The rapid rise of remote work has fueled the phenomenon of digital nomads, creating new opportunities for African countries. With growing appeal, developing infrastructure, and policies still taking shape, the continent could very well become a major player in this new global work landscape.
Since 2020, the way people work has been changing in deep but often unnoticed ways. In only a few years, digital nomadism has evolved from a niche concept into a global trend. This rise has been fueled by the digital shift in many jobs, the growth of remote work, and a growing demand for more flexible living. While it first took hold in large Western cities, the movement is now spreading across Africa, a region with the potential to unlock billions of dollars in economic value if it takes the right steps.
A Global Movement with Local Impact
Digital nomads are workers who use a laptop and an internet connection to work from anywhere in the world. It could be a freelance marketer living in Nairobi for six months, a Senegalese developer dividing her time between Dakar and Bali, or an American designer spending the summer in Zanzibar.
According to 2025 data from Nomads.com, a global digital nomad community platform, there are now more than 80 million digital nomads worldwide—and the number keeps rising. Their financial footprint is significant. On average, a digital nomad earns $124,000 annually and spends between $1,000 and $3,000 per month in their host country on housing, food, entertainment, coworking spaces, and transport. This provides a steady stream of income for local economies, without the strain of mass tourism. Americans make up the largest share, with 46 million nomads. About 88% of global digital nomads come from countries outside Africa.
|
Category |
Subcategory |
Value |
|
Age |
53% are between 31 and 39 years old |
|
|
|
Men |
91% |
|
Gender |
Women |
7% |
|
Other genders |
2% |
|
|
Education |
90% have higher education |
|
|
|
Per city |
63 days |
|
Average length of stay |
||
|
Per country |
167 days |
|
|
Average annual income |
$124,304 |
|
|
|
Full-time employees |
38% |
|
Work Status |
Startup founders |
18% |
|
Freelancers |
18% |
|
|
Top Sectors (Men) |
Software development |
35% |
|
Web development |
28% |
|
|
Startup founders |
28% |
|
|
Marketing |
16% |
|
|
Top Sectors (Women) |
Marketing |
16% |
|
Creative industry |
15% |
|
|
Startups |
12% |
|
|
Software development |
10% |
|
|
Motivations |
Work setting + getaways in Africa |
Africa Steps Into the Spotlight
Africa is starting to gain recognition as an appealing destination for remote workers. Cities like Cape Town, Johannesburg, Marrakech, Accra, Dakar, Abuja, Luanda, Libreville, and Cotonou are seeing growing interest. These places attract a new wave of remote workers seeking authentic experiences, lower living costs, and meaningful social connections. Many of these cities offer reliable high-speed internet, electricity, modern accommodation and workspaces, and access to food, transport, and healthcare—making it possible to balance productive workdays with tourist exploration.
This trend is not limited to foreign visitors. A growing number of young Africans in digital fields—web development, design, content creation, community management—are also embracing a mobile lifestyle, often within the continent. This intra-African nomadism is supported by countries offering full or partial visa exemptions, such as Senegal, Benin, Kenya, Ghana, and Rwanda. These policies are reshaping how professionals move and work in Africa’s digital age.
Billions in Economic Opportunity
According to global immigration firm Newland Chase, the 35 million digital nomads counted in 2021 contributed $787 billion to the global economy. Although detailed data for Africa is lacking, a modest projection suggests the continent could earn $6 billion per year if it hosted 500,000 foreign digital nomads spending $1,000 monthly. If Africa attracted just 2% of the world’s estimated 80 million nomads in 2025—that is 1.6 million individuals—the continent could bring in close to $20 billion annually through direct local spending.
Beyond daily spending, digital nomadism can fuel growth in sectors such as short-term housing, food and hospitality, internet services, local transport, and leisure activities like hiking and tourism. Thousands of small businesses—especially in urban areas—stand to benefit from this expanding market.

Early but Promising Initiatives
Some African countries have already started tailoring offers to digital nomads. In 2020, Mauritius introduced its Premium Visa. It is free, valid for one year (renewable), and available to citizens of 114 countries. Applicants must prove that their main income is earned outside Mauritius and show a minimum monthly income of $1,500.
