Investment commitments in the digital sector are crucial for African development. With its vast underserved population, Africa can greatly benefit from enhanced digital connectivity. These investments address critical barriers like affordability and adoption, fostering an inclusive digital society.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) announced, on May 27, $4.8 billion in new investment commitments to boost global connectivity. This brings total pledges through its Partner2Connect Digital Coalition (P2C) to $50.96 billion, nearing its $100 billion target for 2026.
The announcements were made at the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS)+20 Forum in Geneva. The new pledges leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance digital access and inclusion.
"Closing the digital divide requires a team effort, and today we scored a huge win for global connectivity," said ITU Secretary-General Doreen Bogdan-Martin.
Key commitments include $106 million from Elle International to improve digital connectivity for 20 million women and girls in South Africa and a new pledge from Microsoft to prioritize AI projects that include people with disabilities, among others.
According to the ITU, approximately 5.4 billion people (67 percent of the world’s population) were using the Internet as of 2023, leaving 2.6 billion people still offline. This statistic underscores the significance of ongoing investments in digital connectivity, particularly in regions like Africa. With a substantial portion of the global population still disconnected, initiatives aimed at increasing digital inclusion are crucial for fostering a more inclusive digital society.
Hikmatu Bilali
Bilateral relations between Italy and Tunisia date back to the 1980s. Over time and with the evolving global context, the two countries have successfully expanded their exchanges in various fields. They now aim to extend this cooperation to the fourth industrial revolution.
On Monday, May 27, Italy and Tunisia declared their commitment to intensifying collaboration in the digital realm. This new phase emphasizes the promotion of economic and industrial collaboration initiatives in artificial intelligence (AI) and digital transition research. A memorandum of intent was inked by Adolfo Urso, Italy’s Ministry of Enterprises and Made in Italy (Mimit), and Nizar Ben Néji, Tunisia’s Minister of Communication Technologies.
According to the Tunisian Ministry of Communication Technologies, this announcement mirrors a mutual aspiration to bolster economic and industrial cooperation initiatives, boost investments, and foster joint ventures between Tunisian and Italian firms via business forums, seminars, and workshops. These events are organized with the participation of governmental institutions and the backing of associations and organizations representing entrepreneurs.
The ministry further explained that this new phase stems from a mutual interest in fostering bilateral cooperation for technology transfer. This is achieved through the exchange of experiences and knowledge in research, innovation, and skill development. The shared goal is to facilitate and implement projects in the public, private, and joint sectors, incorporating stakeholders from both nations in the context of applying AI to industry and related research sectors.
This new commitment for digital cooperation follows a previous agreement on September 29, 2023. On that day, the two nations, represented by Tunisia’s National Cybersecurity Agency (ANCS) and its Italian equivalent, signed a memorandum of understanding on bilateral cooperation in cybersecurity and digital trust services. This agreement aimed to intensify the exchange of experiences and expertise between the two institutions, develop specialized skills to safeguard cyberspace, ensure digital sovereignty, and enhance response speed and vigilance levels to effectively identify and address cyber risks.
Italian Minister Adolfo Urso also announced the establishment of a center dedicated to sustainable development in Tunisia, in partnership with Italy and the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). He described the center as an opportunity to draw in expertise and investment, contributing to inclusive growth and enhancing the quality of services provided to institutions and citizens. According to Urso, this multilateral platform can serve as a catalyst for the development of AI technology and its multiple applications at both national and cross-border levels.
To assist African entrepreneurs in developing their businesses on the continent, both legally and administratively, two tech entrepreneurs have developed a tailored solution.
Legafrik is a legaltech solution developed by an Ivorian startup, providing users in several countries across the continent access to legal services via its web platform. The startup, based in Abidjan, was founded in 2017 by Youssouf Ballo and Daouda Diallo.
"Our goal is to make basic legal services accessible to as many people as possible in the OHADA [Organisation for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa] countries. Today, there is a lot of talk about financial inclusion, but I think it's also important to talk about legal inclusion. Our mission is to allow everyone to access legal services at very affordable rates," the startup explains.
Legafrik does not have a mobile application. Users need to access the startup's website through a browser. They must then click on the "client access" button in the upper right corner to reach the login page and then sign up.
Once the account is created, users have access to a workspace from which they can kick-start various services and track their progress. Legafrik offers services including company creation in several African countries, assistance with opening bank accounts, debt recovery, company domiciliation, as well as license and administrative approvals.
