Tech (1163)
Access to the internet is now a necessity. It improves access to education, healthcare, financial services, and job opportunities. This milestone in Kura is a powerful example of how rural connectivity can directly transform lives—and why it’s urgently needed across Nigeria.
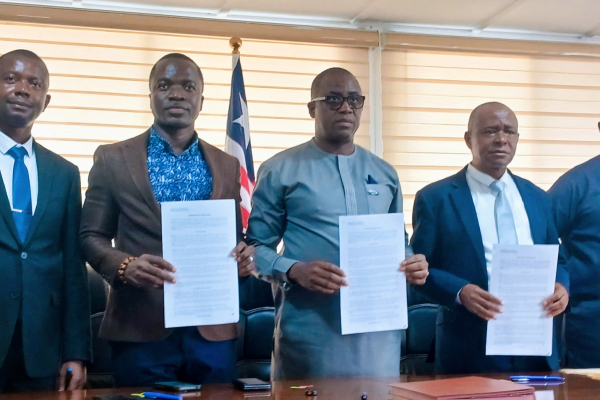
For the first time, the 12,000 residents of Kura, a rural community on the outskirts of Abuja, have access to mobile network and internet services, Minister of Communications, Innovation and Digital Economy, Dr Bosun Tijani, announced on May 29. This development is thanks to a landmark partnership between a rural connectivity initiative, Huawei, and telecom provider Glo.
The new telecom tower was deployed in just two days. Within 48 hours of going live, Kura residents consumed 81.4GB of data and logged 13,144 minutes of voice calls. The site has maintained 100% uptime, with peak LTE download speeds reaching 5.0 Mbps, the minister revealed.
Beyond personal connectivity, the project also supports vital community infrastructure. The local health centre is now linked to global doctors via Huawei’s telemedicine solutions, enabling remote diagnostics and consultations. Meanwhile, the school in Kura is equipped with digital classroom technology, providing students with access to high-quality online learning resources and global educational content for the first time.
A free public WiFi zone has also been launched, ensuring that the entire community, not just those with mobile devices, can benefit from the new digital access.
This pilot is a blueprint for future deployments across Nigeria’s underserved regions. As the project scales, millions more Nigerians could soon experience the transformative power of digital inclusion, from better education and healthcare to economic opportunities and beyond.
Over 20 million Nigerians still live without internet access, according to the Minister. To close this digital gap, the Federal Government has launched a major initiative to deploy 7,000 new telecommunications towers across underserved communities, aiming to connect those who remain entirely cut off from mobile and internet services.
Hikmatu Bilali
• Liberia launches digital health insurance pilot for vulnerable groups
• MoU signed by LTA, NIR, and NICOL to oversee digital infrastructure
The Liberian government is embarking on a pilot program to expand health insurance access for its most vulnerable citizens by leveraging digital technologies. A memorandum of understanding to launch the initiative was signed on Tuesday, May 27, by the Liberia Telecommunications Authority (LTA), in partnership with the National Identification Registry (NIR) and the National Insurance Company of Liberia (NICOL).
The pilot project, set to begin enrollment on July 1, will initially target 5,000 individuals. "The MoU is a pilot project that will provide coverage for groups often underprivileged, including persons with disabilities, unemployed women and youth, pregnant women without support, and children engaged in street trading," the LTA stated in a Facebook post.
Under the agreement's terms, the collaboration will utilize digital identification systems provided by the NIR to ensure robust beneficiary verification and efficient data management. The LTA will oversee the technological infrastructure, guaranteeing secure communication and high-quality service delivery.
This initiative aligns with President Joseph Nyuma Boakai's pledge during his inaugural State of the Nation address to establish a national health insurance scheme, aiming to provide affordable healthcare to the country's most disadvantaged. Abdullah Kamara, acting chairman of the LTA, highlighted that studies in other nations demonstrate technology's potential as a catalyst in this domain. Liberia is also pursuing a broader digital transformation agenda.
Officials emphasize that this is currently a pilot program. A successful outcome will allow for comprehensive evaluation of enrollment procedures, service quality, and beneficiary feedback, with the goal of refining the system for a potential large-scale rollout.
However, limited digital penetration, particularly in Liberia's rural areas, could pose implementation challenges. Data from the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) indicates that internet penetration in Liberia stood at just 23.5% in 2023. The ITU also reported that 59% of Liberians owned a mobile phone, though it did not specify the number of smartphone users.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
-
Togo launches recruitment for "Digital 2025–2030" strategy consultant in bid to update its digital roadmap
-
New strategy targets digital inclusion, innovation, and economic growth
-
Focus areas include skills, cybersecurity, and tech startups
The Togolese government, through its Ministry of Digital Economy and Digital Transformation, has initiated a recruitment process to select a consultant to develop the nation's next digital strategy. Dubbed "Togo Digital 2025–2030," this new roadmap is designed to update the country's existing strategic framework from 2020, integrating the latest technological advancements and addressing emerging national priorities.
The forthcoming strategic document will outline a series of priority programs and projects aimed at strengthening the digitization of public services, boosting digital entrepreneurship, expanding access to digital services for marginalized populations, and fostering economic growth through innovation.
This initiative underscores Togo’s ambition to establish itself as a significant digital player in West Africa, capable of attracting investments in information and communication technologies. In 2022, the digital sector contributed approximately 4% to the national GDP, a growing figure, though still short of the long-term goal to reach 10% in the coming years.
Despite recent progress, significant challenges persist. In 2023, the Regulatory Authority for Electronic Communications and Posts (ARCEP) reported that internet penetration reached 84.72%, with over 7.8 million mobile subscribers in a population estimated at 8.9 million. However, the utilization of digital services remains uneven across different regions and social groups within the country.
The "Togo Digital 2025–2030" strategy is expected to focus on several key areas, including improving network coverage, developing local digital skills, strengthening cybersecurity measures, and bolstering the tech startup ecosystem.
The new strategy will also build upon the achievements of its predecessor. Notable progress from the previous framework includes the launch of the e-Gouv government platform, the establishment of digital service centers, and the adoption of crucial legislative texts on cybersecurity and personal data protection.
Through this refreshed roadmap, Togolese authorities aim to stimulate innovation, enhance technological sovereignty, and accelerate the country’s socio-economic transformation.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
-
Algeria and Russia sign cybersecurity MoU to strengthen digital defenses
-
Agreement includes research, tailored solutions, and training
-
Deal builds on 2023 Algeria-Russia strategic pact amid rising cyber threats
Proxylan SPA, an Algerian state-owned economic enterprise and a subsidiary of the Centre for Scientific and Technical Information Research (CERIST), signed a memorandum of understanding on Sunday, May 25, with Russian cybersecurity firm Positive Technologies. The agreement aims to bolster Algeria's information system protection capabilities as the North African nation accelerates its digitalization efforts across both public and private sectors.
"This is an extremely positive step for the development of cybersecurity programs to benefit Algerian businesses and institutions across all digital sectors," said Idris Si-ahmed, CEO of Proxylan. "Such a partnership illustrates the strong ties between Algeria and Russia."
Specifically, the memorandum outlines joint projects focused on research, the design of cybersecurity solutions tailored to the Algerian context, and the deployment of training programs to strengthen local expertise. The cooperation could also expand into other technological domains, including smart cities, e-government systems, and critical digital services, particularly in the banking sector.
This partnership follows a strategic agreement signed in 2023 between Algerian President Abdelmadjid Tebboune and Russian President Vladimir Putin, which sought to deepen bilateral relations in forward-looking sectors.
Through this initiative, Algeria aims to establish a sovereign digital infrastructure capable of supporting its ongoing digital transformation. In this context, cybersecurity has become a strategic pillar, especially as cyberattacks targeting institutions and businesses are on the rise. Data from Kaspersky indicates that over 70 million cyberattacks have targeted Algeria, partly driven by the increase in remote work and widespread connectivity. This situation underscores the critical need for customized solutions and specialized skills to protect vital infrastructure.
On the Russian side, Positive Technologies, founded in 2002 and listed on the Moscow Stock Exchange, is considered a leader in the cybersecurity sector. The company already serves sensitive entities in North Africa and the Middle East. The partnership with Algeria could enable Positive Technologies to expand its footprint in North Africa while addressing the increasing demand for cybersecurity solutions adapted to specific national requirements.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
• Algeria will launch “Chabab Tech” program to train youth in cloud computing, AI, cybersecurity, and IoT
• Rollout will start via four existing “Skills Centers” but implementation timeline unclear
The Algerian government is set to launch "Chabab Tech," a new program aimed at equipping young people with essential digital skills in areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things. This initiative marks the latest government effort to bolster digital proficiency among the nation's youth.
A framework agreement for the program was formally signed on Saturday, May 24, by Sid Ali Zerrouki, Minister of Post and Telecommunications, and Mostapha Hidaoui, Minister of Youth and head of the Higher Council for Youth.
"Through this initiative, the ambition is to train a generation of 'ambassadors of digital transformation,' exemplary in innovation and responsibility, and capable of actively contributing to the promotion of digital culture and the building of a more competent Algerian society prepared for the challenges of tomorrow," the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications stated in a press release.
"Chabab Tech" builds on previous government efforts to enhance digital literacy. In February, Algeria began rolling out "Skills Centers" to provide free digital training to young individuals. These centers are currently operational in the wilayas of Annaba, Sétif, Oran, and Chlef. The "Chabab Tech" program will initially be implemented through these existing centers, with plans for expansion to other wilayas to ensure equitable national coverage.
These initiatives align with Algeria's "Digital Algeria 2030" strategy, which identifies skills development as a cornerstone among its five main pillars. The strategy underscores the government's commitment to advancing the information society by integrating information and communication technologies (ICTs) across all economic sectors. The executive aims to cultivate a new generation of talent capable of leading the country's digital transformation. While Algeria is not part of Sub-Saharan Africa, the World Bank's estimate that nearly 230 million jobs in that region will require digital skills by 2030 highlights the broader importance of digital training for African nations' development.
However, the government's efforts to enhance youth digital capacities are still in their nascent stages. For instance, the "Skills Centers" currently cover only four of the country's 58 wilayas. Furthermore, a precise timeline for the full implementation of the "Chabab Tech" program remains unspecified, with authorities indicating that details regarding registration and participation will be announced at a later date.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
Africa is steadily embracing digital transformation. While most countries on the continent face challenges in fostering an environment that supports globally competitive, cutting-edge technological innovation, a growing number are proving to be exceptions.
Thirteen African countries have secured spots in the global Top 100 for best startup ecosystems, a report published Wednesday by research firm StartupBlink revealed.
The "Global Startup Ecosystem Index 2025" leverages 33 indicators, categorized across "quantity," "quality," and "business environment," to assess global startup landscapes. These indicators include the number of startups, co-working spaces, and accelerators; total investment in startups, the presence of unicorns, and R&D centers established by major international tech companies; and internet connection speed, internet cost, and R&D expenditure.
South Africa (52nd globally) maintained its lead as the continent's top startup ecosystem. Kenya (58th globally) ascended five places from its 2024 ranking to claim the second spot in Africa.
The rest of the African Top 10 includes Egypt (65th globally), Nigeria (66th), Cape Verde (75th), Ghana (81st), Tunisia (82nd), Namibia (85th), and Morocco (88th). Senegal (92nd globally) rounded out the top ten, followed by Uganda (94th), Rwanda (96th), and Somalia (100th).
Overall, ten African countries improved their rankings from the previous edition, while two (Senegal and Nigeria) experienced a drop. South Africa was the sole country to retain its position. Tunisia saw the largest jump, climbing eight places, followed by Ghana (+7), Kenya (+5), and Morocco (+4).
In its city-level ranking of 1,000 startup ecosystems worldwide, StartupBlink highlighted only Lagos (76th globally) and Cairo (90th globally) within the Top 100. Both cities were recognized for their vibrant ecosystems, which boast multiple unicorns, a high concentration of successful startups, and prominent incubators and accelerators.
Walid Kéfi
The centre is one of many steps Nigeria is taking to bridge the digital divide and build a resilient, inclusive, and innovation-driven economy.
The Federal Government, through the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA), has announced plans to establish at least 1,600 Information and Communication Technology (ICT) centres across Nigeria in the coming years as part of its push for inclusive digital transformation.
Speaking on May 15 during the inauguration of a new ICT centre in Akesan, Lagos, NITDA Director-General Kashifu Inuwa said the initiative aims to ensure every Nigerian—regardless of location or background—has access to digital tools, skills, and opportunities. According to Inuwa, NITDA has already established 222 ICT centres in the last two years, spread across three categories: school ICT facilities, community centres, and innovation hubs. So far, 18 community centres and three ICT hubs have been completed.
“Our goal is to build over 1,600 centres nationwide. We want every Nigerian to be part of our digital prosperity,” Inuwa said, stressing the importance of a sustainable model to operate these centres efficiently without relying on NITDA for minor issues.
He linked the initiative to President Bola Tinubu’s Renewed Hope Agenda, which identifies economic diversification and digital inclusion as top priorities. One of the Agenda’s seven key pillars is focused on accelerating diversification through industrialization, digitization, innovation, and the creative economy. “That’s why NITDA is building these centres—to ensure no Nigerian is left behind in our digital economy,” Inuwa explained.
Also present at the event, Minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy Dr. Bosun Tijani—represented by Johnson Bareyei, Director of e-Government—described the centre as a vital extension of government policy aimed at decentralizing opportunity and embedding innovation in everyday life.
He noted that the centre will support the 3 Million Technical Talent (3MTT) programme, serve startups and tech entrepreneurs, offer regulatory guidance, and foster collaboration among government, private sector, and local communities.
The establishment of ICT centres aligns with Nigeria’s National Digital Economy Policy and Strategy (2020–2030), which emphasizes digital literacy and job creation as key pillars. The centres are instrumental in supporting innovation ecosystems by providing co-working spaces, tech incubation, and mentorship for startups. This is vital for a country seeking to diversify away from oil, where the ICT sector already contributed 16.66% to GDP in Q4 2023.
Hikmatu Bilali
Africa has been progressing steadily in its digital transformation, driven by increased mobile internet usage, fintech advancements, and the rise of e-commerce platforms. However, internet shutdowns disrupt these vital sectors, create uncertainty, deter potential investors, and restrict growth opportunities for startups and entrepreneurs.
Tanzania has blocked access to X, formerly known as Twitter, following the hacking of the Tanzania Police Force’s official account, according to internet watchdog NetBlocks. The social media platform became unreachable across major Tanzanian internet service providers, including Halotel, Airtel, Liquid Telecom, Habari Node, and Vodacom.
⚠️ Confirmed: Live metrics show X (formerly Twitter) has become unreachable on major internet providers in #Tanzania; the incident comes as a compromised police account posts claims the President has died, angering the country's leadership pic.twitter.com/aLbrDmvkAd
— NetBlocks (@netblocks) May 20, 2025
NetBlocks reported that the police account, which has over 470,000 followers, was compromised early Tuesday and posted false claims, including that President Samia Suluhu had died. The account even broadcast live before authorities regained control and announced they were pursuing the hackers.
This incident occurred amid heightened political tension after several East African activists and lawyers were arrested or deported while attempting to observe opposition leader Tundu Lissu’s treason trial in Tanzania. Among those detained were Kenyan activist Boniface Mwangi and Ugandan journalist Agather Atuhaire, who remain missing despite lawyers being informed they were to be deported, according to Amnesty International.