Cape Verde launched a similar visa in 2020, targeting both tech and tourism. The visa lasts six months (renewable) and requires payment. Digital nomads in Cape Verde are exempt from income tax and local taxes. While there is no official income threshold, applicants must show an average bank balance of at least €1,500 over the previous six months.
In 2024, South Africa joined in with its digital nomad visa, allowing stays from three months to three years. Applicants must provide three months of bank statements showing a gross annual salary of at least 650,796 rand (about $36,782).
Other countries like Namibia and Kenya also launched digital nomad visas in 2024 to attract skilled professionals and boost their economies. However, Africa still lags behind Latin America and Southeast Asia, which already offer nomad visas, tech hubs, tax incentives, and tailored services.
Challenges That Remain
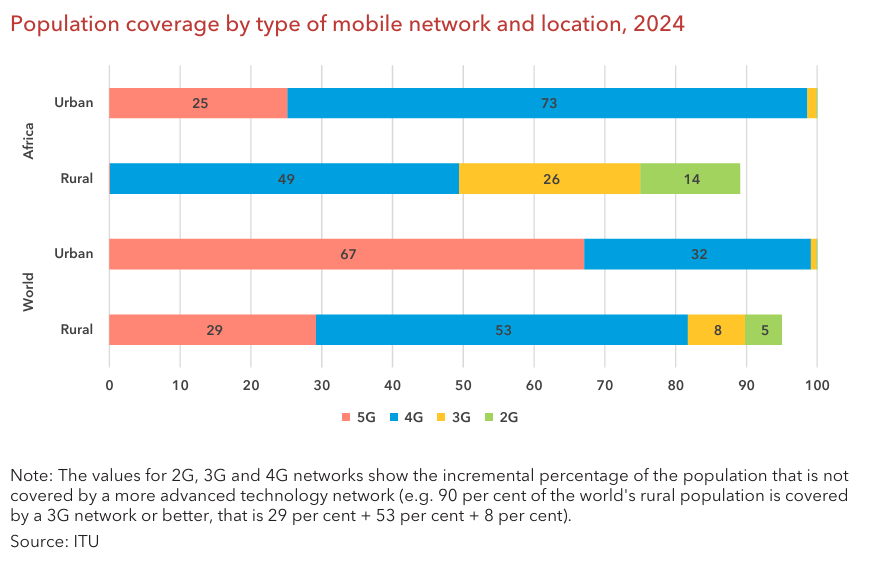
Africa has clear potential to benefit from digital nomadism. Internet coverage is improving across the continent. According to the International Telecommunication Union, 4G now covers 71% of the population, while 3G covers 86%. However, 5G still only reaches 11%. In urban areas, 4G covers 73% and 5G reaches 25%. Countries like South Africa, Senegal, Mauritius, Nigeria, Botswana, Ethiopia, Seychelles, Tunisia, and Lesotho already offer 5G access in their capitals. In rural areas, coverage is lower—49% for 4G, 26% for 3G, and 14% for 2G. While major cities usually offer stable internet, many secondary regions do not.
Another barrier is cost. The cheapest mobile data plan (2GB) costs 3.9% of the average monthly gross national income (GNI) per person, while fixed internet (5GB) costs 13.4% of GNI. These rates are considered high, exceeding the United Nations target of 2% of GNI for affordable access. Globally, the average cost is closer to 1% of GNI for mobile and 2.3% for fixed internet.
Other obstacles include political and security concerns, especially in areas affected by instability—although these are a minority. The lack of a clear legal status for digital nomads also makes many destinations less appealing. Tourist visas are not designed for extended stays and lack tailored benefits. To change this, digital nomadism needs to be integrated into national policies on tourism, entrepreneurship, and youth employment.
Digital nomadism is not just a trend or a lifestyle for Western elites. It reflects a deep shift in how the world works. Africa has a real chance to play a leading role—if it invests, plans, and innovates wisely.
• Cape Verde is exploring digital cooperation with South Korea after a recent technical mission
• Talks focus on data governance, public service digitization, and cybersecurity
• No agreement yet, but South Korea is seen as a key potential partner
Cape Verde's government is exploring a partnership with South Korea in digital transformation. To advance this initiative, a delegation led by the Directorate General of Telecommunications and Digital Economy recently completed a technical mission to South Korea.
In a statement released Monday, July 7, the Ministry of Digital Economy explained that discussions focused on how integrated data governance, the digitization of public services, and cybersecurity can strengthen citizens' trust, boost the digital economy, and improve state efficiency.
