Tech (1163)
- Cape Verde launched a technology park aimed at becoming a regional tech hub
- The park offers international-standard infrastructure and tax incentives
- It supports economic diversification and youth employment
Cape Verde officially inaugurated TechPark CV on Monday, a regional technology center designed to boost innovation and digital transformation both within the island nation and beyond its borders.
The project, backed by a 45.59 million euro ($51.7 million) investment from the African Development Bank (AfDB), is a key strategic move for Cape Verde as it aims to establish itself as a technology hub in West Africa.
"TechPark CV offers a welcoming space where innovators from diverse backgrounds and cultures can collaborate and flourish together," stated Carlos Monteiro, President of TechPark CV. "Through this initiative, we are not simply constructing a digital center; we are cultivating a community where technology fuels economic growth and sustainable development for Cape Verde and our international partners."
The technology park aligns with the nation's broader economic diversification strategy and is a component of Cape Verde’s 2030 digital economy development plan. The investment represents nearly 2% of the country’s gross domestic product, underscoring the significant emphasis placed on digital technology within its growth model.
International-Standard Infrastructure
The technology park features data centers, co-working spaces, a training facility, a business center, and a conference center, all interconnected by high-speed infrastructure. Its designation as a Special Economic Zone for Technologies (ZEET) provides appealing tax benefits, including VAT exemption, reduced import duties, and a lowered corporate tax rate of 2.5%.
Operating across two campuses located in Praia on Santiago Island and Mindelo on São Vicente Island, TechPark CV already houses 23 companies and has the capacity for up to 1,500 professionals. It aspires to become a focal point for innovation, training, and experimentation, while also attracting foreign investment.
Beyond attracting domestic and international businesses, TechPark CV aims to be a catalyst for the development of crucial technology sectors such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, fintech, big data, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Cape Verde also intends to strengthen its regional cooperation through a partnership with the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) to contribute to the expansion of digital innovation in West Africa.
The project prioritizes the integration of local talent. It fosters partnerships with academic institutions and seeks to create job opportunities for Cape Verdean youth, thereby contributing to the development of human capital and the strengthening of the national economy.
Samira Njoya
- India pledged digital infrastructure support to Angola, including cooperation in e-governance, space, and healthcare
- $200M defense credit line and will help implementdigital public infrastructure model, enabling digital IDs, e-payments, and social registries in Angola.
India has pledged to share its expertise in digital public infrastructure with Angola. The announcement came after a meeting in New Delhi on Friday, May 3, between visiting Angolan President João Lourenço (photo, left) and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi (photo, right). The initiative aims to enhance e-governance and streamline citizen access to public services in Angola.
According to a joint statement, India has "approved a $200 million credit line for Angola's defense and will collaborate in the areas of digital public infrastructure, space, and healthcare." The partnership seeks to introduce Angola to India's model of digital public infrastructure (DPI), an interoperable system that digitizes administrative services, promotes financial inclusion, and connects citizens with essential services.
This collaboration could enable Angola to implement digital identification systems, electronic payment platforms, and unified social registries. It also includes provisions for cooperation in the space sector and training in digital skills.
The announcement underscores a growing strategic alignment between the two nations, which are marking 40 years of diplomatic ties this year. It also reflects India's ambition to expand its technological influence across the African continent. India has already deployed similar systems in Africa, notably through its Modular Open Source Identity Platform (MOSIP), which countries like Morocco, Sierra Leone, Guinea, and Ethiopia have adopted or are in the process of implementing. Furthermore, India is collaborating with several African nations to develop digital payment systems inspired by its Unified Payments Interface (UPI), with advanced discussions underway, particularly with Rwanda.
Ultimately, this partnership has the potential to accelerate the modernization of Angolan government services, improve administrative efficiency, and stimulate local innovation. It represents strategic support for Angola as it strives to improve its standing in international digital governance rankings. According to the United Nations, Angola currently ranks 156th out of 193 in the 2024 e-Government Development Index, with a score of 0.4149, falling below both the African average (0.4247) and the global average (0.6382).
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- African tech startup funding dropped from $5.2B in 2021 to $2.2B in 2024, with fintech most affected; global VC slowdown and investor caution cited as key causes.
- Healthtech remains resilient, attracting over $1B in five years; startups like Ilara Health (Kenya) and Waspito (Cameroon) are addressing critical healthcare access issues.
- Connectivity and affordability remain major hurdles, with limited mobile internet access and high smartphone costs slowing healthtech adoption despite infrastructure gains.
A recent dip in funding for African tech startups reflects a broader slowdown in venture capital and increased investor caution due to global economic uncertainties. Following a boom in investment in 2021, the global venture capital market, including in Africa, underwent a correction in 2022 and 2023.
"Two years into the global downturn, it's clear the African tech ecosystem is experiencing the full severity of it even though it's faring much better than the Latin America and Southeast Asia regions," Cyril Collon, General Partner at the transatlantic fund Partech, noted in 2024.
He added that "despite this correction, over the last 10 years, the African tech ecosystem has still grown nearly tenfold in transactions and funding amount with about $20 billion invested in roughly 3,000 deals, 68% of it in the last three years."
According to Partech Africa, African startups collectively raised $5.2 billion in equity funding in 2021, a figure that dropped to $2.2 billion in 2024. Fintech, historically the most attractive segment for investment on the continent, also felt the impact of this capital squeeze. In 2021, African fintech companies raised $3.2 billion, representing 63% of total funding, compared to $1.35 billion in 2024.
A Resilient Ecosystem
Despite the funding pullback, healthtech has attracted over $1 billion in Africa over the past five years, according to Ecofin Agency. From $18 million in 2018, funding surged tenfold the following year to $189 million, peaking at $230 million in 2021. These investments have enabled innovators to proliferate e-health solutions across the continent, ranging from telemedicine platforms to drone delivery of medication and blood in road-inaccessible areas.
In Kenya, Ilara Health provides affordable diagnostic tools to healthcare providers in rural areas. The company partners with artificial intelligence services integrated into its technology platforms distributed to doctors, thereby improving the organization of patient care in rural settings. Since its 2019 launch, Ilara Health has secured approximately $10.8 million in investment to fuel its activities.
Cameroonian healthtech startup Waspito connects patients and doctors for instant video consultations through its mobile app available on iOS and Android. Launched in 2020, Waspito has raised around $8.7 million, according to Crunchbase, to develop its technology and expand into other African countries such as Gabon, Côte d’Ivoire, and Senegal.
These startups are tackling the critical shortage of healthcare professionals and infrastructure across the continent. In 2021, sub-Saharan Africa averaged 2.3 doctors and 12.6 nurses/midwives per 10,000 inhabitants, compared to 39.4 and 89.5 in Europe, for example. The World Health Organization (WHO) projects that Africa will face a deficit of 6.1 million health professionals by 2030, a 45% increase from 2013 estimates.
"The severe shortage of health professionals in Africa has disastrous implications. Without adequate and well-trained staff, tackling challenges such as maternal and infant mortality, infectious and non-communicable diseases, and the provision of essential health services like vaccination remains a difficult battle," said Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa, in 2022.
Scaling Healthtech: Overcoming Hurdles
Expanding access to healthtech solutions faces the significant challenge of limited internet access across the continent. Data from the GSM Association (GSMA) indicates that sub-Saharan Africa had 320 million mobile internet users in 2023, with a penetration rate of 27%. This figure is projected to grow annually by 6.2% to reach 520 million by 2030, representing a penetration rate of 37%.
This limited access is attributed to the cost of smartphones, the price of internet service, and infrastructure limitations. The GSMA emphasizes "an urgent need to reform taxation to improve the affordability of smartphones and mobile services, whose cost is a major barrier to mobile broadband adoption."
Africa's Telecommunications Infrastructure Index (TII) score in 2024 was 0.4534 out of 1, according to the United Nations. This represents a 27.8% increase from 2022, when the score was 0.3548. The global average, in contrast, was 0.6896 out of 1.
If these various obstacles can be overcome, healthtech has the potential to become a strategic cornerstone for the sustainable improvement of Africa's healthcare sector. By leveraging digital tools to bring care closer to the population, startups in this sector are reinventing healthcare delivery. The crucial question remains whether the ecosystem can once again attract the necessary funding to move beyond pilot projects and achieve systemic integration.
- IMF supports Madagascar's AI-driven customs reform, with experts training officials on integrating AI to boost efficiency and transparency.
- AI tools already in use—such as image analysis and risk assessment systems—helped increase customs revenues by 68% year-on-year in January 2025.
Madagascar's customs authority is currently receiving technical support from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to accelerate its digital transformation. Two specialists, Victor Budeau and François Chastel, began their mission in Antananarivo on Thursday, April 24th. Their assignment, scheduled to conclude on Wednesday, May 7th, includes intensive training focused on incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into customs procedures.
The objective is to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and transparency of operations. During a working session, the Director General of Customs, Ernest Zafivanona Lainkana (pictured, center), underscored the significance of centralizing data within a unified database to fully harness the potential of AI. He also affirmed that this technology must now become a fundamental component of customs tools.
This initiative is not merely an experiment but rather part of an ongoing strategy. The customs administration is already using several AI-driven solutions: automatic image analysis (RESNET), Smart Scanning, and the Enhanced Risk Assessment (ERA) system. These tools have contributed to a 68% increase in customs revenues in January 2025 compared to January 2024.
Given these positive outcomes, the IMF has designated Madagascar as a pilot project in Africa for the integration of AI into customs services. This strategic recognition could lay the foundation for a continent-wide strategy. By 2029, Madagascar's customs authority aims to extend these technologies to additional control sectors, strengthen its digital infrastructure, and share its expertise at the regional level.
- Kenya launches 2025–2030 national AI strategy focused on ethical, inclusive, and innovation-driven adoption across key sectors like health, agriculture, and public services.
- Strategy emphasizes data sovereignty and responsible governance, outlining future regulations on privacy, cybersecurity, and cross-border data flows.
- Plan aims to position Kenya as a regional AI leader, aligning with African Union initiatives and aiming to attract global partnerships and investment.
Kenya has unveiled its inaugural national artificial intelligence strategy, covering the years 2025 through 2030. The document articulates a distinct vision for the ethical, inclusive, and innovation-led integration of AI technologies. This initiative forms part of the nation's wider digital transformation agenda and serves as a clear indicator to international technology firms closely observing regulatory developments within emerging markets.
While formulated at the national level, the strategy mirrors a broader trend: the adaptation of global AI governance norms to the specific circumstances of emerging economies. It organizes Nairobi’s ambitions around several core pillars, encompassing infrastructure development, data sovereignty, sector-specific applications, and responsible innovation. The strategy also lays the groundwork for future legislative action.
Data governance stands out as a pivotal element of the document. Kenya signals its intent to cultivate an AI ecosystem anchored in local frameworks, adhering to principles of privacy, cybersecurity, and ethics. This approach could introduce new obligations for multinational corporations operating through cloud infrastructure or engaging in cross-border data transfers, particularly concerning data localization requirements or consent protocols.
The sectors identified for targeted AI deployment are those where the technology has the potential for rapid and significant impact: healthcare, agriculture, financial services, and public administration. Use cases such as AI-assisted diagnostics, personalized medicine, and the automation of administrative processes are prioritized, with a strong emphasis on managing potential ethical risks.
The strategy also envisions the development of a robust national digital infrastructure, fostered through collaborations between the public and private sectors. Data centers, cloud computing resources, and technology research centers will be central to this transformation. These investments could unlock substantial commercial opportunities while simultaneously establishing new compliance requirements, especially for cloud service providers and telecommunications operators.
Although the document does not yet carry the force of law, it outlines a prospective regulatory framework for AI within Kenya. The strategy addresses sensitive areas including risk classification, regulatory oversight mechanisms, and algorithmic governance.
Through this strategic document, Kenya aims to position itself as a key voice in the African AI discourse. While other nations on the continent, including Nigeria, Rwanda, and Algeria, have already adopted their own national AI strategies, Nairobi seeks to assert its unique vision, strengthen international partnerships, and proactively anticipate evolving global standards. The strategy thus aligns with several pan-African initiatives, notably those spearheaded by the African Union, the East African Community (EAC), and the Africa Smart Alliance.
The primary challenge will be the practical implementation of this vision. Success may hinge on the ability to mobilize both public and private sector investments, establish a governance framework that is both open and rigorous, and enhance local expertise—particularly through training programs, research initiatives, and the development of technology innovation hubs.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Most African countries lack core AI infrastructure, including internet access, fiber networks, and data centers; Egypt and South Africa lead regional efforts.
- Low digitalization and weak data systems hamper AI development; only South Africa and Mauritius score high in e-government readiness.
- Africa faces a major AI skills gap, but hubs like Nigeria, Kenya, and Egypt are expanding talent pools through tech partnerships and training.
As artificial intelligence reshapes global economies, its adoption in developing countries—particularly in Africa—raises critical issues. It can accelerate progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by supporting smart agriculture and energy networks, optimizing production and supply chains, improving water management and urban planning, and much more. Case studies show that AI boosts productivity and improves living conditions, if backed by suitable policies and skillsets. UNCTAD, in its Frontier Technologies Readiness Index, assesses countries' capacity to integrate AI. Three critical points emerge for the effective adoption and development of AI. The assessment for Africa on these indicators reveals striking disparities with the rest of the world, also highlighting crucial investments needed for a full and successful 4.0 transformation.
Infrastructure
This indicator refers to digital connectivity and computing power, as well as the networks, architecture, and associated resources needed to create, train, and use AI solutions within a community or country.
Countries best prepared for AI infrastructure
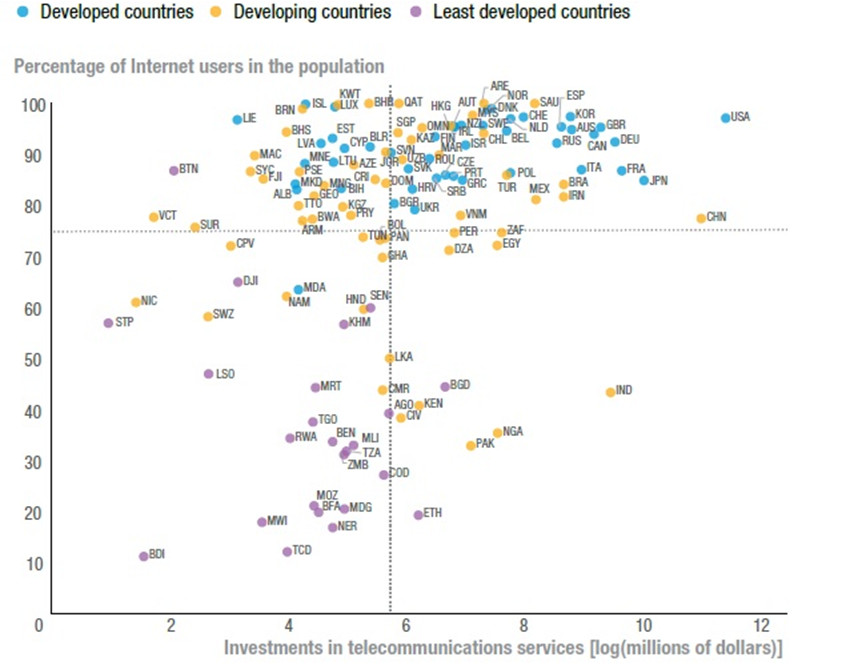
Source: UNCTAD
Many African countries rank among the least prepared for AI globally. In fact, the vast majority of the continent lags significantly in Internet penetration and investments in telecommunications services. In 2024, only 38% of Africans had Internet access compared to a global average of 68%, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). According to Africa Analysis, the total inventory of operational terrestrial fiber optic networks in Africa was about 1,337,158 km, with 112,373 km under construction. However, some North African countries, such as Egypt and Morocco, exceed global averages in Internet penetration and telecom investments, partly thanks to submarine cables. Egypt, due to its geographic position and connections with numerous submarine cable operators, could become a hub linking three continents. The country alone is connected to more than fifteen submarine fiber optic cables. It boasts nearly 90% Internet penetration.