Since its launch, the startup has supported more than 7,000 entrepreneurs and completed over 20,000 legal and administrative formalities. In addition to Côte d'Ivoire, Legafrik operates in Benin, Morocco, Senegal, DRC, Burkina Faso, Guinea, Togo, and Cameroon.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Boasting a youthful population, Africa is experiencing a boom in its startup industry. Digital innovations are flourishing, with countries like Nigeria and Kenya at the forefront of this new economic driver. This has fostered a technically advanced environment, albeit one with some lingering weaknesses.
Africa's innovative ecosystem has seen explosive growth over the past decade, according to the International Trade Center (ITC). In 2010, the continent had just a handful of tech hubs, essential support structures for young, resource-constrained businesses. By 2021, that number skyrocketed to 1,031, a 60% increase from the 643 hubs recorded in 2019. The ITC attributes this boom, at least in part, to the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated digitization across Africa.
Nigeria, South Africa, and Kenya Lead the Way
The report, "Tech Hubs in Africa, accelerating start-ups for resilient growth" (3rd edition), reveals that Nigeria leads the continent with 164 tech hubs, followed by South Africa (96) and Kenya (90). Interestingly, 53% of African tech hubs prioritize community building, while only 45% offer business support programs.
Eight Models of Support
The ITC categorizes tech hubs into eight distinct models based on their business models and services. Accelerators provide intensive, cohort-based programs with mentorship. Incubators offer early-stage startups resources like training, mentoring, and sometimes funding. Innovation centers foster creative ideas and help entrepreneurs build their businesses.
For hands-on creation and testing, hackerspaces, makerspaces, and fab labs offer access to equipment, tools, and skills development. Coworking spaces provide physical workspaces that boost productivity, collaboration, and networking. Venture builders help high-growth companies access resources for rapid expansion. Tech parks cluster tech companies to stimulate innovation and interaction. Finally, venture capital firms offer capital, mentorship, and access to new technologies.
Spécificités
Among the various hub types, incubators are the most prevalent. However, access to local venture capital remains a significant hurdle.
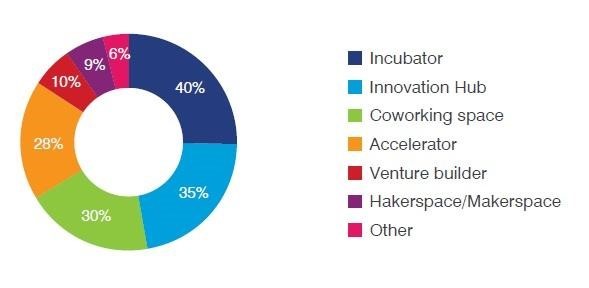
Source : ITC
Training and networking events are the most commonly offered services, with financing being a weaker area.
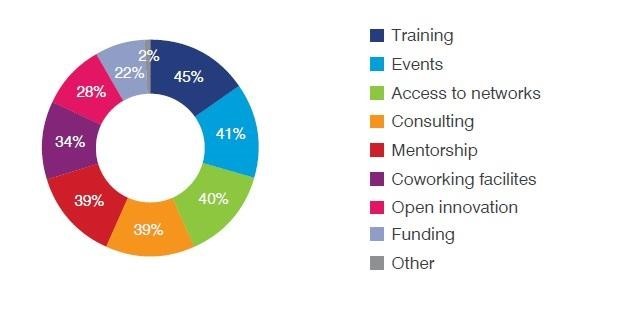
Source : ITC
Specialization for Impact
Many tech hubs are moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach. By specializing in specific demographics or sectors, they can optimize their support. Over half (52%) of hubs target specific sectors in their programs, with agriculture (22%), fintech (17%), and e-commerce (11%) leading the pack. These sectors are not only highly active in terms of investment and startups, but also offer immense opportunities for social impact.
Gender Focus
Many hubs also prioritize supporting specific populations. While many cater to various groups, young people and students are the most common targets, followed by female founders and women in general.
