Public Management (605)
Nigerian states are ramping up initiatives to accelerate their digital transformation in line with the federal government's objectives. This effort spans all sectors of the economy, including education.
In Nigeria, the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) plans to distribute over 1,000 laptops to its secondary schools. Valued at approximately 990 million naira (around $589,000), the acquisition was approved by the FCT Executive Council during a meeting on Monday, November 25.
According to Danlami Hayyo, the FCT Secretary for Education, the laptops will come preloaded with educational content and learning materials focused on vocational skills.
“FCT schools will now transform into the digital education system, we will now move from normal teaching and learning classroom to media education system of learning,” said Chidi Amadi, Chief of Staff to the FCT Minister.
The laptop acquisition is part of a broader strategy to digitize the education system and improve teaching quality in the FCT. The Executive Council recently approved a contract for procuring examination materials. Earlier, in September, the FCT launched a program to train 3,000 primary school teachers in digital teaching methods.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) highlights two key benefits of digital technology in education. “First, it can improve instruction by addressing quality gaps, increasing available time and opportunities to practise, and personalizing instruction. Second, it can engage learners by varying how content is represented, stimulating interaction and prompting collaboration,” according to the 2023 Global Education Monitoring Report.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Guinea, confronted with the need for administrative modernization, is turning to digital solutions to streamline its processes. This initiative represents a significant step forward in public resource management, prioritizing innovation and international cooperation.
Guinea is looking to Rwanda as a model for its first-ever digital public procurement system. A strategic agreement was signed on Wednesday between the Guinean government and the Rwanda Cooperation Initiative (RCI).
“We have proven expertise in digitizing public procurement, particularly in public financial management, and it is this experience we aim to share with Guinea. We signed this contract to formalize our commitment and support the country in establishing its digital system,” said Patricie Uwase, Director-General of the Rwanda Cooperation Initiative.
This agreement builds on a collaboration that began in 2023 between RCI and Guinea as part of the E-Procurement project. Championed by the transitional president, Mamady Doumbouya, the project seeks to enhance transparency, improve administrative efficiency, and optimize public resource management. It is also a critical tool in the fight against corruption—a persistent issue in Guinea’s public procurement sector, frequently criticized for its lack of transparency and questionable practices.
The new digital system aims to simplify and tighten control over procurement processes, ensuring greater traceability of transactions. Additionally, the digitization of public procurement is expected to reduce both delays and associated costs while boosting the confidence of foreign investors drawn to transparent and modern administrative practices.
By leveraging Rwanda’s recognized expertise, Guinea hopes to lay the groundwork for effective and transparent governance. If successful, this initiative could redefine public procurement standards in West Africa, positioning Guinea as a model for digital innovation and anti-corruption efforts. The government is targeting swift implementation, aiming for full digitalization of all public procurement plans by January 1.
Samira Njoya
Cloud technologies are essential to modern IT, enabling businesses to create scalable and resilient applications. However, a shortage of skilled professionals hinders adoption. Training African developers in this field opens access to high-paying tech jobs locally and globally.
Global talent outsourcing company Andela announced on November 15 a partnership with the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) to train 20,000 to 30,000 African developers in cloud-native basics. This initiative is part of a three-year program aimed at addressing the growing global demand for cloud-native expertise.
Andela CEO Carrol Chang highlighted the growing demand for skilled tech professionals in Africa. ”We are excited to partner with CNCF to extend training and, ultimately, enhance job opportunities for African workers. The continent is emerging as one of the most important markets in the world […] and its young workforce will be key to solving the tech talent shortage,” she stated.
The training program will take participants six to nine months to achieve certifications and is designed to ensure graduates are equipped to meet the needs of the global cloud-native ecosystem. It will focus on key cloud-native tools, including Kubernetes, and prepare participants for industry certifications like the Kubernetes and Cloud Native Associate (KCNA) and Certified Kubernetes Application Developer (CKAD).
The program will be available to Andela’s talent marketplace of over 150,000 professionals, predominantly from Africa. Andela’s talent marketplace in Africa spans 49 countries; including Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana.
According to The Rise of the African Cloud 2023 report by Xalam Analytics, the African cloud market has emerged as a multi-billion-dollar opportunity, experiencing annual growth rates of 25% to 30%. This represents a transformative opportunity for the continent and global technology ecosystems through the creation of high-demand roles in IT.
