He began his career in finance before shifting to entrepreneurship, where he created digital tools for commerce and logistics. He developed platforms for individuals, businesses, and transport companies.
Senegalese tech entrepreneur Racine Sarr is the founder and CEO of ShopMeAway, an e-commerce platform that facilitates international trade for individuals and businesses across French-speaking Africa.
Founded in 2016, ShopMeAway aims to simplify access to products from global retailers like Amazon, eBay, and AliExpress. The platform acts as an intermediary, removing obstacles related to payments, delivery times, and geographical restrictions.
In addition to its international business, the startup promotes local products through a dedicated "Made in Senegal" section, giving artisans and producers broader market access. The company also launched SAWA, a digital logistics platform in 2019 that connects transportation stakeholders across Africa to digitize and standardize a fragmented sector.
SAWA supports the movement of goods and B2B services, with the goal of reaching two million direct users, including online shoppers, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and logistics professionals. The platform aims to enhance service interoperability, reduce costs, and promote regional trade as it prepares to expand into Uganda and broaden its partnerships across the continent.
Sarr graduated from Paris Dauphine-PSL University with a master's degree in finance in 2004. He began his career in 2005 as a project manager at Exane, a French investment bank. He later joined BNP Paribas Securities Services as a Forex trading assistant.
In 2007, he became a consultant at CSC, a global technology company, before moving to Société Générale Corporate and Investment Banking in 2008 as a special operations manager.
Melchior Koba
She's transforming local food supply chains by blending innovation with last-mile distribution, reshaping the informal economy and increasing access to essential products.
Kenyan entrepreneur Khadija Mohamed-Churchill is using technology to address social challenges as the founder and CEO of Kwanza Tukule, a company that specializes in distributing affordable, nutritious food.
Founded in 2018, Kwanza Tukule leverages modern technology and a local distribution network to make healthy food accessible to a large low-income population, particularly street vendors, a key segment of the local informal economy.
The company develops food products tailored to the needs of micro-entrepreneurs. It offers innovative ordering methods via a mobile app, WhatsApp, or a call center, and organizes optimized delivery to ensure a fast and reliable service, guaranteeing the continuity of its clients' businesses.
Kwanza Tukule currently has 4,755 business clients and employs 80 people. The company plans to expand in both Kenya and Uganda and will introduce credit solutions to further support its merchants.
After earning a bachelor's degree from the University of Nairobi, Khadija Mohamed-Churchill went on to Imperial College London, where she completed a master's degree in business administration in 2010. Her professional career began in 2005 as a project manager at Standard Chartered Bank in Kenya. In 2007, she became the bank's head of change in London.
In 2010, she joined Infosys Consulting in London as a senior consultant. After a sabbatical from 2017 to 2018, she launched Kwanza Tukule.
Melchior Koba
Driven by the rapid growth of mobile phones, Africa has transformed the device into a powerful banking tool. Millions of people who were previously excluded from the financial system now have access to transfer, savings, and payment services. This profound and quiet shift is reshaping economies and challenging traditional financial models.
Over the past 15 years, mobile money has become one of the most transformative forces in Africa’s financial system. The service, which allows people to send, receive, and store money with a mobile phone, has reshaped financial habits across the continent.
Traditional banking still struggles to reach many Africans—57% of the population had no bank account in 2021, according to the report Digital Banking in Sub-Saharan Africa by BPC and Fincog. Mobile money has filled much of that gap, expanding at a rapid pace.
Launched in Kenya in 2007, the service counted 57 million subscribers in sub-Saharan Africa by 2012. By 2021, the figure had risen to 621 million. In 2024, Africa reached 1.1 billion registered accounts, representing 53% of the global total, and processed 81 billion transactions worth $1.1 trillion, or 66% of worldwide value, according to GSMA.
What began as a simple money transfer tool has become a major industry. Mobile money now drives growth, expands financial inclusion, and creates socio-economic opportunities. From Nairobi to Dakar, Abidjan to Lagos, mobile phones have become pocket banks, reshaping access to financial services and making a measurable contribution to GDP and daily life.