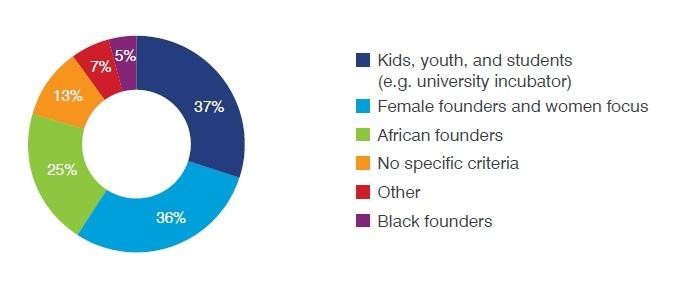
Source : ITC
Challenges and the Road Ahead
The COVID-19 pandemic forced 73% of tech hubs to close their physical locations in 2020. While the remaining 27% adapted with strict safety protocols, the closure significantly impacted platform revenue, leading to the closure of 8% of hubs. Many transitioned to remote training models, but financing remains the biggest challenge. The ITC report emphasizes the need for sustainable funding models, potentially through grants or external support. Additionally, favorable policies that attract investors and encourage innovation are crucial for the continued growth of Africa's dynamic tech hub ecosystem.
Muriel Edjo
The National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) unveiled the 'Digital Literacy for All' initiative on May 26, aiming to narrow Nigeria's digital gap and promote inclusive growth.
The program, set to achieve a 70% literacy rate by 2027, seeks to provide universal access to digital literacy. It empowers citizens with critical digital skills such as online resource utilization, cybersecurity awareness, effective communication, and proficiency in digital tools.
Statistics Botswana announced on May 16 that it will conduct the 2024 Botswana Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Household Survey from June to August 2024, collecting data from selected households nationwide.
The survey aims to produce indicators for evaluating ICT development goals, provide benchmarks for international comparisons, monitor progress towards building an information society, and offer critical data to enhance digital economy growth.
Data will encompass household ICT access, online safety, e-waste awareness, individual device usage, digital skills, e-education, e-commerce, e-government, security, privacy, and media habits.
A fervent believer in the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics to propel growth for businesses and institutions across Africa and beyond, he has channeled this passion into his startup, eWaati.
Fousseyni Dembele (photo) is a Malian entrepreneur and artificial intelligence and robotics expert. He is the co-founder and CEO of eWaati, a startup specializing in AI and robotics technologies. His mission, as stated on his LinkedIn profile, is "to create smart and interconnected solutions that promote the growth of private enterprises across all sectors globally."
Founded in 2019, eWaati offers facial recognition and data analysis technologies for various sectors, including public security, business management, finance, education, and marketing. The company aims to transform the daily operations of businesses, institutions, and public services in Mali and Africa.
eWaati's flagship solution is a digital system for managing employee attendance and work hours, equipped with facial recognition technology. This device, bearing the startup's name, aims to improve punctuality and security within companies and institutions. Additionally, eWaati offers eSchool, a comprehensive digital solution for school management.
Before eWaati, Fousseyni Dembele founded Heat Decision in 2018, a startup focused on providing IT solutions to help business leaders and managers make informed decisions.
Fousseyni Dembele holds a master's degree in computer applications, obtained in 2017 from Djillali Liabes University in Sidi Bel Abbès, Algeria. Before venturing into entrepreneurship, he worked from 2017 to 2019 at NG System Technology, a company developing web and mobile solutions, where he held the position of software developer.
Melchior Koba
Benin has set its sights on becoming the digital hub of West Africa since President Patrice Talon took office in 2016. The country has pursued this goal by digitizing numerous services, with a significant acceleration following the COVID-19 pandemic in 2021.
Benin's Directorate General of Taxes (DGI) unveiled new online services on Thursday, May 23rd, aimed at streamlining tax payment procedures for small businesses and property owners in Cotonou. The initiative, with plans for a nationwide expansion, leverages technology to improve efficiency and convenience for taxpayers.
"We live in an era where information and communication technologies play a crucial role in all aspects of our lives, and the tax domain is no exception. [...] We are providing micro and small businesses and property owners with modern tools to secure and facilitate the fulfillment of their tax obligations. This platform significantly reduces the cost of tax compliance and the time required," said Nicolas Yenoussi, Director General of Taxes.
Building on Benin's 2017 launch of the "e-services.impots.bj" portal, which marked the beginning of tax administration digitization, the DGI has implemented a phased rollout, adding functionalities over time. The introduction of these new services aligns with this strategy.
