next 10 to 15 years. However, to unlock this potential, massive investments in education and training are essential to equip the continent’s youth for the challenges of tomorrow.
More than 4,000 young people across the seven member states of the East African Community (EAC) have acquired digital skills through the “Innovative Skills in East Africa” (dSkills-EA) project. The participating countries include Burundi, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda. The program, supported by German development cooperation through GIZ and implemented by the Inter-University Council for East Africa (IUCEA), aims to enhance youth employability and foster digital innovation within the region.
Launched in 2021, dSkills-EA is scheduled to conclude on March 31, 2025, after a four-year implementation period. In a statement released on Wednesday, March 26, the EAC lauded the project's impact and announced new initiatives to build upon this momentum. “dSkills-EA demonstrates the strength of collaboration between governments, academia, and industry. By equipping thousands of young people with future-proof skills, we have laid the groundwork for a thriving digital ecosystem in East Africa. The EAC AI Regional Alliance will build on this success, expanding AI infrastructure and regional capabilities to secure East Africa’s place in the digital future,” stated David Roos, Director of the dSkills-EA project.
Addressing the Digital Skills Gap
The EAC economy faces challenges related to low productivity and competitiveness, which contribute to high unemployment rates, particularly among young people. According to GIZ, socio-economic development is heavily reliant on innovation and the integration of information and communication technologies (ICT). However, universities still struggle to adequately meet the demands of the private sector and young entrepreneurs.
To address these shortcomings, dSkills-EA introduced short-term training programs tailored to industry needs, provided support to young entrepreneurs in developing digital solutions, and enhanced the master's curriculum in embedded and mobile systems at the Centre of Excellence for ICT in East Africa (CENIT-EA), hosted at the Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology (NM-AIST). The initiative brought together over 300 private partners and 100 universities, establishing a solid foundation for digital transformation in East Africa.
A Critical Issue for Africa's Future
According to a study by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), 230 million jobs in Africa will require digital skills by the year 2030. Yet in 2022, the continent registered a digital skills gap index between 1.8 and 5, significantly below the global average of 6, according to the World Bank. The institution also noted that 12 of the 20 countries with the lowest levels of digital skills are located in Africa, hindering the growth of a competitive digital economy.
Initiatives like dSkills-EA are crucial for bridging this gap and preparing Africa’s youth for the jobs of the future. By offering targeted training aligned with market needs, dSkills-EA enables young people to quickly enter the workforce by providing them with the technical and practical skills necessary for fast-growing sectors.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji