In February 2023, Bolt announced it would invest $500 million over the following two years to accelerate its growth in Africa. Since the beginning of 2024, the startup has entered several additional markets on the continent.
Estonian e-mobility start-up Bolt has launched in Cairo, Egypt, co-founder Martin Villig announced on X (formerly Twitter), on Monday. This makes Egypt the fifteenth country the ride-hailing startup is entering and the second in North Africa (After Tunisia in 2019).
The startup intends to establish itself in the Egyptian market by eliminating the 15% commission charged to drivers for the first six months and offering a 50% discount to customers.
Eduard Suchanek, Bolt's Regional Director for the Middle East and North Africa, says: "Bolt’s entry into one of the largest economies in North Africa underscores our commitment to revolutionizing mobility in the region. By offering ride-hailing services tailored to both individual and corporate needs, Bolt aims to provide Egyptians with convenient, reliable, and affordable transportation options."
Bolt is expanding in Africa in a context marked by a global tech investment slowdown. Tech investments on the continent fell 54% to $2.3 billion in 2023, according to Partech Africa. E-mobility was particularly hard hit, with funding down 75% from 2022.
It is worth noting that the entry into Egypt is in line with the ride-hailing startup’s plan, announced in February 2023, to invest $500 million in its African expansion plan in two years.
With its new expansion in Egypt, Bolt aims to conquer North Africa and the Middle East (MENA), a region where it has little presence and which is dominated by the American Uber and the Emirati Careem.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
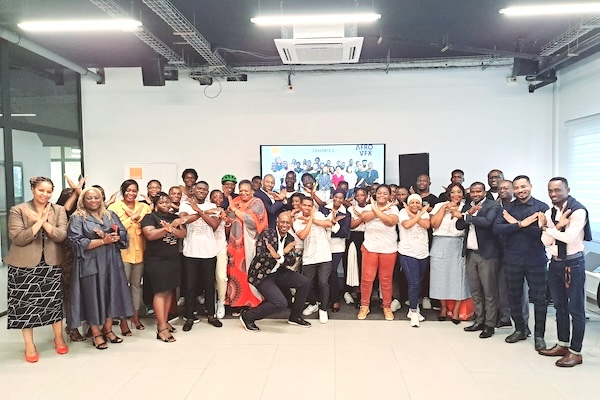
This new session increases the number of skilled labor available in Africa’s booming entertainment industry.
The second cohort of the “Afro VFX” training program, a joint initiative by EM&MB, the Orange Digital Center (ODC), and the Canadian Embassy, was launched on Thursday, February 29, 2024, at the ODC in Abidjan’s Plateau district.
The program, which focuses on training young talent, producing high-quality cinematic works, and fostering the growth of the African industry, will provide thirty individuals with intensive four-month training in special effects (VFX). The goal is to stimulate the creative industries within the audiovisual sector in the region. Upon completion, participants will gain practical experience through internships with local companies and Afro VFX’s partner studios.
West Africa, primarily driven by the Nigerian film industry, releases nearly 3,400 films annually from production studios, making it the continent’s most productive region in audiovisual production, according to Statista. For Eric M'Boua and Dedy Bilamba, co-founders of EM&MB, Afro VFX positions itself as "a key partner in the VFX ecosystem in French-speaking Africa."
Three students from the first cohort won the “Sony Talent League by THU 2022” competition with a 3D animation series called “Djossi Heroes”, which celebrates self-employed informal workers with superpowers.
The Orange Digital Center has long been dedicated to aiding young Ivorians, offering technical support to enhance their skills and realize their projects. Reminding of that commitment, Habib Bamba, Director of Digital and Media Transformation, stated: “The Afro VFX program is the perfect illustration of Orange Digital Center's commitment to the creative and cultural industries, to make digital an opportunity for all, and thus contribute to the development of the film industry.”
The edtech solution was launched by Osita Oparaugo, a tech entrepreneur, to support the growth of the African digital economy, to reach 10 million users within the next decade.
Nigerian firm Wings of Justice Limited has launched GetBundi, an edtech platform that provides users with access to educational content in science, technology, engineering, mathematics (STEM), and digital skills. The platform, which was introduced in June 2022 by founder Osita Oparaugo, is designed to supplement traditional teaching methods and serve as a study guide for both schooled and homeschooled students.
“GetBundi is not designed to be a replacement for the traditional method of teaching. Rather [...] it supplements the teaching and learning process whether as a teacher’s aid, study companion, revision guide,” Osita Oparaugo explained at the launch of GetBundi.
In addition to its web platform, GetBundi also offers a mobile app available on iOS and Android. Users can create an account to access a variety of content, including courses in artificial intelligence, coding, digital marketing, and cybersecurity. Some courses are offered free of charge.
In its 2032 strategy, GetBundi aims to reach ten million Africans over the next decade. Currently, the platform boasts 107 instructors and 2,733 students, offering 21 live courses and 117 video courses across its web and mobile platforms. Since its launch, the Android version of the app has been downloaded over a thousand times, according to Play Store data.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Nigerian fintech firm BFREE specializing in credit management, announced on Thursday, February 29, that it has successfully raised $2.95 million in a funding round. The company, which has operations in Nigeria, Kenya, and Ghana, plans to use the new capital to expand its risk management solutions for banks and lenders.
Through its programs and resources, hapaSpace supports young people at every stage of their entrepreneurial journey, from developing STEM skills to accessing finance, and from incubating to accelerating innovative ideas.
HapaSpace, a technology and collaborative innovation center located in Kumasi, Ghana, was established in 2016 by CEO Gideon Brefo and CFO Albert Yaw Opoku. The hub helps young people create start-ups and develop skills in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) through workshops, specialized training, meetings, mentoring, and incubation and acceleration programs. It supports the entire business journey, from idea generation to pre-seed financing.
It also offers coworking spaces and fully-equipped offices with reliable Internet connectivity. In addition to physical infrastructure, hapaSpace facilitates access to volunteers, organizes events, and fosters networking opportunities for budding entrepreneurs. Moreover, the center collaborates with venture capital firms, angel investors, and sponsors competitions to provide funding avenues for startups.
Among the programs launched by hapaSpace, SmartWoman aims to equip 150 women with basic digital skills in Adjamesu, in the Ashanti region of Ghana. The program is part of the DigiWorks project sponsored by the Digital Transformation Center of the German Agency for International Development Cooperation (GIZ) and eSkills for Girls.
The center provides technical assistance to companies and individuals. It carries out market research for individual start-ups, companies, and development partners. It has created four active communities to help entrepreneurs build resilient businesses.
The hapaSpace technology community totals over 500 people who support one another. It also has an entrepreneurs' community, an artists' community, and a readers' club. The first counts over 1,000 innovative people, while the second totals around 158 creative artists. In the readers' club, a book is read each month and discussed.
Melchior Koba
In Tunisia, Connect'Innov supports companies by promoting entrepreneurship and technological innovation in the healthcare field. It offers a range of services, from pre-incubation to business acceleration.
Connect'Innov is a Tunisian support institution dedicated to identifying, supporting, and promoting innovation in the healthtech field, particularly e-health, medtech, and biotechnology. It was founded in 2020 by biochemist Wafa Bchir and accountant Hichem Radoine.
It offers pre-incubation and awareness-raising services with ongoing training for entrepreneurs and researchers. It also creates startups and supports innovative projects, providing incubation and acceleration programs and organizing events and meeting sessions to create more partnership opportunities.
Currently, Connect'Innov hosts a range of impactful programs. Among these initiatives is Connect'Innov Prep, a foundational program that introduces participants to entrepreneurship and innovation while providing pre-incubation support. Additionally, Connect'Innov Camp offers a series of concise yet comprehensive training modules focused on fostering entrepreneurial skills and innovative thinking.
Its startup creation initiative, Connect'Innov Studio, cultivates in-house ideas spearheaded by its dedicated team. Furthermore, with its incubation arm, Connect'Innov Lab, Connect’Innov supports startups in the innovation phase. The primary goal of this program is to assist young entrepreneurs in refining their concepts, and comprehensively preparing them for subsequent phases of development.
For startups that have progressed beyond the ideation phase and validated their prototypes, Connect'Innov offers the acceleration program known as Connect'Innov Fab. This initiative helps healthtech companies secure funding and expand their market presence both nationally and internationally.
To date, Connect'Innov has run over 30 programs and events and has logged over 550 hours of support. More than 55 startups have been or are currently being supported, and more than 25 have been accredited. The institution is supported by entities such as the World Bank, Start-up Tunisia, Institut français, Deloitte, and Eurobiomed.