Number of Cloud Infrastructure Services, mid-2024
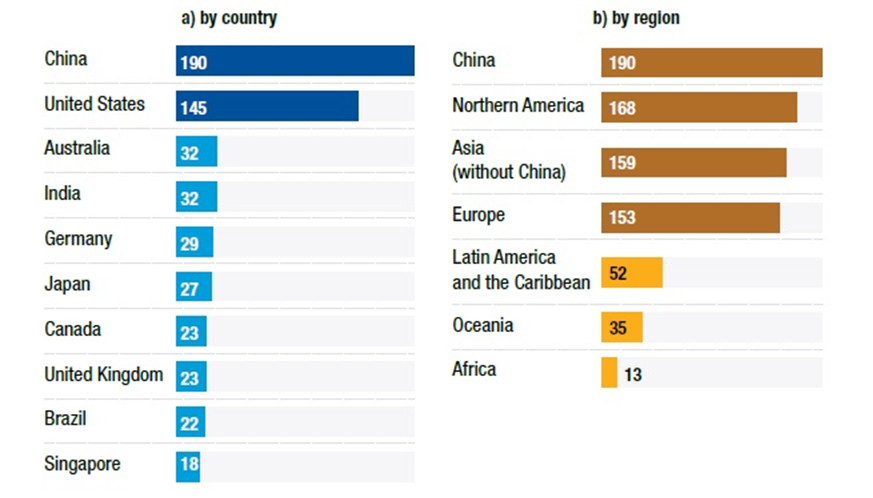
Source: UNCTAD
Africa also lags behind other continents in terms of traffic and participation in Internet Exchange Points (IXPs). Despite its 53 exchange points located in 36 countries, according to the Internet Society, only three countries met the 2010 goal of localizing 80% of all Internet traffic by 2020, with just 20% going through international lines in order to reduce latency and costs.
In terms of cloud infrastructure services, Africa is also behind other regions. South Africa, Kenya, and Nigeria currently host the largest number of data centers on the continent—more than ten centers. Nonetheless, some countries are speeding up digitization, attracting growing interest from investors in data storage and hosting.
Data
Data is essential for training AI models, with dedicated datasets required to apply models to various use cases. Data is not only an input but is also generated by AI systems. Most African countries are considered “laggards” in terms of data readiness for AI, with low potential for adoption and development. The low level of digitization in the majority of African countries deprives the continent of data to feed AI models essential for information analysis. According to the 2024 e-Government Development Index, only two African countries scored very high: South Africa and Mauritius. Seventeen countries had high scores. The remaining thirty-five countries on the continent scored below the global average.
Countries with Internet accessibility favorable for AI
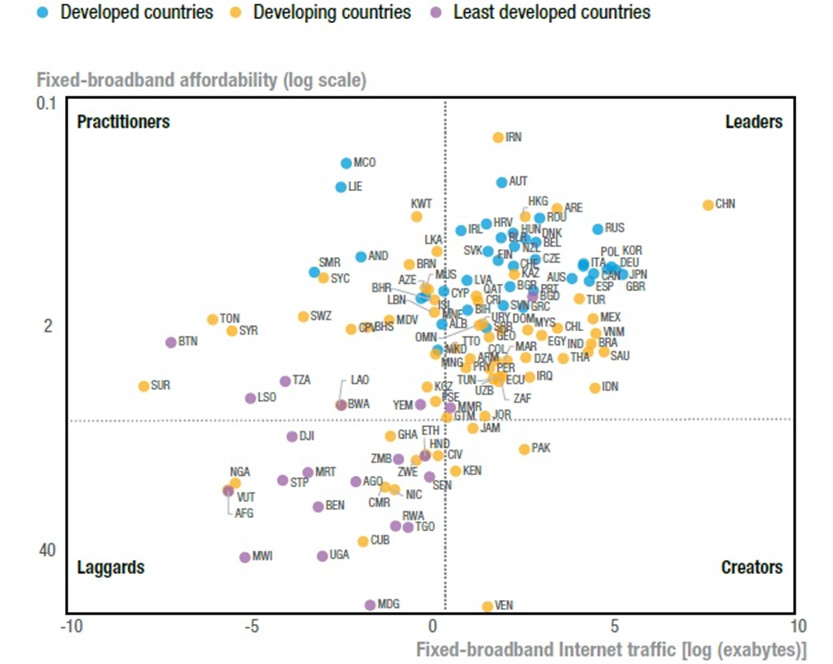
Source: UNCTAD
With regard to fixed broadband data traffic—critical for data flow—Least Developed Countries (LDCs), many of which are African, lag behind other developing nations. In its Mobility Report from November 2024, Ericsson indicates that mobile data traffic will grow by only 21% between 2024 and 2028, rising from 5.4 to 17 gigabits per month. This volume remains well below other regions and even below the global average, which is expected to rise from 19 to 40 gigabits per month.