This initiative aligns with Cape Verdean authorities' ambition to make digital technology a cornerstone of socio-economic development in the coming years. In a recent interview with the economic news agency Ecofin Agency, Pedro Lopes, Secretary of State for Digital Economy, explained that digital technology can accelerate economic transformation despite limited natural resources. He stated, "We are also modernizing tourism, the blue economy, and agriculture through digital solutions, and we are supporting our youth to create globally competitive startups."
South Korea appears to be a strong ally in achieving these goals. The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) considers South Korea a global model in cybersecurity. Regarding digital transformation, it ranked fourth worldwide in the United Nations' 2024 E-Government Development Index (EGDI), with a score of 0.9679 out of 1.
In the same EGDI index, Cape Verde ranks 111th globally, with a score of 0.6238 out of 1. This result is above the West African average but slightly below the global average, which stands at 0.6382. In cybersecurity, Cape Verde falls into the fourth of five categories, according to the ITU's Global Cybersecurity Index. While it performs well on regulatory aspects, the country still needs to strengthen its technical and organizational frameworks, improve international cooperation, and invest in developing human skills.
It is worth noting, however, that talks between South Korea and Cape Verde are still in the early stages. Although Cape Verdean authorities say they have identified concrete opportunities for future collaboration, no formal agreement has yet been signed or announced. Further developments will be needed to assess whether this rapprochement will lead to a genuine partnership and to measure its potential impact.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Digital health is reshaping access to care across Africa. With mobile platforms and community networks, solutions are reaching underserved regions—one of the strongest examples being Mobiklinic, led by Ugandan entrepreneur Andrew Ddembe.
Ddembe, a law graduate from Cavendish University Uganda, founded Mobiklinic in 2019. As CEO, he has steered the healthtech firm toward one goal: bring healthcare to rural and disadvantaged communities in East Africa.
Mobiklinic operates through a hybrid model that combines digital platforms with community-based care. Community health workers, equipped with a mobile app, collect patient data, provide follow-ups, consult doctors remotely, and refer severe cases to nearby health facilities.
The app uses biometric identification to manage medical records, streamlining continuity of care and enabling better vaccination tracking, maternal care, and child health monitoring.
Since launch, Mobiklinic has reached over 120,000 patients. Its network of 1,500 trained agents works closely with local clinics, NGOs, and universities to strengthen services like chronic disease treatment and family planning programs.
Ddembe also runs the Mobiklinic Foundation, which predates the startup. Founded in 2018, the foundation designs digital tools for training and primary healthcare delivery. His influence has extended beyond the region—Ddembe is a member of the WHO Civil Society Commission.
His work hasn’t gone unnoticed. In 2024, Ddembe won the Global Citizen Prize in New York, and Forbes Africa named him to its 30 Under 30 list, spotlighting young leaders in social innovation.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
-
Kenyan entrepreneur Charles Thuo founded Apexloads to digitize freight logistics
-
The platform matches cargo owners with transporters in minutes, not hours
-
Apexloads offers real-time tracking, payments, and logistics management tools
Charles Thuo, a Kenyan entrepreneur, is transforming logistics in Africa through his tech company, Apexloads. Founded in 2019, Apexloads focuses on freight transport and logistics solutions tailored to the African market.
The platform helps manage cargo flows, cut costs, improve shipment visibility, process payments, and ensure compliance and traceability. Apexloads connects cargo owners, brokers, transporters, and freight forwarders through a secure digital interface designed to streamline logistics operations.
“Apexloads creates a controlled environment where brokers can quickly find transporters, reducing the time to match trucks with cargo from several hours to just a few minutes,” Thuo said in 2024.
The platform functions as a freight dashboard, transport management system, CRM, real-time tracking tool, and factoring service. Cargo owners post loads, transporters share truck availability, and an algorithm links them instantly with geo-matching, significantly speeding up the process.
In addition to leading Apexloads, Charles Thuo is a managing partner at Marcus Solutions, a U.S.-based IT services provider. He earned a degree in engineering technology from Oklahoma State University in 2013 and a bachelor’s degree in aerospace, aeronautical, and astronautical engineering from the University of Oklahoma in 2016.