Melchior Koba
After his studies in France, a tech entrepreneur returned home to launch a startup focused on improving service accessibility. The company seeks to participate in the continent's ongoing technological development.
Moroccan startup Jobbers.ma has developed a digital solution that provides users with access to professionals and freelancers in various sectors through its web and mobile platforms. The Fez-based company was founded in 2020 by Driss Bennis.
The solution features a mobile app accessible on iOS, Android, and Huawei devices. After downloading the application, users create an account and enter their details. When registering, they indicate whether they want to sell services as a professional or are looking for professionals in specific fields. Jobbers.ma covers several categories, including artists, animal trainers, teachers, web developers, and more.
To search for professionals on the platform, the startup has set up a search bar where users can enter their location and the category of professionals sought. If the request is complex, users can post a text explaining all the subtleties of their request with all their requirements. Professionals with the necessary qualifications can apply for the job directly on the web or mobile platform. The customer can then contact them to close the deal with the most suitable professional.
With the main aim of improving people's daily lives by making services accessible through usage and price, Jobbers.ma is present in many Moroccan cities. Since its launch, the Android version of the application has been downloaded over a thousand times.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Through KudiGo, a technology platform, the entrepreneur aims to redefine micro and small business operations in Africa. He seeks to transform the continent's retail landscape.
Kingsley Abrokwah (photo) is a young Ghanaian entrepreneur and computer scientist. He is the founder and lead facilitator of KudiGo, a startup that aims to strengthen African retail through local technology solutions.
Founded in 2017, KudiGo offers omnichannel digital commerce infrastructure for micro and small business retailers in Africa. Its solutions include an in-store storefront, a code-free online store, a WhatsApp bot, and enterprise data solutions. The startup also offers white-label infrastructure for FMCGs, banks, fintechs, and other stakeholders.
The Ghanaian holds a higher professional diploma in network engineering obtained in 2010 from the National Institute of Information Technology (NIIT) Ghana Ring Road Centre. Since October 2017, he has been a consultant with Topia Technology Consult, a company specializing in cloud infrastructure, cloud security, and digital strategy. Since February 2024, he has also been a business mentor with Ashesi Venture Incubator, which trains emerging entrepreneurs to integrate outcomes focused on the SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals) into their business models.
Before KudiGo, Kingsley Abrokwah served as the co-founder of Chillax in 2013. Chillax is a mobile application offering personalized going-out suggestions, and Abrokwah led the team until 2015. He has also worked for several companies.
Between 2010 and 2022, he led PentiumTech successively as managing partner and CEO. At the same time, between 2014 and 2015, the entrepreneur worked for Apurimac Media, a digital media and marketing agency based in South Africa, as head of business development. In 2023, he took up the position of interim executive consultant at iJANU, an e-mobility technology company focusing on ecological and equitable mobility in African markets.
Kingsley Abrokwah was a student at the Meltwater Entrepreneurial School of Technology (MEST) between 2013 and 2014. In 2013, he won Startup Weekend Accra with his Chillax solution. He was also a finalist at DemoAfrica in 2017.
Melchior Koba
Smart citiesin Africa leverage technology to drive progress, enhance quality of life, and foster innovation while promoting sustainable development. They use digital solutions for efficient services, environmental initiatives, and strategic urban planning.
On Tuesday, February 27, Minister Uche Nnaji, representing the Nigerian government, formally sealed an agreement with Domineum/Edenbase UK. This collaboration aims to propel the ambitious Abuja Tech City project forward.
The project, outlined in a comprehensive Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), seeks to transform Nigeria’s technological landscape by drawing inspiration from the remarkable achievements of London Tech City.
Conceived as Abuja Tech Village (ATV) under former President Olusegun Obasanjo's administration, Abuja Tech City is envisioned as a smart and environmentally conscious metropolis that will play host to tech startups, industries, and entertainment ventures. Additionally, it is designed as a Free Trade Zone, aligning with global trends and bolstering Nigeria’s burgeoning tech ecosystem.
“Tech Cities are the catalysts for rapid industrialization and enhancement of operational synergy within critical sectors. For this reason, the federal government is committed to ensuring sustainable industrialization through the establishment of Tech Cities across the country,” said Minister Uche Nnaji.
As Nigeria embraces a tech-driven future, the collaboration with UK developers underscores the nation’s commitment to leveraging international expertise for unprecedented growth and innovation. Abuja Tech City promises to position Nigeria as a competitive global technology hub, fostering progress, prosperity, and a brighter future for all.