The collaboration between Andela and CNCF offers African developers the chance to gain in-demand cloud computing skills, addressing the global talent shortage and enhancing their access to international opportunities. This initiative is a significant step toward bridging the digital skills gap, empowering African tech talent, and establishing their role as key contributors to the global technology landscape.
Hikmatu Bilali
African parliaments are increasingly turning to digital technologies to improve efficiency. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge, hindering progress in many regions.
South Africa (8 out of 10), Zimbabwe (8), Burundi's Senate (7), Morocco (7), and Mauritius (7) lead the continent in digital maturity among African parliaments, according to a new report published in October 2024 by the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), a global organization of sovereign state parliaments. The report is based on responses from 115 parliaments or chambers across 86 countries, as well as from supranational parliamentary organizations.
Titled the "World e-Parliament Report 2024," the report offers a comprehensive analysis of digital technology use in parliaments worldwide through a digital maturity index, an innovative benchmarking tool. This index assesses parliaments across six key areas: governance, digital strategy and management; infrastructure; parliamentary systems; user support; digital content and publications; and citizen engagement.
“The purpose of benchmarking is not to create a league table of ‘good’ or ‘bad’ parliaments. Rather, it supports strategic decision-making on the use of digital technologies by highlighting the factors that can affect maturity,” the IPU stresses.
In addition to the leaders, Tunisia (6), Burundi's National Assembly (5), and Malawi (5) stand out with scores of 5 or higher. However, sub-Saharan Africa remains underrepresented among the top performers. According to the IPU, 50% of parliaments in the region rank among the 30 least digitally mature institutions, a situation attributed to a lack of modernization initiatives, insufficient investment in new digital systems, and an absence of ambitious digital transformation programs.
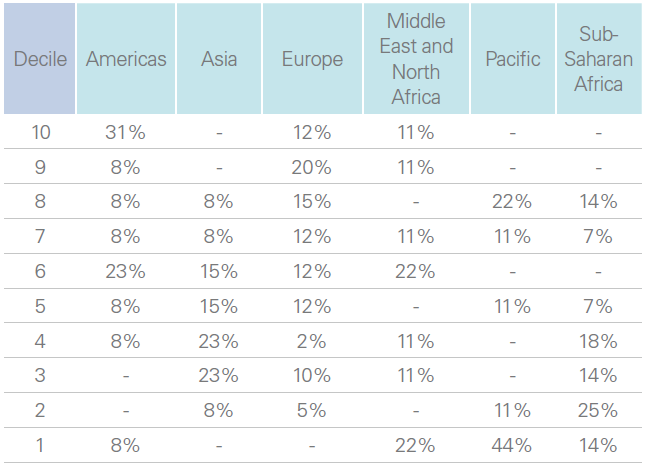
Distribution of parliaments by region for each decile ranking
At the bottom of the index, parliaments in countries like Djibouti, Lesotho, Madagascar, and the Central African Republic scored an average of 1 out of 10, reflecting significant gaps in digital adoption.
To address these gaps, the report recommends that institutions and governments develop clear strategic visions and comprehensive digital strategies; allocate adequate financial, human, and technological resources; establish robust governance frameworks; invest in capacity building; prioritize citizen participation; and strengthen inter-parliamentary collaboration.
Additionally, generative artificial intelligence is highlighted as a strategic lever to accelerate parliamentary digital transformation, offering the potential to deliver valuable insights and enhance the accessibility of parliamentary processes.
Samira Njoya
Lire aussi:
Anambra aims to integrate information and communication technologies across all sectors of the economy. It previously initiated projects to strengthen digital infrastructure, notably through a project to establish an Internet Exchange Point.
Anambra State, Nigeria, plans to develop its own data management platform as part of efforts to fast-track its digital transformation. With an estimated budget of 97.08 million naira (about $57,200), the project received approval last week during a State Executive Council meeting.
“By enabling better data integration across sectors, the platform will ensure that vital information is accessible in real-time for decision-makers, supporting data-driven governance,” said Law Mefor, Anambra’s Commissioner for Information.
The initiative is part of Anambra’s broader ambition to leverage technology to improve governance and drive development. Guided by its strategic vision, "Everything Technology, and Technology Everywhere," the state government aims to establish a digital economy that attracts investors, innovators, and businesses.