Internet Exchange Point traffic and number of members, mid-2024
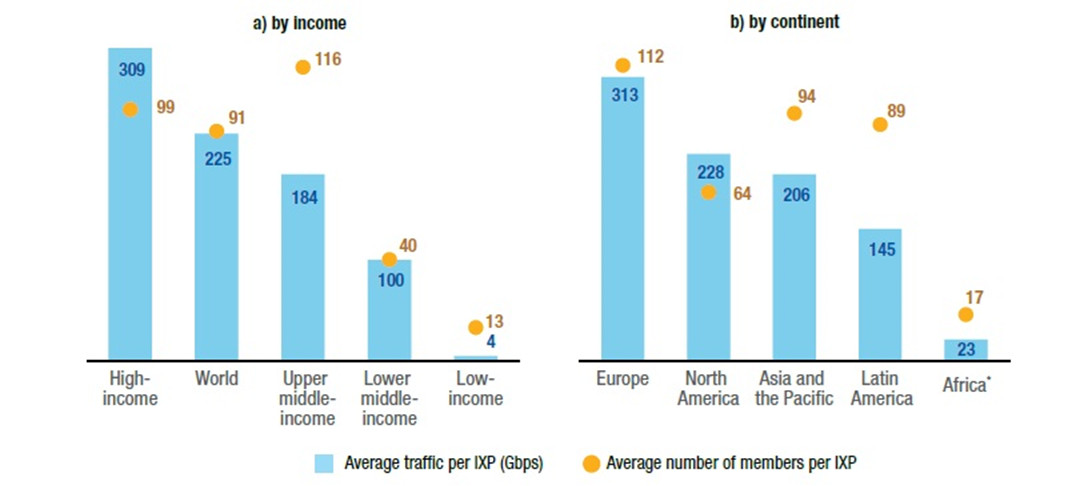
Source: UNCTAD
Delays in Internet exchange points and their transformation also weigh on Internet consumption and data generation.
Skills
On average, LDCs—many of which are in Africa—score significantly lower than developing and developed countries across all dimensions of the Frontier Technologies Readiness Index, with the skills index showing the largest gap.
African countries record relatively low scores in terms of developers per working-age population and in the share of the working-age population with higher education, notes UNCTAD.
Countries with AI-related skills (AI readiness)
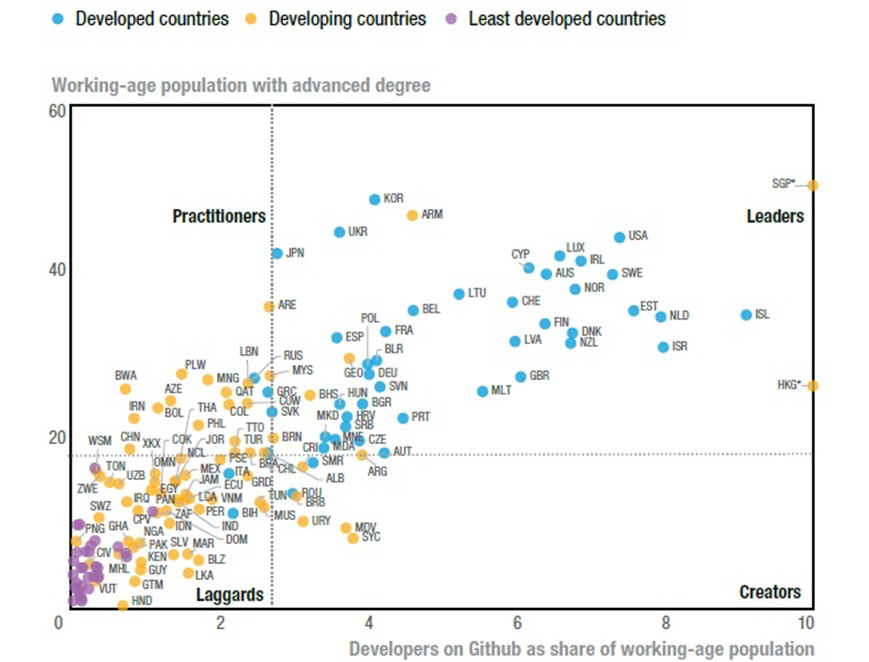
Source: UNCTAD
However, countries like South Africa, Nigeria, Ghana, and Kenya have seen rapid growth in the number of developers, becoming promising hubs for tech companies and fertile ground for tech innovation. Ethiopia and Egypt are also seeing fast growth in the number of people with intermediate and high-level digital skills, thanks to a surge in international partnerships. Private initiatives such as Andela and others backed by major groups like Microsoft, Google, and Huawei also offer hope for Africa’s future workforce.
UNCTAD's report draws a clear conclusion: Africa is currently ill-prepared for the AI revolution. Yet strong signals suggest the continent can catch up by accelerating investments in digital infrastructure, unlocking the potential of data, and scaling up tech skill development. Countries like Egypt, Kenya, and Nigeria are showing the way. If these efforts become widespread, Africa could not only adopt AI, but also become a major player, creating solutions tailored to its unique challenges.