Thuo began his career in 2010 at Great Plains Coca-Cola in the U.S. as a route settlement specialist. In 2013, he joined the U.S. Army as a quartermaster and chemical equipment repair technician. In 2016, he became a structural analysis engineer at Cessna Aircraft Company and, in 2017, a payload design engineer at Boeing. He also served as a combat engineer in the Oklahoma National Guard from 2016 to 2024.
• Cameroon launched its AI strategy to become Africa’s leading hub by 2040, with goals for jobs, training, and GDP growth.
• It focuses on governance, infrastructure, local language models, edge computing, talent, and regional cooperation.
• The IMF ranks Cameroon low in AI readiness (0.34/1), citing gaps the strategy aims to close.
On Monday, July 7, Minister of Posts and Telecommunications Minette Libom Li Likeng unveiled Cameroon’s National Artificial Intelligence Strategy (SNIA) during the second edition of the National Consultations on AI. This strategy, anchored in a vision for 2040, aims to position the country as a continental AI hub by focusing on sovereign, inclusive, and sustainable solutions rooted in African cultural realities.
The SNIA seeks to make Cameroon "the leading AI hub in Africa" by promoting solutions based on African values. Its key targets include training 60,000 individuals, with 40 percent being women. The strategy also aims to create 12,000 direct jobs, generate a GDP contribution from AI of between 0.8 percent and 1.2 percent, and develop 12 sovereign, high-impact AI solutions. Special attention is given to linguistic diversity through the development of multilingual models that incorporate national languages.
Seven Structural Pillars to Deliver the Strategy
The strategic document is built around seven interdependent pillars. The first pillar focuses on governance and digital sovereignty. This includes establishing a Cameroonian AI Authority, a Presidential Council on AI, and drafting a framework law that addresses ethical considerations and inter-ministerial coordination mechanisms. The second pillar addresses data and digital infrastructure, calling for the creation of a government Data Lake, mass digitization of public services, interoperability standards, and a targeted Open Data policy.
The third pillar promotes multilingual and inclusive AI through the development of a local language model, referred to as "GPT Cameroon." It also emphasizes enhancing national languages via linguistic research and voice data collection. The fourth pillar targets sovereign technological infrastructure, including the deployment of 15 regional Edge Computing nodes powered by solar microgrids to strengthen energy resilience.
The fifth pillar is dedicated to training, research, and human capital. Plans include establishing five AI centers of excellence, training 4,000 people annually, implementing a diaspora talent return program, and providing greater support for local research. The sixth pillar centers on innovation and sector-specific use cases. This aims to support startups through accelerators and encourage AI adoption in key areas such as health, agriculture, justice, and education.
Lastly, the seventh pillar emphasizes cooperation and regional outreach. This involves creating an AI network for Central Africa, strengthening international partnerships, and exporting "Made in Cameroon" digital solutions.
According to the 2024 AI Preparedness Index published by the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Cameroon scores 0.34 out of 1. This places it in the lower half of the global ranking. The country lags in digital infrastructure and innovation but shows promising potential in human capital. The national strategy specifically aims to address these gaps by accelerating regulatory alignment and encouraging AI adoption across public services.
With this roadmap, Cameroon aims to align with the continent’s broader digital transformation momentum and fully harness emerging technologies to support its socio-economic development.
Samira Njoya
• Burkina Faso and the U.S. discussed digital cooperation, focusing on cybersecurity and infrastructure
• 2025 plans include data centers, network expansion, digital IDs, and a $150M transformation project
• Talks are early-stage; U.S. firms like Starlink and AWS may benefit as Burkina Faso seeks to close its digital gap
The Burkinabe government is exploring stronger digital cooperation with the United States. This was a key topic last week during a meeting between Aminata Zerbo/Sabane (photo, right), Minister of Digital Transition, and Joann Lockard (photo, left), the U.S. Ambassador to Burkina Faso.
"The government of Burkina Faso is undertaking many initiatives to support digital transition," Ambassador Lockard stated. "The American experience can be of great help in making this transition a success, particularly in the fields of cybersecurity and data control to protect citizens." She expressed confidence in the potential of American companies in the digital sector to support Burkinabe authorities' projects.