The DGI underscores the initiative's goal of creating a more modern, transparent, and user-friendly tax environment. They report that the gradual digitization of services has contributed to a 13.1% increase in tax revenue between 2017 and 2021, compared to a 5.7% increase over the previous five-year period (2012-2016).
Adoni Conrad Quenum
A logistics professional by training, he aims to facilitate the transport of goods in Africa. After accumulating several years of experience with various companies and transport organizations, he founded his own startup, Buur Logistics.
Amadou Dieng (photo) is a Senegalese logistics professional and entrepreneur. He is the founder and CEO of Buur Logistics, a startup operating in the transport and logistics sector.
Founded in 2019, Buur Logistics provides services for connecting and optimizing the transport of goods across North and West Africa. The company collaborates with over 3,000 African service providers and offers a tracking system that allows real-time location of trucks and goods.
Buur Logistics boasts a fleet of over 3,500 geolocatable trucks that can be mobilized at any time. The company also owns certified warehouses for goods storage and handles cargo for its clients. To date, it has served 3,200 clients across 120 different areas.
In 2021, Amadou Dieng was a laureate of the Orange Corners program and received support from the Orange Fab accelerator in Senegal in 2022. He will participate in GITEX AFRICA, held from May 29 to 31, 2024, in Marrakech, Morocco.
Amadou Dieng graduated from the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers, where he earned a higher technician diploma in logistics and port management in 2018, followed by a bachelor's degree in international trade and logistics development in 2019. He began his professional career in March 2018 at the Senegalese Consortium of Maritime Activities (COSAMA) as a port agent.
In November 2018, he joined DHL Global Forwarding, which provides air, sea, and land freight services, as a customs agent. In 2019, he joined Kemtar, a digital platform facilitating connections between transporters and professional or individual clients in West Africa, where he was the logistics operations manager.
Melchior Koba
Digital technologies are crucial for driving economic growth, innovation, job creation, and social inclusion. However, Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) grapples with significant challenges in digital development, such as underdeveloped infrastructure and costly connectivity. Entry into the African telecom market with 5G infrastructure is pivotal for African development, promising to enhance digital inclusion, spur economic growth, reduce costs for local telecom operators, and hasten technological progress.
Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) is set to enter the African telecom market by providing 5G shared network infrastructure through its subsidiary Radisys, in collaboration with Next-Gen Infrastructure Co. (NGIC), backed by the Ghanaian government. Radisys announced this on May 27.
"By bringing Fixed Wireless Access alongside 4G and 5G cellular services to help drive economic growth and digital inclusion, Radisys looks forward to helping Ascend and NGIC build a disruptive and affordable shared broadband infrastructure across Ghana," said Arun Bhikshesvaran, CEO of Radisys.
Radisys, owned by RIL's unit Jio Platforms Ltd (JPL), along with Tech Mahindra and Nokia, will collaborate with NGIC to develop 4G and 5G networks across Africa, starting with Ghana. NGIC plans to invest $200 million in this initiative over the next three years, offering the networks as shared resources to local mobile operators to cut costs. With partnerships already established with AT Ghana and Telecel Ghana, NGIC aims to replicate India's low-cost, high-speed data model, providing affordable and efficient digital services across the continent.
This investment aligns with the strategy outlined in August 2023 by Owusu-Ekuful, Ghana’s Minister for Communication and Digitisation, during the 12th African Peering and Interconnection Forum (AfPIF). She disclosed the government's decision not to issue a 5G license, which would require significant investment from telecom operators. Instead, the government plans to establish a neutral shared infrastructure company to provide the necessary networks to operators.
Andrew Dabalen, the World Bank's Chief Economist for Africa, emphasized that increasing mobile internet usage could create jobs and spur economic recovery. A 2023 World Bank report (Digital Transformation Drives Development in Africa) revealed that extreme poverty decreased by around 7% in Nigeria and Tanzania, and labor force participation increased by up to 8% after three or more years of internet coverage. Addressing these gaps is crucial for fully harnessing digital technologies' potential in SSA.
Hikmatu Bilali
More...
E-health is rapidly transforming Africa's healthcare landscape. By leveraging information and communication technologies, e-health solutions are making it easier for patients to connect with healthcare professionals, while also increasing the accessibility and availability of medical expertise across the continent.