Economic weight
The impact is no longer marginal. GSMA data show that in 2023, the combined GDP of countries offering mobile money services was $720 billion higher than it would have been without them. In sub-Saharan Africa, the sector’s direct contribution rose from $150 billion in 2022 to $190 billion in 2023. Regional disparities remain, but the overall trend is one of deepening economic influence.
 Source: GSMA
Source: GSMA
“Mobile money had a greater impact on the GDP of West African countries than elsewhere on the continent. This is evident when comparing countries in Sub-Saharan Africa (Figure 12). In Benin, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea Bissau, Senegal and Liberia, mobile money contributed more than 5% to GDP. In East Africa, mobile money contributed more than 5% to the GDPs of Kenya, Rwanda, Uganda and Tanzania. Elsewhere in Sub-Saharan Africa, mobile money’s contribution to GDP has been mixed. In Central Africa, Cameroon, Congo and Gabon each saw a contribution between 5% and 8%. In Southern Africa, where mobile money is less established, contributions to GDP generally remain lower than 5%. As mobile money use grows across Sub‑Saharan Africa, its impact on national GDP may also rise over time”.
Tangible social impact
Beyond the macroeconomic figures, mobile money is changing lives. In Mali, startup OKO, working with Orange Money, has helped more than 41,000 farmers buy index insurance against climate shocks. In Ethiopia, partnerships between Lersha, Telebirr, and M-PESA provide group loans and crop insurance to strengthen food security. In East Africa, pay-as-you-go (PAYG) solar kits, paid for via mobile, are accelerating rural electrification.
These examples show why GSMA links mobile money to 15 of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals, from poverty reduction and gender equality to education access.
The service has expanded far beyond transfers. Today, Africans can save directly from their phones, access credit, buy insurance, pay school fees and utility bills, and make merchant payments. This diversification has effectively turned mobile phones into pocket-sized banks for populations often living far from traditional branches. In 2024, every region of Africa recorded growth in mobile money usage.
Regional Growth in Africa (2024)
|
Region |
Services |
Registered Accounts |
30-day Active Accounts |
Transactions |
Value of Transactions |
|
Sub-Saharan Africa |
N/A |
1.1 billion (+19%) |
286 million (+12%) |
81 billion (+22%) |
$1.1 trillion (+15%) |
|
West Africa |
74 |
485 million (+21%) |
97 million (+13%) |
22 billion (+15%) |
$357 billion (+5%) |
|
East Africa |
57 |
459 million (+15%) |
149 million (+12%) |
52 billion (+25%) |
$649 billion (+23%) |
|
Southern Africa |
15 |
27 million (+19%) |
4 million (-20%) |
543 million (-9%) |
$6 billion (+4%) |
|
Central Africa |
19 |
104 million (+24%) |
32 million (+13%) |
7 billion (+22%) |
$83 billion (+7%) |
|
North Africa |
13 |
25 million (+24%) |
3 million (+44%) |
262 million (+63%) |
$10 billion (+53%) |
Source: Ecofin Agency
Market leaders
The rise of mobile money has spurred heavy investment from telecom operators, with a few clear leaders now dominating the market.
Orange
Launched in Côte d’Ivoire in 2008, Orange Money has grown into one of Africa’s biggest financial inclusion platforms, with 40 million active users and €164 billion in transactions recorded in 2024. The service, now present across 16 African markets, processes 25 million transactions a day.
Speaking at GITEX Morocco on April 15, 2025, Jérôme Hénique, then CEO of Orange Middle East and Africa, said the value of Orange Money transactions more than doubled between 2021 and 2024, rising from €46 billion to €164 billion. The platform now channels up to €700 million in transfers each month. Orange has also expanded into savings and credit through Orange Bank Africa, which counted 1.7 million customers in 2024, alongside partnerships with local banks in markets where its own bank is absent.