This development reflects a growing trend across Africa, where deliberate internet shutdowns have led to significant economic consequences. In 2024 alone, the continent suffered losses of approximately $1.56 billion, affecting more than 111 million users, according to Top10VPN data.
As mobile technology and internet access continue to expand, such disruptions pose a serious threat to Africa’s digital economy. They undermine communication, interrupt business operations, stall essential services, and ultimately deepen the digital divide, hindering inclusive economic growth and digital transformation efforts.
Hikmatu Bilali
-
Benin launches new AI-powered customs platform
-
The platform enhances data sharing among trade actors, aiming to reduce fraud, speed up goods processing, and attract investment.
Benin has rolled out a new national intelligent customs management system, developed by trade facilitation technology firm Webb Fontaine, marking a significant stride in the West African nation's digital transformation efforts.
Webb Fontaine announced the official launch of Customs Webb on Wednesday, May 21. The new system is now operational across all of Benin's customs offices, including ports, airports, and land border posts, replacing the older ASYCUDA (SYDONIA) software.
Anicet Houngbo, Managing Director of Webb Fontaine Benin, stated that Customs Webb is designed to foster a "more efficient, less burdensome, transparent, and intelligent environment for customs operations," enabling Benin to fully leverage this technological advancement.
The platform's deployment was accelerated over 14 months without any disruption to ongoing customs activities. It incorporates artificial intelligence tools aimed at boosting transparency, efficiency, and the fluidity of trade. Since its implementation, the system has already processed over 100,000 customs declarations, recorded more than 200,000 payments, and issued 100,000 vehicle passes. It currently supports 800 active users and connects 95 organizations.
This initiative aligns with the Beninese government's digital strategy, launched in 2016, with the goal of positioning the country as a regional hub for digital services in West Africa. As part of this broader strategy, Benin previously rolled out the Single Window for Foreign Trade between 2018 and 2024, also in partnership with Webb Fontaine. This process included the progressive integration of tools such as the Port Community System and an electronic cargo tracking solution.
The new system significantly enhances the interconnection of Benin's primary trade platforms, enabling automatic data sharing among customs, port authorities, transporters, and banks. This improved interconnection is expected to expedite goods processing, mitigate fraud risks, and optimize tax revenue collection. Ultimately, it aims to bolster Benin's appeal to investors by offering a more transparent, faster, and more secure business environment.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
This move marks a significant milestone in Nindohost’s pan-African strategy, positioning it as a key player in enabling reliable and scalable digital infrastructure for startups, SMEs, and large enterprises.
Moroccan-based hosting provider Nindohost announced, on May 19, its expansion into 13 African countries, reinforcing its mission to deliver robust, ultra-efficient, and locally adapted cloud and hosting infrastructure across the continent.
“For nearly two decades, Nindohost has been forging excellence in hosting in Morocco. Today, we export this know-how to 13 countries in Africa — from Senegal to Kenya, Ghana and South Africa,” the company stated.
As part of this expansion, users across Africa will experience ultra-low latency and full compliance with local data regulations through Nindohost’s strategic Points of Presence. The company’s service portfolio now includes multi-tenancy hosting, virtual private servers, dedicated servers, managed cloud solutions, and advanced cybersecurity services—all designed to meet a wide range of business needs. Customers will also benefit from 24/7 multilingual support in French, English, and Arabic, delivered by locally based expert engineering teams. To ensure accessibility and convenience, Nindohost has introduced flexible billing options, including local currency transactions and country-specific payment methods.
Traditionally, many African websites have relied on servers located outside the continent, resulting in higher latency, increased costs, and potential regulatory challenges. Nindohost's expansion into 13 African countries directly addresses these issues by offering localized hosting solutions tailored to the continent's needs.
Local hosting significantly strengthens Africa’s digital infrastructure by enhancing website performance, ensuring data sovereignty, reducing operational costs, and improving cybersecurity. It also enables better compliance with regional regulations while fostering local innovation and job creation through investment in tech infrastructure.