Among the major projects announced for 2025 are the completion of data centers, already 70 percent finished, and extending network coverage to at least 500 additional underserved localities. The ministry also plans to digitize more administrative services, carry out a large-scale population enrollment for electronic unique identification, and launch the Digital Transformation Acceleration Project, estimated at $150 million.
While no specific companies have been named yet in connection with this outreach, these projects could offer tangible opportunities for several U.S. firms already active in Africa. For instance, American Tower, a telecom infrastructure provider, and Starlink, for satellite internet access, might be considered for expanding network coverage. Other companies specializing in digital transformation, such as Microsoft, Oracle, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cybastion, or Cisco, could also fit into this dynamic.
Furthermore, the United States is among the most advanced countries in digital governance. The United Nations ranks it 19th globally in the E-Government Development Index (EGDI), with a score of 0.9195 out of 1. In cybersecurity, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) considers the U.S. a benchmark in its 2024 Global Cybersecurity Index. The U.S. scores 97.4 out of 100 on the ICT Development Index for 2025.
In contrast, Burkina Faso ranks 175th in the EGDI with a score of 0.2895, well below the global average of 0.6382. For cybersecurity, the country falls into the third of five categories, indicating that further efforts are needed, particularly to strengthen technical capacity and develop human capital.
Discussions between the two parties remain at a preliminary stage. No agreement has been signed or officially announced yet. The progression of these talks will need to be monitored to assess concrete partnership prospects and the actual involvement of American companies in Burkina Faso’s digital transformation.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
The newly announced reforms are crucial steps in democratizing digital access, preparing the workforce for the future, and positioning Ghana as a leader in Africa’s digital economy.
Ghana’s Minister for Communication, Digital Technology and Innovations, Samuel Nartey George, has outlined reforms and key milestones in the country’s digital transformation agenda. This was during the Ministry’s second quarter (Q2) briefing held at the Information Services Department Press Centre on July 3.
The Minister announced that, effective July 1, all major mobile network operators have revised their data tariffs to provide greater value. MTN bundles have increased by 15%, while Telecel and AirtelTigo bundles have risen by 10%, allowing consumers to access more data at existing price points.
According to the Minister, these changes are part of broader sector reforms involving spectrum reviews, new licensing models tied to consumer pricing, and strengthened regulatory engagement to make internet access more affordable and equitable.
Hon. George announced that the Ministry has completed a review of existing ICT laws and is drafting 15 new bills. These include amendments to data protection and cybersecurity legislation and new frameworks to govern artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and digital trade.
He further revealed that the Ghana Startup Bill, which proposes tax incentives and regulatory clarity for startups, is on track for passage by December 2025. Additionally, a draft National Anti-Misinformation Bill is set to be presented to Parliament to combat the spread of false information online, while safeguarding freedom of expression.
Looking ahead, the Minister unveiled that Ghana’s draft National AI Strategy will be reviewed by Cabinet and launched in the third quarter of 2025. The strategy positions Ghana to become a leading AI hub in Africa by 2028.
On 5G deployment, Minister George reported that the Next Generation Infrastructure Company (NGIC) is on schedule to activate over 350 5G-ready cell sites by Q4 2025, including at least 50 sites going live in Accra and Kumasi. He emphasized that there would be no further deadline extensions, reaffirming the Ministry’s commitment to ensuring universal 5G access.
Addressing digital payments, the minister revealed ongoing collaborations with the Bank of Ghana to restore full PayPal access and broaden digital payment solutions for individuals and businesses. He also highlighted ongoing talks with platforms such as TikTok and MultiChoice Ghana on issues related to content safety, fair compensation for creators, and subscription pricing — part of wider efforts to strengthen consumer protection and grow the digital economy.
Together, these measures make Ghana’s digital ecosystem more inclusive, affordable, secure, and globally competitive, supporting the country's vision to become a leading digital economy and technology hub in Africa.
Hikmatu Bilali
BusyMed, a South African healthtech startup, is transforming how patients access medicines through its mobile app. Founded in 2018 by Mphati Jezile in Port Elizabeth, BusyMed allows users to order pharmaceutical products directly from their homes.
“BusyMed seeks to solve a challenge that many South Africans face – not having access to affordable and convenient primary healthcare services. COVID-19 has made us all realise the strain our healthcare system is under, which means more services like BusyMed are essential in supporting the struggling healthcare system,” Jezile said in July 2022 to Disrupt Africa.