MTN
MTN’s mobile money service has also expanded rapidly. By 2024, MTN MoMo reported over 63 million active monthly users across 14 of its 16 markets. Customers executed more than 20 billion transactions worth over $320 billion, according to the company. Like Orange Money, MTN MoMo offers a full suite of financial services including payments, e-commerce, insurance, loans, and money transfers.
Airtel Africa
Bharti Airtel’s African subsidiary reported 38 million Airtel Money customers in 2024, up 20.7% year-on-year across 14 markets. The platform offers money transfers, wallet payments, microloans, savings, and international remittances. It generated $837 million in revenue in 2024, a 32.8% increase at constant exchange rates compared with $692 million in 2023.
Vodacom Group
Vodacom, including its Safaricom unit, reported 87.7 million mobile financial services customers for the fiscal year ending March 2025. Its VodaCash and M-Pesa platforms, active across eight markets, processed $450.8 billion in transactions during the year, up 18.3%. Financial services revenue rose 17.6% on a normalized basis, representing 11.6% of group service revenue. Safaricom alone generated 22.6 billion rand from financial services.
M-Pesa, the cornerstone of Safaricom’s business in Kenya and Ethiopia, recorded revenue of 161.1 billion Kenyan shillings ($1.2 billion) from 37.1 million users.
Obstacles ahead
Despite mobile money’s sweeping impact on Africa’s economies and millions of lives, several challenges continue to hold back its full potential.
One is the persistent mobile ownership gap. In low- and middle-income countries, women are still 8% less likely than men to own a phone—a prerequisite for using mobile financial services. The gap varies by country: in Ethiopia, more than one-third of women still lack a handset.
The gender divide also extends to mobile money account ownership. GSMA data show that in most countries surveyed in 2023, little or no progress was made in narrowing the gap in 2024. In some, the divide has stagnated for a third straight year. In Senegal, account ownership is now almost universal for men, but more than a quarter of women remain excluded. Nigeria showed modest improvement: the gender gap shrank from 46% to 41%, with account ownership rising among both men and women in 2024.