Hikmatu Bilali
Known for his innovations, the Tunisian video game entrepreneur invests in digital entrepreneurship. He also holds board positions in multiple organizations.
Walid Sultan Midani, a Tunisian entrepreneur and video game enthusiast, founded YouRun, an independent video game development studio based in Malta, Europe, in 2018. The studio, which publishes the 2D arena shooter Warshmallows, aims to combine elements of casual games, e-sports, and animated series to provide a unique gaming experience.
Midani is also a stakeholder in Bravvo, an AI-powered cloud platform designed to enhance employee engagement. The platform assists African companies in implementing top-tier employee engagement programs, allowing employees to acknowledge and reward each other’s work achievements.
Midani serves on the boards of La FrenchTech Tunis and Game for Change Africa. The former is a community comprising a broad network of digital economy players, aiming to generate services and actions beneficial to the Tunisian entrepreneurial ecosystem. Game for Change Africa, on the other hand, leverages the power of games to drive social impact and economic growth in Africa.
Additionally, Midani is a founding member of the Pan Africa Game Group (PAGG), a network comprising over 200 game development talents across the continent. The Tunisian entrepreuneur, who earned an engineering degree in computer systems and networks from the Ecole supérieure privée d’ingénierie et de technologie (ESPRIT) in Tunis in 2008, founded DigitalMania Studio, a video game studio, in 2011. He served as the CEO of the studio until November 2023. From April 2022 to January 2023, he co-founded and served on the board of Makers Factory, an initiative aimed at accelerating innovation in creative sectors such as gaming.
DigitalMania Studio received Microsoft’s Best Performing Start-up Award in 2012 and was selected for the Europe4startups program the following year. In 2014, Midani, along with DigitalMania Studio, received the award for the best pitch and business model among the 10 international entrepreneurs participating in the PITME program in Silicon Valley. In 2017, Quartz named him one of the African innovators.
Melchior Koba
More...
The startup enables access to professional coaches for various activities.
Artybe, a digital solution developed by a Togolese start-up, allows users to book sports, urban, and cultural activities with a specialized coach. The solution was officially launched in 2022 by co-founders Laura Nouhova Kpegli and Yawovi David Senyo.
"Artybe brings together worlds that haven't met much until now, but which are looking for each other: creative and precarious sportspeople and users with "a leisure budget", diasporans and local populations, young people and senior citizens," Laura Nouhova Kpegli explains to We Are Tech Africa.
While the mobile app for the solution is not yet available, Kpegli explains that Android and iOS versions would be accessible on the Play Store and App Store respectively from March 2024. Currently, users can access Artybe’s services via its web platform, where they can create a profile, browse various activities, and book and pay for them using mobile money.
"Our solution is flying off the shelves because it solves a problem people were desperate to fix. Before, finding the right help for your sports or hobbies was a nightmare. We've changed that. Talented coaches are out there, just waiting to share their skills. People with a passion for growth are ready to invest in themselves. Our digital solution brings them together," explains Laura Nouhova Kpegli.
Artybe plans to extend its reach from the capital cities of French-speaking West Africa to the rest of the continent. To achieve this, it needs funds to develop data systems, finance market research in other parts of the continent, and recruit staff to strengthen its team.
The startup has already received several accolades. In 2022, it was selected as one of the 10 flagship projects of the PAPRICAI incubator (Tech & ICC), voted one of the 5 “Best Media/Tools” at the Togo Digital Awards 2022, and was among the top 10 artificial intelligence start-ups on the continent at the World Africa Startup Summit in 2021.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
With over twenty years of experience working around the globe, he founded Open Access Energy. The startup is the embodiment of his passion for using technology to simplify energy transactions and promote sustainable energy.
Gerjo Hoffman (photo) is a South African entrepreneur and Stellenbosch University graduate with Bachelor's degrees in Information Science, Afrikaans, and Dutch obtained in the year 2000, followed by a Bachelor's degree in Journalism in 2003. He is the co-founder and CEO of Open Access Energy, a company established in 2021 with Christoff Albertyn to enhance energy accessibility. His platform facilitates the automated matching of energy generation and consumption loads, allowing for transparent energy transactions between producers and consumers.
Open Access Energy introduces two key solutions: Amptera and Energypro. Amptera serves as an all-in-one energy billing tool empowering municipalities, utilities, and homeowners. On the other hand, Energypro addresses the intricacies of private energy distribution through advanced technologies.