This expansion comes at a pivotal moment as Africa experiences a surge in digital transformation, driven by rising internet penetration and growing demand for secure, scalable digital services. Nindohost’s presence in new markets empowers businesses to scale their digital operations efficiently, while maintaining regulatory alignment and global standards. With the African web hosting market projected to reach $3.21 billion in revenue by 2025 and grow to $6.26 billion by 2029 at an annual rate of 18.14%, according to Statista, the need for robust, locally anchored hosting infrastructure has never been more urgent.
Hikmatu Bilali
More...
As AI adoption grows across industries—from telecommunications and energy to healthcare and insurance—the demand for advanced GPU processing is rising rapidly. The partnership is set to accelerate the availability of powerful AI infrastructure to African businesses, making it easier and more cost-effective for them to adopt technologies.
Cassava Technologies, a pan-African technology provider, has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Sand Technologies, a global enterprise AI solutions provider. The announcement, made during the Global AI Summit on Africa in Kigali, marks a major milestone in expanding access to AI and GPU-as-a-Service (GPUaaS) solutions across the continent.
“By providing Sand Technologies with access to our GPU solutions, we are enabling them to develop advanced AI applications for clients while expanding Cassava’s presence across multiple sectors,” said Hardy Pemhiwa, President and Group CEO of Cassava Technologies. “Our GPU-as-a-Service model offers African businesses scalable, affordable AI computing capacity essential for competing in a digital-first world.”
Sand Technologies will use Cassava’s NVIDIA-powered GPU infrastructure to build and deploy enterprise-grade AI solutions globally. The companies will jointly identify pilot projects and co-create industry-specific solutions that leverage AI to drive efficiency, productivity, and innovation across the continent.
AI development, especially machine learning and deep learning, requires powerful GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). These are often expensive and complex to maintain in-house. The delivery of AI solutions and GPU-as-a-service (GPUaaS) across Africa significantly benefits African businesses by providing affordable, scalable access to high-performance computing power necessary for developing and deploying AI tools. This removes infrastructure and cost barriers, enabling startups and SMEs to integrate AI into operations such as customer service, data analysis, and automation.
As digital transformation accelerates across Sub-Saharan Africa, artificial intelligence is emerging as a key driver of economic opportunity. The United Nations projects that AI could contribute up to $1.5 trillion to the region’s economy by 2030, unlocking new pathways for productivity, innovation, and inclusive growth. Yet access to scalable computing infrastructure remains a significant barrier. This partnership addresses that gap by combining Cassava’s GPU infrastructure with Sand Technologies’ enterprise AI capabilities.
Hikmatu Bilali
-
Côte d’Ivoire signs three AI-related MoUs at first National AI Conference
-
Agreements support rollout of National AI Strategy (SNIA)
On Monday, May 19, Côte d’Ivoire’s Ministry of Digital Transition and Digitalization signed three memorandums of understanding with technology firms during the country’s first National AI Conference, held in Abidjan. These agreements are part of a broader push to foster local innovation, build digital skills, and support the rollout of the National Artificial Intelligence Strategy (SNIA).
The first agreement, signed with the Digital and Technologies Center of Excellence (CEDITECH), aims to launch training programs tailored to the needs of the Ivorian market while supporting digital entrepreneurship. A second deal, with Amini Corp—a startup specializing in AI-powered environmental data—focuses on strengthening the country’s digital sovereignty and promoting inclusive technological innovation. The third partnership, with local hardware distributor TBI, will provide training for public sector employees on how to use AI tools effectively.
These initiatives fall under the SNIA, adopted in March, which aims to build a robust ecosystem for innovation, digital inclusion, and youth capacity building. They also come amid growing interest in AI’s potential on the African continent. A recent McKinsey study estimates that AI could add as much as $1.2 trillion to Africa’s GDP by 2030, representing a 5.6% increase.
Through this national strategy, the government seeks not only to modernize public administration but also to create high-quality job opportunities for young people, who account for over 70% of the population. The ultimate goal is to position Côte d’Ivoire as a regional tech hub in West Africa, as AI applications gain traction across key sectors, including agriculture, healthcare, education, and financial services.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
• Kenya plans to establish a Regional Center of Competence focused on digital skills and AI.