Low levels of digital financial literacy also limit the use of advanced mobile money features. GSMA noted that in 2024, gender gaps persisted even for basic services such as deposits, withdrawals, and peer-to-peer transfers, as well as for ecosystem transactions and related financial products.
Among adults who had used mobile money, women in nearly every surveyed country were less likely than men to rely on the service. In Senegal, only 5% of women reported receiving wages or salary payments through mobile money, compared with 16% of men. In Nigeria, just 25% of women said they received client payments this way, against 41% of men. In Kenya, half of women respondents had made a merchant payment by phone, compared with two-thirds of men.
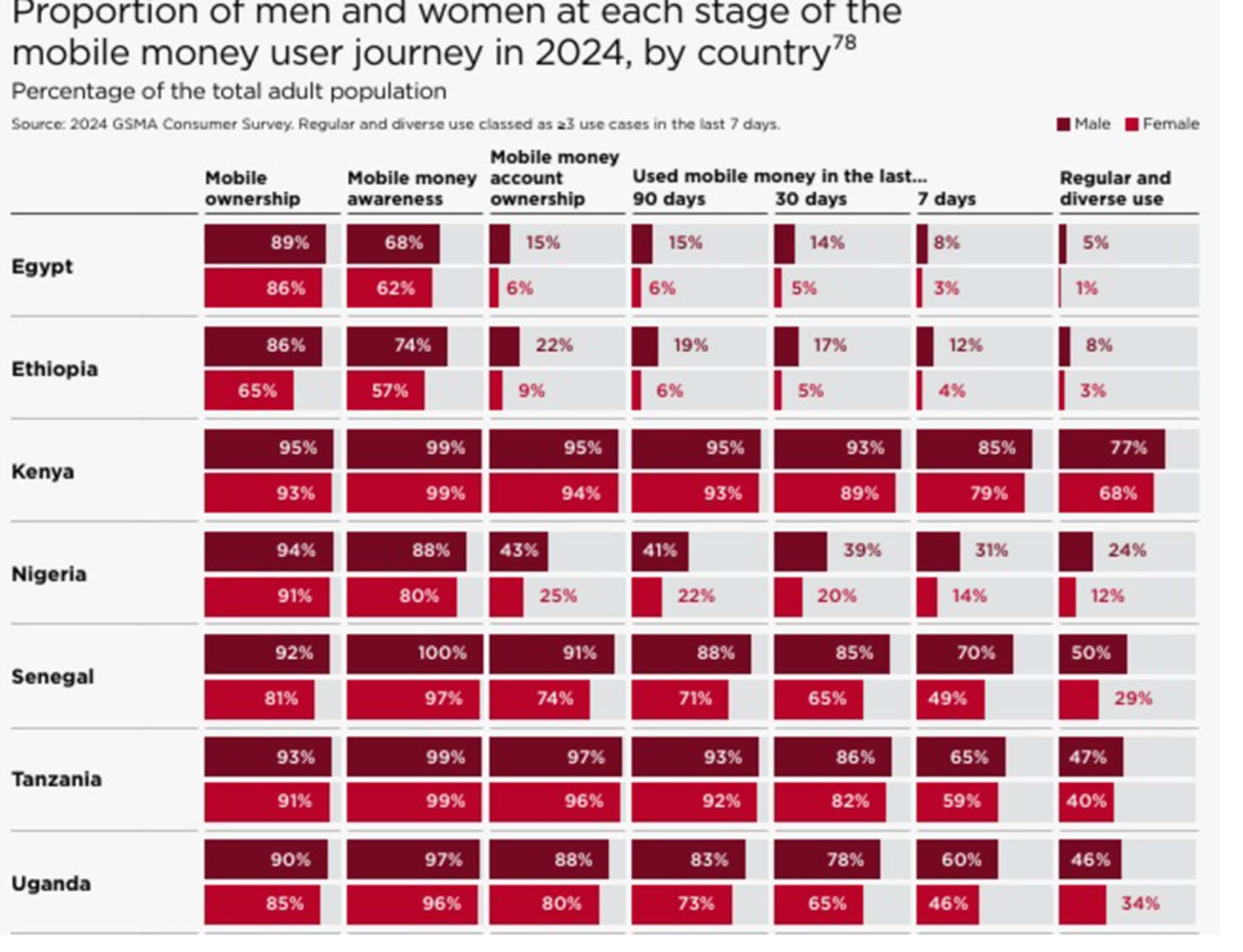 Source : GSMA
Source : GSMA
As global financial ecosystems become increasingly interconnected, the risk of fraud has risen. In many countries across Africa, Asia, and Latin America, mobile money has been affected by identity theft, insider fraud, cyberattacks, and fraud by agents. GSMA notes that each threat breaks down into specific types, such as social engineering, man-in-the-middle attacks, and malware.
Yet responses remain uneven. According to GSMA, more than 70% of mobile money providers say law enforcement is ineffective in tackling fraud due to limited technical skills, insufficient resources, and corruption. Regulators, meanwhile, are seen as only moderately supportive in the fight against mobile money crime.
An industry set to carry more weight
Mobile money is now recognized as a structural driver of Africa’s development. No longer just a tool for inclusion, it has become an integrated industry able to generate revenue, strengthen household resilience, and support strategic sectors such as agriculture and energy.
With transactions surpassing $1 trillion in 2024, mobile money has cemented itself as a pillar of Africa’s digital economy. Its future will rest on two priorities: achieving full international interoperability to make cross-border transfers seamless between telecom operators, and building greater trust through stronger regulation and tighter fraud prevention.
Muriel Edjo
Faced with a shortage of doctors and the isolation of African villages, telemedicine is opening a new path. Using digital technology, local startups are developing solutions to bring medical care closer to rural populations that have long been left behind.