Before his involvement with Open Access Energy, Gerjo Hoffman co-founded Qikcommerce in 2012, offering an intuitive e-commerce solution for businesses venturing into online product sales. This platform enables users to swiftly establish their online stores.
Hoffman's professional journey includes roles at various companies. At WeChat Africa, a technology platform supporting diverse communication modes like group chat and multimedia messaging, he served as the Head of Marketing from 2013 to 2014. Subsequently, at Tencent Africa, he held positions such as Head of Operations (2014-2017), Director of Innovation (2017-2018), and Director of Sales and Marketing (2019-2021).
Between 2018 and 2019, Gerjo Hoffman assumed the role of Managing Director at JET8 Africa and later became the Global Head of Sales and Marketing for JET8, a social commerce technology platform.
Melchior Koba
In his address to the youth on February 11, the Head of State once again urged Cameroonians towards self-employment. It is then essential to provide the technical framework necessary to support the youth in that direction.
On Wednesday, February 28, Jacques Fame Ndongo, Cameroon’s Minister of Higher Education, laid the foundation stone of the digital innovation and business incubation center at the International School of Digital Engineering in Sangmélima, southern Cameroon. The center is a part of the Congo-Cameroon Inter-State University (UIECC) and is being constructed by military engineers. The project, funded to the tune of XAF450 million (US$743,000) by the Development Bank of the Central African States (BDEAC), is one of the eleven priority integration projects in the CEMAC region.
The two-story center, spanning approximately 1,675 square meters, is designed to identify, support, and assist students and young graduates of the International School of Digital Engineering with digital business startup projects. It will provide entrepreneurship training, networking, mentoring, and administrative services, facilitating the implementation and monitoring of innovation and digital entrepreneurship projects.
According to Marcel Fouda Ndjodo, the coordinator of the Congo-Cameroon Inter-State University and director of the digital engineering school, the school itself is an incubation center where students are already engaged in profitable economic activities. The school, which opened less than five years ago, has reportedly supported around thirty startups by engineering students. The director expressed the school’s ambition to transform Sangmélima into a hub for digital activities.
Cameroon’s new higher education law, enacted on June 25, 2023, redefines the role of university institutions, transforming them into “university companies” and elevating students to “student entrepreneurs” to combat youth unemployment through self-employment. “In a liberal economy like ours, in which the private sector should be the primary provider of jobs, one of the fundamental roles of the university is to support economic diversification through the detection, training, and incubation at the university of potential and future captains and leaders of the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary sectors,” said Minister Jacques Fame Ndongo.
The Congo-Cameroon Inter-State University, established on December 21, 2012, by the heads of state of Cameroon and Congo, Paul Biya and Denis Sassou Nguesso, began its training activities in the 2020-2021 academic year with the opening of the Sangmélima Engineering School. The school currently enrolls 450 engineering students, including 250 Cameroonians and 200 Congolese nationals.
The Ugandan government is committed to accelerating digital transformation and supporting all sectors of the economy. To this end, it is multiplying partnerships likely to help achieve this objective.
Mastercard announced on Tuesday, February 27, a memorandum of understanding with Uganda’s Ministry of ICT and National Directions. The agreement aims to stimulate socio-economic development, enhance services, and foster financial inclusion in Uganda.
The partnership includes Mastercard’s technical assistance to bolster the Ugandan government’s efforts toward digitization and financial inclusion. This encompasses the digitization of traditional services like Posta Uganda and the national postal service, to generate new revenue streams and provide integrated, user-friendly experiences.
The collaboration also aims to enhance the capabilities of Ugandan startups, enabling them to thrive in the digital era. Specifically, micro and small merchants will be equipped with the necessary tools to connect to the global digital economy and accept electronic payments, thereby broadening their market reach and reinforcing their contribution to Uganda’s economic growth.
This initiative aligns with Uganda’s digital transformation goals outlined in the “Vision 2040” digital strategy. It seeks to empower citizens by aiming for universal inclusion, sustainable development, economic advancement, and poverty eradication through digital innovation across various sectors.
The partnership aligns with Mastercard’s goal of enhancing financial inclusion by integrating one billion unbanked and underserved individuals into the digital economy by 2025. This includes empowering 50 million micro and small traders and supporting 25 million businesses owned or led by women.
Samira Njoya