BusyMed integrates local pharmacies on its platform so patients can check real-time stock, place orders, and receive medicines within hours. The app also lets users submit prescriptions, consult healthcare professionals, and make secure payments.
The platform especially serves people in rural and remote areas, where medicine shortages and long waits at pharmacies are common. BusyMed’s model digitizes the entire pharmaceutical supply chain, building an integrated system around community-based healthcare.
Beyond delivering medicine, BusyMed plans to expand its app with teleconsultation and treatment management features. “Our goal is to offer primary healthcare businesses in the public and private sector the technology and resources they would need to serve the communities they are based in, and beyond, from the comfort of the patient’s home, at an affordable price,” Jezile emphasized.
This article was initially published in French by Adoni Conrad Quenum
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
Morocco is stepping up efforts to make digital technology a key driver of development and technological independence. The country plans to open an engineering school focused on digital transition and artificial intelligence.
On July 4, Minister of Digital Transition and Administrative Reform Amal El Fallah Seghrouchni signed a partnership deal with Minister of Higher Education Azzedine El Midaoui and André Azoulay, president of the Foundation for Research, Development and Innovation in Science and Engineering (FRDISI). The agreement sets up the Higher School of Engineers in Digital Transition and Artificial Intelligence and launches specialized training programs.
The Ministry of Digital Affairs said the initiative aims to align academic programs with real-world needs. The goal is to match training to the demands of local regions, the economy, and national technology priorities.
This project supports Morocco’s “Digital Morocco 2030” strategy, which targets training 100,000 young people annually by 2030 and creating 240,000 digital sector jobs. The plan follows the National AI Forum held last week in Salé, where nine agreements were signed with public and private partners. The forum stressed the importance of building human capital and developing a national roadmap for ethical and responsible AI use.
The new school will train engineers who can create and implement innovative digital solutions across sectors like public services, healthcare, industry, and education. Morocco aims to solve internal challenges while preparing young people for the jobs of the future.
Beyond education, the project will boost Morocco’s digital sovereignty, drive innovation, and help position the country as a magnet for tech startups and regional R&D centers.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Edited in English by Ange Jason Quenum
• Emeka Ajene leads Afri.capital, focused on early-stage African tech investments
• The firm links global investors, the African diaspora, and innovation opportunities
• Ajene previously co-founded Gozem, a major super app in Francophone Africa
Nigerian entrepreneur, mentor, and investor Emeka Ajene (pictured) is helping connect global capital with Africa’s growing technology startup ecosystem. He is the founder and CEO of Afri.capital, a venture capital firm dedicated to investing in and supporting tech startups across the continent.
Founded in 2023, Afri.capital serves as a bridge between international investors, the African diaspora, and high-potential opportunities in Africa’s innovation economy. The firm also publishes insights, analysis, and data through platforms like Afridigest to inform investors.
Afri.capital’s mission is to help institutional investors, business angels, and other stakeholders access, understand, and actively engage in Africa’s digital transformation. The company relies on Africa’s growing digital economy and strong local networks to identify, select, and support promising startups, with a focus on early-stage companies.
The firm is part of a broader ecosystem built by Ajene, which includes Afridigest, focused on market analysis, and Africreate, a strategic consulting platform. Together, these initiatives combine investment, advisory services, and information to help drive the growth of Africa’s tech sector.
Before launching Afri.capital, Ajene co-founded Gozem and served as its CEO until 2023. Gozem (founded in 2018) is a pan-African super app offering mobility, delivery, financial services, and e-commerce solutions across Francophone Africa, including Togo, Benin, Gabon, and Cameroon.
Ajene holds a bachelor’s degree in mathematics and quantitative economics from Morehouse College in the United States. He also earned a postdoctoral law degree and a master’s degree in finance and growth strategy from the University of Michigan.
Before his entrepreneurial ventures, Ajene held leadership positions in Africa’s digital economy. In 2015, he joined Konga Online Shopping in Nigeria as vice president for customer experience and marketing. In 2016, he became director of operations and business development for Uber Nigeria.
More...
A Benin native, he opted to establish his professional career in France. His work now involves balancing corporate duties with youth development programs throughout Africa.
Michel Idjinou (photo), a Beninese engineer and expert in information systems architecture, specializes in data and digital transformation. He is the co-founder of RINTIO, a digital services company, and heads its French subsidiary.