To achieve these digital ambitions, Anambra has been implementing various projects to upgrade its digital infrastructure. In August 2023, the state eliminated right-of-way fees to speed up fiber optic deployment. By July 2024, it had launched an extensive project to lay 2,400 kilometers of fiber optic cable, a move that supports its goal of providing free Wi-Fi across the state. Additionally, the government is planning to establish other essential digital infrastructure, including an Internet Exchange Point (IXP).
This data management platform is expected to contribute to Nigeria’s broader digital transformation, as Africa’s digital economy is projected to reach at least $712 billion by 2050—equivalent to 8.5% of the continent's GDP—according to a joint study by the International Finance Corporation (IFC) and Google. However, the timeline for the platform’s development and implementation has not yet been disclosed.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Digital transformation is a top priority for the Djiboutian government, which aims to establish the country as a technology hub by 2035.
Djibouti wants to strengthen its cooperation with the European Union (EU) to accelerate its digital transformation. The goal was at the center of discussions between Mariam Hamadou Ali, Djibouti’s Minister Delegate for Digital Economy and Innovation, and Denisa-Elena Ionete, the EU ambassador to Djibouti.
This cooperation aligns with the EU’s Global Gateway investment strategy, which aims to drive both digital and green transitions while delivering reliable, sustainable connections for partner countries. Key projects under discussion include e-permits, e-cabinet systems, cybersecurity, and digital skills training.
According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Djibouti currently ranks 17th out of 47 African countries in ICT development, with a score of 61.6 out of 100—down from 16th place in 2023, when it scored 63.6. Additionally, the United Nations places Djibouti among the countries with a mid-range e-government development index (EGDI), scoring 0.2911 out of 1.
In cybersecurity, Djibouti ranks as a Tier 4 country by ITU standards, reflecting a basic government-driven commitment to cybersecurity. Legislative measures are cited as a strength, but the ITU notes that additional progress is needed in technical measures, organizational frameworks, capacity development, and cooperative actions.
The EU’s support is expected to boost the Djibouti Digital Foundation project, which is already backed by the World Bank. This project is aimed at transforming Djibouti into a tech hub by 2035 through the expansion of digital services and the establishment of a supportive environment for private-sector ICT investment.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Earlier last year, Algerian authorities launched the digitization of the national agricultural registry. They have completed the digitization goal ahead of schedule.
On Sunday, November 3, Mohamed Yazid Hambli, President of Algeria's National Chamber of Agriculture, announced the completion of the digitization of the National Agricultural Registry (RNA). The announcement was made during the opening ceremony of the second National Exhibition of Agricultural Equipment, Products, Livestock, Agribusiness, and Refrigeration in Mascara.
"The process of digitizing the National Agricultural Registry, initiated early last year and carried out by the National Chamber of Agriculture, is now fully complete. This initiative has allowed for the issuance of digital cards to farmers across all 58 wilayas," stated Mohamed Yazid Hambli (photo, center).
Under President Abdelmadjid Tebboune, Algeria has leveraged digital transformation as a driver of development since 2019, achieving substantial progress on various digital indicators. According to the International Telecommunication Union, Algeria reached a score of 80.9 on the ICT Development Index in 2024, up from 77.8 in 2023, marking a notable advancement in the tech sector.
However, the digitization of the RNA faces several challenges. Farmers and local agents require training to effectively use digital tools, while limited access to telecommunications networks in rural areas hinders connectivity. Robust measures are also essential to protect the privacy and security of farmers' sensitive data. These obstacles could reduce the initiative's effectiveness if not addressed.
If these challenges are overcome, the RNA digitization could transform agricultural resource management by enabling better monitoring of land, crops, and water resources. It would allow for more targeted subsidies and aid based on farmers' actual needs and improve transparency in production chains. By facilitating precise resource management and enhancing transparency in the agricultural sector, this initiative could support more sustainable and equitable agricultural development.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Guinea is making strides in digitalizing its public administration, but there's still room for improvement. According to the United Nations, the country's digital governance score increased from 0.2955 in 2022 to 0.4006 in 2024. Despite this progress, Guinea remains behind and is working to accelerate its digital transformation.
The Guinean Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Small and Medium Enterprises recently announced the upcoming launch of an administrative document management platform (PLAGED) on November 13. This platform aims to simplify administrative procedures for citizens, marking a significant step toward digital governance in Guinea.