Muriel EDJO
- Senegal has adopted a national digital health policy to coordinate health sector digitization and improve service efficiency and data governance.
- A draft digital health law is being finalized to regulate the use, security, and confidentiality of medical data.
- The $150M World Bank–funded PAEN project supports this effort, including expanding electronic patient records to six more regions in 2025.
Senegal has officially adopted a digital health policy framework designed to structure the digitization of its medical sector. Approved on Monday, April 28th, by Health and Social Action Minister Ibrahima Sy, this document aims to integrate digital technologies into healthcare services while enhancing their governance and efficiency.
Speaking about the new framework, Minister Sy stressed the importance of better coordinating the numerous digital initiatives already in progress, which are often implemented in a disjointed manner. A primary goal is to prevent redundancy and optimize resources. He also underscored the urgent need for a strong legal framework to ensure the security and confidentiality of citizens' health data.
In line with this, a draft law on digital health is being finalized and will soon be submitted to the General Secretariat of the Government. This legislation seeks to formally regulate the use of technology within the health system by establishing clear guidelines for the collection, storage, and utilization of medical data.
These initiatives are part of the Digital Economy Acceleration Project (PAEN), a $150 million initiative financed by the World Bank through 2028. PAEN notably aims to strengthen high-speed connectivity resilient to climate risks and to promote the adoption of online public services, including the electronic patient record (EPR).
The program plans to expand the electronic patient record (EPR) to six additional regions starting this year, following a pilot phase conducted in several facilities in Dakar. These included the Abass Ndao and Thierno Birahim Ndao hospitals, the Khadim Rassoul health center, and the HLM Fass health post.
Despite this progress, significant challenges remain. A key concern will be preventing digitization from widening disparities in access to care, particularly in rural or poorly connected areas. The widespread availability of digital tools, the inclusion of the most vulnerable populations, and the training of healthcare personnel will be critical for the success of this transition.
Ultimately, the success of this transformation hinges on robust governance of health data to maintain public trust in these new systems. Therefore, its success will depend on its ability to effectively combine innovation, equity, and security.
Samira Njoya
- Tanzania collected $71.5 million in digital tax revenue from 1,820 online businesses, mainly in betting, between July 2024 and March 2025.
- A national e-commerce strategy is being finalized to modernize regulations, boost tax collection, and support digital sector growth.
- Digital services are taxed under a robust framework, including a 2% DST, 3% withholding tax, and 18% VAT on electronic services.
Between July 2024 and March 2025, the Tanzanian government collected 192.78 billion Tanzanian shillings (approximately $71.5 million) in tax revenue from 1,820 businesses operating online, with the digital betting industry being the primary contributor. Deputy Minister of Industry and Trade Exaud Kigahe disclosed these figures in Parliament on Wednesday, April 29th.
During the same parliamentary session, Kigahe announced that Tanzania is in the final stages of developing a national e-commerce strategy. This plan seeks to adjust the regulatory environment to the evolving digital marketplace and to optimize tax revenue generated by this rapidly expanding sector.
Key components of the strategy include bolstering information and communication technology infrastructure, revising current public policies and regulations, and enhancing communication, transportation, and logistics services. It also underscores the importance of securing online transactions and increasing public awareness regarding the adoption of digital platforms.
This strategy will align with the existing tax framework governing digital services. Since July 2022, Tanzania has implemented a 2% Digital Services Tax (DST) on non-resident providers of electronic services, in addition to a 3% withholding tax on platforms facilitating transactions. These services are also subject to an 18% VAT. This framework is designed to ensure the fair taxation of locally generated revenue, particularly from foreign entities.
Through this strategy, Tanzanian authorities aim to stimulate the use of online commerce, enhance tax collection, and combat undeclared digital activities. The government's challenge now will be to solidify this growth while addressing the risks associated with the digital sector, particularly in sensitive areas like online gambling.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Senegal’s APROSI and Orange Business sign partnership to digitize industrial hubs
- Agreement signed April 28, 2025, to equip sites with fiber optics, private networks, cloud services, and cybersecurity
- Plan includes smart energy management, connected lighting, enhanced security, and improved mobility within industrial zones
On Monday, April 28, 2025, Senegal’s Agency for the Development and Promotion of Industrial Sites (APROSI) and Orange Business Senegal, the business-to-business arm of the SONATEL Group, entered into a strategic partnership to equip the nation's industrial hubs with next-generation digital services.
The alliance seeks to transform industrial sites into smart, connected, sustainable, and competitive platforms capable of meeting the demands of Industry 4.0. Orange Business will contribute its expertise in critical areas such as fiber optics, private networks, cloud services, and cybersecurity. The agreement extends further to include the deployment of intelligent energy management solutions, connected public lighting, security, and mobility within industrial sites.
The partnership also entails support for companies in their digital transition. Concrete applications involving the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), and predictive maintenance will be proposed to modernize production tools. A strategic committee and a monitoring and evaluation mechanism will be established to ensure the effective implementation of projects.