Founded in 2017 and headquartered in Benin, RINTIO also operates in France. The company develops custom IT solutions, offers systems integration services, and works in data science, big data, and artificial intelligence. It supports African and international businesses in their digital transformation, delivering technology tools tailored to specific industry needs.
RINTIO is also committed to training young Africans in digital professions. It regularly hosts bootcamps and hands-on training programs in areas such as software development, AI, and data science. In 2021, it launched E-learning Coraq Lab, an online training platform.
Beyond his role at RINTIO, Idjinou is a business and data architect consultant at La Française des Jeux, the French national lottery operator. He is the founder of Africa TechUp Tour, a training initiative focused on AI and data careers for young people across Africa. He also plays an active role in the nonprofit 10.000 Codeurs, serving as the lead for the data community and mentoring youth toward careers in tech.
Michel Idjinou holds an engineering degree in computer science from Institut National des Sciences Appliquées (INSA) in Lyon, earned in 2010. Since then, he has built over 15 years of experience in information systems architecture, data project management, and digital transformation, working with major firms in France including BNP Paribas, Société Générale, and My Money Bank.
Melchior Koba
In 2023, Orange launched Lead the Future, a new business model driven by responsibility and efficiency. This approach is redefining the boundaries between economic performance and social impact, with visible results multiplying year after year across its markets, especially in Africa.
On June 5, 2025, Orange Middle East and Africa (OMEA) marked the first anniversary of Orange Engage for Change. This program of social and environmental initiatives showcases OMEA's positive impact actions while allowing employees to get directly involved and make a tangible difference in communities and regions. This innovative program, which highlights OMEA’s initiatives through the Orange Foundation, Orange Digital Centers, Orange Villages, and other projects, was simultaneously rolled out across its 17 markets, a first for the continent. The pioneering initiative engages every employee on key societal and environmental issues in the countries where the group operates. Since its 2024 launch, 5,676 employees, nearly a third of the total workforce, have taken part in on-the-ground actions. They have shared their experience, skills, and support in education, digital access, the environment, and social solidarity. Each OMEA employee received three workdays per year from their local entity for community missions. These missions were grouped into over 280 engagement opportunities listed on the program's dedicated platform.
At the 2024 launch, Asma Ennaifer, Executive Director of CSR, ODC and Communications for Orange Middle East and Africa, explained that Orange Engage for Change was born from a desire to empower employees. She emphasized that every initiative and action taken by employees demonstrates their collective ability to bring about significant change. Ennaifer expressed pride in seeing this commitment materialize and witness the positive impact it generates.
The education sector proved the most dynamic, offering 123 engagement opportunities to staff, with 54 specifically dedicated to digital skills development. Regarding OMEA’s investment in skills development, the telecom company highlighted digital inclusion as a powerful lever for reducing inequality and empowering individuals. Orange stated its belief that digital technology should foster equal opportunity, not division, making it a core priority within Orange Engage for Change, its solidarity engagement program. The company affirmed that acting for digital inclusion means acting concretely for shared, sustainable progress, fully aligning with its mission as a responsible operator. Meanwhile, the environmental field provided 53 engagement opportunities for Orange employees in Africa and the Middle East.
Local Initiatives, Global Impact
The success of Orange Engage for Change heavily relies on its local roots. Orange missions are tailored to needs identified by subsidiaries and partner non-governmental organizations, ensuring maximum relevance. In Côte d’Ivoire, 150 volunteers collaborated with a local partner to reforest 30 hectares in the Azaguié forest. In Mali, 350 volunteers planted 1,000 trees and supported efforts to create an urban park for children. In Madagascar, 240 volunteers raised climate change awareness among 1,200 students across each of the country's 24 regions. Overall, the actions span a wide range of fields, including education, culture, digital inclusion, environment, and health, illustrating the program’s rich and broad impact. This diversity is part of a broader vision: to use digital technology as a tool for inclusion and to promote societal responsibility at every level.

Millions of Lives Touched
Orange’s social initiatives across Africa and the Middle East impacted the lives of over 18 million people, either directly or indirectly, in just one year. Through hundreds of missions, thousands of children and youth attended coding workshops at Orange Digital Centers. Project leaders gained skills through mentorship sessions, and hundreds of rural women participated in skills training workshops in digital homes. Urban sanitation drives included trash collection, gutter cleaning, electronic waste recycling, construction of modern school toilets, installation of community drinking water points, and distribution of medications in detention centers.