This initiative follows Guinean Prime Minister Bah Oury’s recent call for a concerted push to improve the country's digital administration, where progress has lagged. Oury attributes this delay to limited familiarity with the rapid evolution of digital technologies. According to the United Nations' report "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," Guinea scored 0.4006 out of 1 on the E-Government Development Index (EGDI), ranking 29th on the continent. This is an improvement from a score of 0.2955 in 2022, reflecting gradual progress in online government services.
The report also noted Guinea’s Online Service Index score of 0.4808, which assesses the technical features of national websites as well as policies and strategies for online service delivery across general and sectoral levels.
Earlier this year, in April, Guinean authorities launched “e-Learning” and “e-Consulting” initiatives to modernize administrative processes with innovative training and management tools. The introduction of PLAGED aligns with these efforts, supporting the government’s digital strategy to improve service delivery and accelerate the adoption of digital tools across public administration.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The Ghanaian government is ramping up efforts to bridge the country’s digital skills gap. Officials recently announced plans to launch a $5 million fund aimed at fostering technological innovation.
Ursula Owusu-Ekuful (photo, left), Ghana’s Minister of Communications and Digitalisation, launched the “eSkills4Jobs” program last week. The initiative aims to equip over 5,000 young Ghanaians with essential digital skills, with a focus on supporting women from marginalized communities and people with disabilities.
The program is a partnership between the Ghanaian government, the World Bank, and the Ghana-India Kofi Annan Centre of Excellence in ICT.
“The digital economy is here to stay, and we must ensure no one is left behind. eSkills4Jobs will focus on creating tailored training programs, mentorship opportunities, and access to resources to enable participants to build relevant skills,” Owusu-Ekuful said.
The initiative aligns with the Ghanaian government’s broader goal of training one million young people in digital skills to meet the demand for a skilled workforce in a rapidly digitalizing economy. According to the International Finance Corporation (IFC), 20% of Ghanaian companies currently rely on foreign recruitment for digital skills, primarily because they cannot find qualified local talent. The World Bank estimates that approximately 625 million Africans will require digital skills by 2030.
The Ghanaian government believes that the skills acquired through the eSkills4Jobs initiative will not only enhance individual employability but also contribute to the overall growth of Ghana’s economy. World Bank data from 2022 shows that 3.1% of Ghana’s active workforce is unemployed.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Mali is undergoing a digital transformation, prioritizing the digitization of a strategic sector to simplify daily life for its citizens.
The Malian government has unveiled a National Strategic Digital Health Plan (PSNSN) for the period 2024-2028, according to local media reports. This initiative, backed by a projected budget of $35 million, aims to significantly improve access to quality specialized healthcare by 2028. Key components of the PSNSN include modernizing health infrastructure, implementing telemedicine solutions, and creating a national health database.
The initiative is supported by several key partners, including UNICEF, the World Bank, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP), the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), and the World Health Organization (WHO). “This plan is an essential tool to modernize our healthcare system and meet the needs of the Malian people,” stated Assa Badiallo Touré, Minister of Health and Social Development.
Launched shortly after the government’s 2024-2028 roadmap, the PSNSN aligns with the broader goal of universal access to primary and specialized healthcare. It is a cornerstone of Mali’s digital transformation strategy, supported by the World Bank.
A major challenge for the project will be ensuring seamless interoperability between different health information systems. To address this, the plan prioritizes centralizing information to securely provide healthcare professionals with access to patient medical records.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
More...
The Covid-19 crisis has highlighted the power of digital technology in education, in Africa as elsewhere. Since then, African governments have been launching initiatives to promote its development and improve access to quality education for all.
On Thursday, October 24, the Ivorian Minister of National Education and Literacy, Mariatou Koné (photo, center), officially presented and launched the National Digital Education Strategy of Côte d'Ivoire (SNDECI). This roadmap, based on recommendations from the National Education and Literacy General Assembly (EGENA), reflects the government’s commitment to elevating the Ivorian educational system to be among the world's best within the next five years.
“Digital education supports traditional teaching and will significantly enhance the quality of our education system without replacing in-person learning. By integrating modern technologies into our schools, we reduce geographical, social, and economic inequalities, allowing the education system to provide more interactive and engaging learning to every child, wherever they are,” stated Mariatou Koné.