This initiative aligns with Senegal's 2050 Economic Transformation Agenda, which positions digital technology as central to the country's growth and competitiveness. It also responds to a regional landscape characterized by increasing competition among West African nations to attract industrial investment. In this strategic contest, the development of connected and high-performing industrial zones could provide Senegal with a significant advantage.
The industrial sector currently accounts for approximately 25% of Senegal's GDP. By equipping it with advanced technologies, the country aims to enhance its productivity, streamline logistics, optimize energy consumption, and strengthen the traceability of value chains. Digital technology thus becomes a strategic tool for building a more resilient, competitive, and future-oriented industry.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Côte d’Ivoire ratifies bill modernizing digital security framework
- National Assembly unanimously adopted the bill on April 24, 2025
- New framework aims to strengthen cybersecurity and align with international standards
Côte d’Ivoire's National Assembly unanimously approved on Thursday, April 24, a bill ratifying Ordinance No. 2024-950 dated October 30, 2024, concerning the security of its digital space. Presented by Minister of Digital Transition and Digitalization Kalil Konaté, the legislation modernizes the legal framework for electronic transactions and bolsters cybersecurity measures within the country.
A key amendment involves the repeal of Article 50 of Law No. 2013-546, which had previously assigned the Telecommunications/ICT Regulatory Authority (ARTCI) responsibility for network security, the auditing and certification of information systems, and the issuance of electronic certificates. These responsibilities are now transferred to the National Agency for Information Systems Security (ANSSI), a specialized cybersecurity body.
Concurrently, Articles 3 and 17 of Ordinance No. 2017-500, pertaining to electronic exchanges between citizens and administrations, are amended to replace references to ARTCI with "the competent body," which now designates ANSSI.
ANSSI's mandate now includes safeguarding the State's networks and information systems, as well as critical infrastructure. It will also coordinate responses to cybersecurity incidents, conduct security audits, certify information systems, and issue electronic certificates to entities operating in Côte d’Ivoire. Furthermore, ANSSI is tasked with promoting cybersecurity best practices among government agencies and economic operators.
This transfer of responsibilities is intended to enhance the protection of Côte d’Ivoire's digital realm by entrusting it to a dedicated and technically proficient agency. It also aims to improve the interconnectedness of public information systems within a framework that ensures transparency, technological neutrality, and security. The ratification of this ordinance sets the stage for the implementation of strengthened digital public policies within a more cohesive legal environment aligned with international cybersecurity standards.
Samira Njoya
More...
Since its inception in 2004, VITIB has aimed to position Ivory Coast as a key player in technological innovation. Now, it's intensifying efforts to attract strategic investments and evolve into a leading technology hub in West Africa.
The Information Technology and Biotechnology Village (VITIB), situated in Grand-Bassam, Côte d’Ivoire, is intensifying its drive to secure $311 million (180 billion CFA francs) to fund its development blueprint through 2028. The initiative aims to transform its special economic zone into a comprehensive technology hub, spurring innovation and economic expansion across West Africa.
To this end, a VITIB delegation recently travelled to India for discussions with investors and prospective collaborators. Conversations focused on investment prospects within the park, infrastructure development, modalities for industrial and financial alliances, and the incorporation of cutting-edge technological solutions. Among the entities engaged were AXL, OKAYA Group, and representatives from the Export-Import Bank of India.
"India occupies a significant chapter in VITIB's history. Shortly after its inception, Côte d’Ivoire’s first technology park benefited from crucial financial backing through a loan from Exim Bank of India, which facilitated the construction of essential infrastructure. As a tribute to this partnership, a section of the technology park was named after Mahatma Gandhi," VITIB stated.
Spanning more than 600 hectares, VITIB is organized into three distinct zones: manufacturing, administrative, and residential. It is home to pioneering enterprises in the fields of information technology and biotechnology. It provides a favorable tax climate, featuring a five-year tax holiday followed by a lowered rate, alongside contemporary infrastructure such as data centers, fiber-optic connectivity, and a single-window service streamlining business establishment.
Its strategic roadmap aims to generate 40,000 skilled employment opportunities and attract $1.6 billion (1,000 billion CFA francs) in foreign direct investment. VITIB thereby aspires to establish Côte d’Ivoire as West Africa’s technological vanguard by cultivating an environment that fosters innovation and competitiveness.
This promotional tour in India forms part of a wider campaign to raise the profile of the technology park, draw new participants from the technology and biotechnology sectors, and investigate novel financing avenues. Leveraging its established relationship with India, VITIB seeks to inject fresh impetus into its project and solidify Grand-Bassam's position as a pivotal innovation hub in Africa.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- RASCOM and Egypt’s Nilesat sign MoU to boost Africa’s space sector
- Agreement signed April 23 aims to enhance satellite capacity use, training, and innovation
- Parties to collaborate on infrastructure, platforms, and marketing of satellite services
- A dedicated marketing services contract was also concluded alongside the MoU
The Regional African Satellite Communications Organization (RASCOM) signed a memorandum of understanding on Wednesday, April 23, with Nilesat, the Egyptian national satellite operator. The two parties thus demonstrate their willingness to collaborate further to accelerate the development of the African space sector.
The main areas of collaboration focus on the commercialization of satellite capacities, training, innovation, and research. Both parties commit to pooling their expertise, platforms, applications, and satellite infrastructures. A marketing services contract was also concluded between them.