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, for example, the Kisenso General Referral Hospital in Kinshasa received water and electricity storage equipment to improve working conditions for medical staff and patient care. In Guinea, Senegal, Burkina Faso, and Cameroon, digital kits were donated to schools in rural or underprivileged areas to improve students' access to richer learning resources. In Botswana, Madagascar, and Guinea-Bissau, several initiatives were launched at Digital Homes to help women develop entrepreneurial skills and build greater autonomy.
Hélène Ndogmo, a housekeeper and member of the Widows’ Association of Douala 5th, was among the women who discovered digital crafts through workshops organized by Orange Cameroon. She learned to design creations using a drawing program and produce them with a laser cutting machine. Ndogmo expressed great pride in her training, recalling that she previously thought computers were only for college students, not for older mothers like herself.
In the Central African Republic, Noelle Jessica Gandou, a senior-year student in the G2 track at the Technical High School of Bangui, benefited from a sanitation operation led by Orange Centrafrique. After the campaign, which involved removing paper and plastic waste, clearing brush, maintaining green spaces, and cleaning up areas to combat malaria and harmful insects, the teenager expressed her delight. She looked forward to seeing their playground clean and gathering area beautified with flowers, anticipating a lovely view in a few months.
Transformed Employees
One of the key anticipated effects of this program is the transformation observed among the employees themselves. Taking part in field missions provided them with a new perspective on their role in the company and strengthened their sense of social purpose.
Jacqueline Diomandé, an Orange Côte d’Ivoire customer, views Orange Engage for Change as essential. She called it a fantastic initiative, noting the difficulty for office workers to find time to get out and give back to humanity, which everyday habits often inadvertently harm.
In Madagascar, where 563 employees participated, Domoina Randriamananoro, PMO for Technical Logistics, joined colleagues in preparing and delivering care packages to children in hospitals. She explained her involvement as a way to find personal joy through helping and showing solidarity. Randriamananoro spoke of the pleasure of giving and receiving satisfaction in return, expressing pride in making her small contribution and working alongside people who share the same values in the company's varied and far-reaching humanitarian work.
Prisca Mihanta Randrianarisoa, an advertising manager at Orange Madagascar, participated in a digital education workshop for students at a public school in Ambohidratrimo. She happily recounted teaching them how to use tablets, which she believes will benefit their studies and prepare them for the future.
Omar Al-Majali of Orange Jordan added that participating in the reforestation was a unique experience. He noted that it strengthened the bond among colleagues and deepened their commitment to the environment.
Toward a Scaling Up of the Program
Buoyed by the success of this second edition, Orange plans to expand and intensify the program. The goal is to involve one out of every two employees in Orange Engage for Change, increasing team participation in high-impact societal actions. With this new social engagement initiative, OMEA is no longer simply supporting causes; it is actively engaging its people in a process of social transformation. This model is built on the belief that large corporations have a vital role to play in building more just and resilient societies. However, one of the main challenges facing OMEA as it scales up the initiative will be ensuring that the supported projects continue to thrive after employee involvement ends.
African payments technology company Flutterwave has announced it has secured 20 new Money Transmitter Licenses (MTLs) across the United States, significantly expanding its ability to offer faster and more reliable cross-border payment services.
The newly acquired licenses mean customers across more U.S. states and territories can now send money more easily and securely to countries including Nigeria, Ghana, Egypt, and Cameroon.
The new licenses reinforce the company’s mission to simplify international payments and strengthen economic ties between the U.S. and Africa.
African payments company Onafriq launched its new cross-border payment service on July 3 in Accra. This ushers in a transformative way for individuals and businesses to move money seamlessly across African borders.
The new service directly connects banks, fintechs, and mobile money operators, enabling instant transfers from Ghanaian mobile wallets to Nigerian bank accounts and wallets. This integration allows traders to settle cross-border transactions more efficiently, families to remit money to loved ones, and businesses to streamline payments to suppliers and employees.
The service launch marks a significant step toward reducing reliance on costly and slow traditional remittance channels, making it easier for millions of Africans to participate in regional economic activities.