Beesiha is an e-health solution developed by an Algerian startup. It allows users to book medical appointments with just a few clicks via its web and mobile platforms. The startup, based in the Said Hamdine district of Algiers, was founded in 2019 by Said Admane and Amine Babou.
The mobile application is available on both iOS and Android, where it has already been downloaded over 10,000 times, according to Play Store statistics. After downloading the app, users can register using their Facebook account or by providing information such as their name, surname, and phone number. Once registered, they can log in and access the various services offered by the startup.
Using a search bar where the user can enter the medical specialty, medical facility, or city they are looking for, Beesiha provides the most relevant results. Users can book appointments for free based on the availability of the selected doctor. It is also possible to book an appointment for a third party, such as a friend or family member.
To ensure patients don't miss consultations, Beesiha sends frequent appointment reminders. For added convenience, the platform offers remote consultations, with patients benefiting from a digital medical record storing test results, prescriptions, and consultation history – all under their complete control.
For doctors, Beesiha offers a digital agenda, allowing them to schedule their working hours as they see fit. The platform includes most medical specialties, making it easier to adopt the solution. Since its launch, Beesiha boasts more than 800 healthcare professionals available on its web and mobile platforms and over 215,000 appointments booked.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
The COVID-19 crisis significantly impacted the postal sector, and the subsequent surge in digitalization has further disrupted the market, forcing postal services to contend with innovative competitors. This challenge is particularly acute in Africa, where postal services must adapt and reinvent themselves to remain relevant.
Equatoguinean investors, represented by INVERFIN, met with Gabon's Minister of Communication and Media, Laurence Ndong, on Thursday, May 23rd, to discuss potential investments in the country's postal and telecommunication sectors.
The investors signaled their interest in supporting Gabon's postal service (La Poste SA) in its digital transformation initiatives. The discussions also explored backing an economic group formed by La Poste SA, Télédiffusion Gabon (TDG), and Universal Services for expanding telecom network coverage in underserved areas.
According to a Facebook post by Minister Ndong, INVERFIN expressed willingness to "fully finance La Poste SA's digital projects" across the tri-border zone (Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon) and beyond. The investment seeks a return based on a memorandum of understanding (MoU) currently under legal review by La Poste SA and the Ministry.
This financial support aligns with Gabon's Digital Plan and the Universal Postal Union's (UPU) directives, emphasizing the need for La Poste SA to adapt and capitalize on e-commerce, e-government, and digitalized financial services. The UPU's 2023 Integrated Index for Postal Development (2IPD) ranks Gabon's postal development as "weak" with a score of two out of ten.
“INVERFIN representatives are expected to return to Libreville in a few weeks for the final signing of the memorandum of understanding,” Minister Ndong's post informs.
The Organization of Information and Communication Technologies Professionals in Senegal (OPTIC) recently announced the 7th edition of the International Fair for Professionals of the Digital Economy (SIPEN). This event is scheduled to take place on June 27-28 in Dakar. The event will focus on the theme "Accelerating Digitalization: A Powerful Lever for the Competitiveness of the Senegalese and African Economy."
Informal sector traders across Africa are often excluded from the traditional financial system. Recognizing this issue, tech entrepreneurs have developed innovative solutions to offer alternatives to conventional financial institutions.
Proboutik is a fintech solution developed by Senegalese startup ProXalys to transform the way informal sector traders manage their financial operations. Launched in 2021 by Thierno Sacko and Abdoulaye Faye, Proboutik enables local merchants to digitize their financial transactions, bringing them into the fold of modern financial systems.
In January 2024, ProXalys raised $500,000 to support the growth of Proboutik. The mobile application, available on both iOS and Android, has already been downloaded over 10,000 times from Playstore. Users can register with their phone numbers and access various financial management services. These include cash flow management, customer portfolio management, real-time tracking of receivables and payables, automated payment reminders via SMS, and the generation of account statements and reports.
"The application records all your deferred payment transactions, ensuring transparent traceability and better management of your business operations," explains the startup. Additionally, Proboutik offers financing to users based on the credits they have extended to their customers. This feature aims to facilitate business growth and prevent financial strain for traders.
Proboutik provides two subscription options: a monthly plan priced at 990 CFA Francs (approximately $1.63) and an annual plan at 10,000 CFA Francs. On May 23, Proboutik was selected, along with 19 other African fintechs, for the second cohort of Visa's acceleration program.
Adoni Conrad Quenum