“This partnership marks a strategic convergence of our common objectives: to stimulate innovation, promote knowledge sharing, and advance satellite services in the region. Together, we aim to provide enhanced connectivity and promote skills development in the space sector,” said Hesham Lotfy Sallam, Commercial Director at Nilesat.
The establishment of this partnership comes shortly after the launch of the African Space Agency (AfSA), intended to structure the continent’s space initiatives. The agency is dedicated to the collection, analysis, and sharing of spatial data, in service of the continent’s sustainable development. This cooperative dynamic illustrates the growing momentum of the African space sector, with a multiplication of national initiatives. Last March, Botswana launched BOTSAT-1, its first satellite. Seventeen other countries on the continent have also already put satellites into orbit. Egypt leads the list with 14 spacecraft, followed by South Africa (13) and Nigeria (7).
Africa seeks to strengthen its position in the global space market, whose growth is accelerating. According to data recently cited by the Senegalese government, the global market is expected to exceed 737 billion dollars in the next decade. Space in Africa indicates that the value of the African market was estimated at 22.6 billion dollars in 2024.
Beyond these economic prospects, space technologies offer strategic advances in precision agriculture, natural resource management, environmental monitoring, and telecommunications. For this latter area, the Global System for Mobile Communications Association (GSMA) estimates that satellites have the potential to provide universal coverage in Africa, where a large part of the population is still deprived of mobile phone and Internet services.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
- State Minister Nguilin met World Bank officials in Washington on April 24
- Discussions focused on overhauling public services, e-learning, and civil registry digitization
- World Bank signaled readiness to expand support beyond e-procurement to full-service digital platforms
Chad is accelerating its digital transformation efforts and is counting on enhanced support from the World Bank to modernize its public services. On the sidelines of the Spring Meetings in Washington, State Minister Tahir Hamid Nguilin met on Thursday, April 24, with Michel Rogy, the World Bank’s Regional Director for Digital Development, and Jana Kunicova, Sector Director for West and Central Africa, to discuss the way forward.
During the meeting, the Chadian official stressed the urgent need to overhaul financial administrations, improve connectivity, and leverage digital technologies to make government services more accessible, efficient, and transparent. The government has identified key priorities, including the digitization of civil registry records, the digital transformation of school curricula, the expansion of e-learning, and the promotion of local innovation.
These goals are part of the Digital Transformation Support Project, already funded by the World Bank. Launched six months ago, the project has reached a disbursement rate of 8%, which the institution has welcomed as a promising sign. The World Bank reiterated its willingness to go beyond e-procurement support by helping establish an integrated digital platform for public services.
Still, accelerating progress will require substantial technical assistance. Chad faces several hurdles: patchy internet connectivity, a shortage of digital skills, and fragile infrastructure. Enhanced backing from the World Bank could help foster a structured, inclusive, and sustainable digital ecosystem—one designed to improve access to public services and strengthen governance.
According to the ICT Development Index 2024 published by the International Telecommunication Union, only 12.2% of Chadians currently have internet access. The country faces a stark digital divide between urban and rural areas. Additionally, Chad scores just 0.1194 out of 1 on the digital infrastructure development index—one of the lowest ratings globally. Against this backdrop, the World Bank’s support could play a critical role in building a coherent and resilient digital ecosystem that serves citizens and enhances effective governance.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji
- Rwanda signed a trilateral memorandum of understanding with C4IR UAE and C4IR Malaysia during Dubai AI Week 2025.
- The partnership focuses on ethical, inclusive, and sustainable approaches to AI development.
- Key areas include governance frameworks, skills development, and technological innovation.
On Wednesday, April 23, during Dubai AI Week 2025, Rwanda inked a three-way memorandum of understanding with the Centres for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR) of the United Arab Emirates and Malaysia. Ambassador John Mirenge, representing the Rwandan government, finalized the agreement, signaling a significant stride in international collaboration on artificial intelligence.
This partnership aims to build on the momentum generated by Rwanda's AI fellowship program and foster deeper collaboration among the three nations. It will support joint efforts in areas such as governance frameworks, skills development, and technological innovation, with a focus on ethical, inclusive, and sustainable methodologies.
The agreement comes after Kigali hosted the inaugural Global Summit on Artificial Intelligence in Africa. That event, which convened experts, government officials, and private sector partners, underscored Rwanda's aspirations in AI and its increasing prominence in global discussions concerning technology governance.
Since 2022, Rwanda has operated its own Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, established in partnership with the World Economic Forum. This center spearheads AI projects and develops appropriate regulatory structures. An ambitious initiative to create 50 artificial intelligence applications over four years was launched this month, aiming to accelerate the digital transformation of key sectors including healthcare, education, agriculture, finance, and public administration. This program aligns with the national digital development strategy and the country's Vision 2050.
This closer relationship could also enable Rwanda to leverage the advanced experience of the United Arab Emirates, which has already integrated AI into numerous government services, and Malaysia’s expertise in applying technological innovation to industry. For Kigali, this represents a strategic opportunity to expedite the growth of its own artificial intelligence ecosystem while solidifying its standing on the global technology stage.
By Samira Njoya,
Editing by Sèna D. B. de Sodji