In sub-Saharan Africa, about 57% of the population—nearly 700 million people—lives in rural areas. In some countries like Burundi, this proportion exceeds 85%. These isolated regions often face a shortage of health infrastructure, a lack of qualified professionals, and limited access to specialized care. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the region is expected to have a shortage of 6.1 million healthcare workers by 2030, a 45% increase from 2013. This scarcity leads to preventable deaths, delayed diagnoses, and increased pressure on urban hospitals.
Startups Innovate to Bridge the Gap
Telemedicine, which includes remote consultations, monitoring, and expert support, uses technology to provide care from a distance. It helps overcome geographical and logistical barriers, offering a practical solution for communities far from health centers.
Several African startups are emerging in this field. In Kenya, Ilara Health provides affordable diagnostic tools to rural clinics, enabling doctors to perform high-quality examinations without extensive infrastructure. A similar approach is being developed in Cameroon by Waspito, which connects patients and practitioners via a mobile app, offering video consultations, medication delivery, and access to lab tests.
In remote villages in Chad, Telemedan is installing solar-powered telemedicine kiosks, ensuring consultations are accessible even where infrastructure is lacking. In Ghana, Diagnosify uses artificial intelligence for the early detection of skin diseases, directing patients to dermatologists and extending access to specialized care in the most isolated areas.
Governments are also beginning to incorporate e-health into their public policies, often with support from partners like the World Bank and the WHO. The digitization of medical records, official teleconsultation platforms, and online training for health workers are supplementing local initiatives to strengthen healthcare systems sustainably.
Challenges of Telemedicine in Rural Africa
Telemedicine in Africa's "medical deserts" faces several obstacles. Connectivity remains a significant issue in many areas. In 2024, only 23% of people in rural Africa used the internet, compared to 57% in urban areas, according to the International Telecommunication Union. In addition to this digital divide, challenges include a lack of training for healthcare professionals and patients, the persistence of traditional beliefs that hinder technology adoption, and the absence of strong frameworks to protect medical data.
Despite these difficulties, the potential is enormous. Telemedicine offers an opportunity to redesign healthcare, relieving pressure on urban hospitals and bringing medical services closer to remote areas. It could help reduce health inequalities by guaranteeing every patient, regardless of their location, access to quality medical care. Investing in these e-health startups is a crucial lever. These young companies, with their local focus, are designing solutions tailored to on-the-ground realities: apps for basic phones, solar-powered kiosks, and platforms in local languages. By filling the gaps left by traditional structures, they are shortening the distance between practitioners and patients and providing a vital lifeline for the most isolated populations.
Samira Njoya
-
Morocco's CNSS launches $4.4M tender for cybersecurity upgrade
-
Move follows major data breaches impacting millions of users
-
Project aims to modernize systems, ensure legal data protection
Morocco's National Social Security Fund (CNSS) has launched an international tender worth 40 million dirhams ($4.4 million) to strengthen its cybersecurity following a series of cyberattacks that compromised sensitive data. The initiative aims to modernize the institution's digital systems and secure the personal information of millions of employees and affiliated companies.
The tender is divided into two parts. The first, valued at 6 million dirhams, is for accelerating the institution's overall digital transformation. The second, estimated between 19.99 and 39.98 million dirhams, is for acquiring specialized expertise, implementing advanced technical solutions, and deploying security systems that comply with Law 09-08 on personal data protection.
The tender's specifications impose strict guarantees, including the destruction of files after contracts are executed, a ban on unauthorized data use, and the adoption of agile methodologies to ensure the effectiveness of the security measures.
This initiative comes amid the growing vulnerability of Moroccan digital infrastructure to cyber threats. A massive attack on April 8 by the group Jabaroot compromised the data of nearly 500,000 companies and two million employees. A second intrusion reported in September highlights the persistent system vulnerabilities and the lack of a robust, proactive security architecture, despite the CNSS's strategic importance to the country's social safety net.