• The center will back the Kenya Digital Master Plan 2022-2032, which aims to train 300,000 civil servants by 2030.
The Kenyan government is set to establish a Regional Center of Competence focused on advancing digital skills and artificial intelligence (AI), a move aimed at bolstering the capabilities of civil servants to enhance the quality of public services for the populace.
The initiative is backed by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and will be affiliated with the Kenya School of Government, an institution dedicated to the ongoing professional development of public administration executives and civil servants. The center's launch was discussed last week during a meeting between John Tanui (photo, right), Principal Secretary for Digital Economy and ICT, and his counterpart responsible for Public Service and Human Capital Development, Jane Kere Imbunya (photo, left).
This undertaking aligns with the Kenyan government's broader digital transformation agenda, which seeks to harness digital technology for socio-economic progress. Cultivating the digital proficiency of civil servants stands as a key pillar of the "Kenya Digital Master Plan 2022-2032." The government has set an ambitious target to train 300,000 civil servants in digital services by 2030, representing 85% of public employees.
This approach finds support from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). In its report, "Developing skills for digital government: A review of good practices across OECD governments," the OECD emphasizes that to facilitate the transition to digital administration, nations must invest in developing the skills of their civil servants. This comes against the backdrop of a World Bank estimation that nearly 230 million jobs in sub-Saharan Africa will demand digital skills by the year 2030.
However, the specific timeline for the center's operationalization remains undetermined. Furthermore, the OECD cautions that the effectiveness of civil servant training will hinge on its design and implementation. The organization recommends that governments identify crucial digital skills, assess the existing competencies of public employees, address any gaps with customized training programs, and subsequently evaluate the impact to refine future initiatives.
By Isaac K. Kassouwi,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
• Egypt is investing $59 billion to build a futuristic smart city 45 km east of Cairo as part of its Vision 2030 strategy.
• The city will feature AI, IoT, connected transport, automated public infrastructure, and intelligent surveillance
Egypt is channeling $59 billion into the development of a futuristic smart city, a flagship project under its Vision 2030 strategy. This high-tech megacity, currently under construction 45 kilometers (about 28 miles) east of Cairo, is intended to ease congestion in the capital and establish Egypt as a frontrunner in digital urban planning across Africa.
Conceived as a regional technology hub, the new administrative capital will integrate cutting-edge digital solutions, encompassing artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), automated management of public utilities, interconnected transportation networks, and intelligent surveillance systems. The initial phase, requiring an investment of $8.4 billion alone, is largely complete, exceeding 70% progress. Subsequent phases are projected to continue until 2027, with potential adjustments based on economic developments.
This ambitious megaproject aligns with a rapidly expanding global trend. Worldwide, the smart city market is experiencing significant growth. Valued at $1.36 trillion in 2024, it is forecast to reach $3.84 trillion by 2029, demonstrating an average annual growth rate of 23.21%, according to data from Mordor Intelligence.
While Africa currently constitutes a modest portion of this global market, the continent is progressively emerging as a significant player. Countries such as Egypt, Morocco, Rwanda, Nigeria, Kenya, and South Africa are prioritizing smart urban initiatives to tackle urban population growth, governance challenges, transportation issues, and sustainability imperatives.
In Egypt's case, this smart city is designed to accommodate 6.5 million residents. It will house key government functions, including headquarters and ministries, foreign embassies, and centers for digital innovation. Buildings throughout the city will be equipped with smart sensors to optimize energy and water consumption, enhance security, and manage mobility efficiently.
Despite criticism concerning investment priorities in a nation grappling with high inflation and increasing public debt, Egyptian authorities maintain a long-term perspective. They are banking on the project's potential to generate economic benefits, create skilled employment opportunities, and drive the digital transformation of government administration as catalysts for sustainable progress.
Samira Njoya