The new strategy aligns with the 2021-2025 National Digital Development Strategy and the country’s national development plan, which aim to transform Côte d'Ivoire's economy through the integration of digital technologies across all sectors, including education. It is built on three pillars: infrastructure, organization, and training. The strategy, with an estimated budget of 220.7 billion CFA francs (about $364 million), will include training for teachers and administrative staff, the acquisition of digital equipment, and the installation of modern technological infrastructure in schools.
The implementation of this strategy is expected to bring multiple benefits, enhancing the accessibility and equity of the education system. It will bridge quality gaps between regions, particularly in rural areas, and provide students with the digital skills needed to thrive in a transforming economy.
According to United Nations projections, Africa’s population will reach 2.4 billion by 2050, with more than half under the age of 25. This youth demographic presents a significant opportunity for Africa, but it also underscores the urgency of developing modern, inclusive education systems capable of meeting the needs of a digital workforce and fostering sustainable economic growth on the continent.
Samira Njoya
Morocco is ramping up efforts to establish itself as a leading technology hub on the continent. Following the launch of several digital platforms, it is now assessing its progress in various sectors.
Morocco's Minister of Justice, Abdellatif Ouahbi (photo), told the House of Representatives, on Monday that since January 2024, 51,000 criminal record extracts have been issued online out of 60,613 requests. Additionally, 6,727 electronic applications for Moroccan nationality certificates have been submitted remotely.
These updates are part of the initial assessment following the launch of several digital platforms by the Ministry of Justice. During the session, Ouahbi also noted that the state collected 16 million dirhams (approximately $1.6 million) through the electronic payment service for fines issued by fixed radar cameras. The platform for tracking court cases and files recorded 23 million visitors in 2023 and 12 million between January and July 2024.
The digitization of Morocco's judicial sector is advancing under the "Digital Morocco 2030" plan, which aims to leverage digital technologies as a driver of social and economic development. The plan seeks to position Morocco as a leading African nation in the digitization of public services by 2030, with the goal of ranking among the world’s top 50 countries in this field.
According to the "E-Government Survey 2024: Accelerating Digital Transformation for Sustainable Development," Morocco ranks fourth on the continent in the online administration development index, scoring 0.6841 out of 1, ahead of Seychelles (0.6773) and just behind Tunisia (0.6935).
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Last July, Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed launched a program aimed at training young people in digital skills. A few months after its launch, authorities are now assessing its progress.
Ethiopian authorities have trained 31,000 citizens in coding within three months, according to a recent statement by Belete Mola, Ethiopia’s Minister of Innovation and Technology. He made this announcement while reviewing the results of the past fiscal year.
Belete Mola stated, “Over 246,000 citizens have enrolled in the training, and 31,000 of them have been certified. The young people trained as coders and the tech startups with creative potential will receive special support.”
The "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" initiative, launched last July by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed in partnership with the United Arab Emirates, is part of the "Digital Ethiopia 2025" plan. Its aim is to provide training in programming, Android app development, data science, and fundamental digital skills in artificial intelligence.
This initiative aligns with Ethiopia’s broader goal to establish itself as a major tech hub in East Africa. The World Bank estimates that nearly 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030. Through the "5 Million Ethiopian Coders" program, Ethiopian youth are being prepared to meet this demand.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
To achieve universal health coverage for its population, Ghanaian authorities are relying on various technological solutions. They have opted for a public-private partnership to reach their goal.
Ghanaian authorities are set to launch, today Octyober 16, the electronic health management system, known as E-Health, which will create digital patient records accessible across all hospitals in the country.
The implementation of this system is a public-private partnership between Ghana’s Ministry of Health and Lightwave e-Health Solutions, a U.S.-based company specializing in e-health.
“Going forward, medical records and the history of patients can be gathered under a single database, which can be accessed by any networked hospital when the patient visits. This digitization effort has increased efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity in service delivery in our health facilities,” stated Ghana’s Vice President, Mahamudu Bawumia (photo).
This launch comes just months after the introduction of drone delivery solutions for medical supplies and online medicine purchasing from pharmacies. It aligns with the 2023-2027 Digital Health Policy and Strategy document, which aims to provide all communities in Ghana with timely, quality, and comprehensive healthcare through the use of information and communication technologies.
According to the Ministry of Health, the new system is expected to generate annual savings of between €50,000 ($54,000) and €300,000. It should also improve patient wait times by 35% to 40% in health centers and district hospitals, while regional and university hospitals could see a more than 40% reduction in wait times.
Adoni Conrad Quenum