The project is designed to significantly boost the CNSS's digital resilience and restore public trust. By securing its systems, the institution can ensure more reliable data processing and the continuity of essential services such as mandatory health insurance, which covers low-income households and non-working individuals. This effort will also supplement the government's ongoing legal and regulatory actions to protect public and private infrastructure from rising cyber threats.
Samira Njoya
-
Côte d'Ivoire secures $95M UAE funding for digital projects
-
Funds target AI, cloud, and civil service modernization
-
Deal boosts Abidjan-Abu Dhabi tech and governance ties
Côte d'Ivoire's Minister of Public Service and Administrative Modernization, Anne Désirée Ouloto-Lamizana, has secured a $95 million funding commitment from the United Arab Emirates. A letter of intent is scheduled to be signed by mid-October, with the funds expected to be released by the end of the year, the Ivorian Press Agency reported on Sunday, September 14.
The funding, which will be managed by a joint steering committee, is earmarked for several key projects. These include the construction of a modular data center and a sovereign cloud, the creation of a center of excellence for artificial intelligence and innovation, and the enhancement of the Integrated Management System for Civil Servants and State Agents (SIGFAE) through the integration of AI-powered features. The objective is to accelerate the digitalization of government services while improving human resource management and public service quality.
This initiative is part of the Ivorian government's broader effort to strengthen governance and position the country as a major technological player in West Africa. It also highlights the growing cooperation between Abidjan and Abu Dhabi in strategic sectors like digital innovation, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence.
If the project materializes, it could reinforce Côte d'Ivoire's role as a hub for administrative technology and innovation in the region. It is also expected to foster talent development and professional integration for young people, including in the UAE. However, the project's success will depend on the rigorous implementation of the announced reforms and the country's ability to secure and sustain these infrastructures in the face of ongoing digital sovereignty and cybersecurity challenges.
Samira Njoya
- Cameroonian startup Quicky Africa launched "Quicky Services," a mobile application connecting clients with service providers across multiple sectors.
- The app, available on iOS and Android, has over 500 downloads and emphasizes vetted professionals and transparent pricing.
- The platform faces challenges including logistical reliability, quality control, and coverage in less dense areas.
As on-demand mobile services gain traction, Cameroonian startup Quicky Africa has introduced a suite of applications. Its success will depend on its ability to retain both end-users and service providers.
Quicky Services, a mobile application developed by Quicky Africa, aims to link service providers and clients across various sectors. The offering encompasses transport, maintenance, repair, wellness, and lifestyle services. Ossoe Pierre Harisson and Liliane Mitambo launched the Yaoundé-based startup in 2025.
Its solution includes a mobile application accessible on both iOS and Android platforms, where it has garnered over 500 downloads, according to Play Store data. Users create accounts by providing personal information; upon account validation, they access diverse service providers in the aforementioned fields.
The startup claims to prioritize reliability by selecting professionals whose profiles undergo background verification, which enhances user trust. Service prices are presented unequivocally at the time of booking and, importantly, during payment. Regarding payment methods, the application integrates mobile money from telecom networks, but cash payments are also permitted.
The user experience incorporates geolocation, proximity-based provider selection, and features for comparing offers. The iOS version specifically mentions the distance between the requested address and each provider. However, the solution still faces challenges including logistical reliability, quality control, and coverage in less dense areas.
This article was initially published in French by Adoni Conrad Quenum
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
• Algiers airport to deploy AI systems from December 2025
• Upgrades include facial recognition, smart gates, contactless travel
• Plan aims to make airport a major African and global hub
Algerian authorities plan to integrate artificial intelligence (AI) into services at Algiers International Airport starting this December. The modernization effort aims to elevate the airport's service quality to meet international standards.
Mokhtar Mediouni, CEO of the Algiers Airport Services and Infrastructure Management Company (SGSIA), announced the initiative on Sunday, September 14, at a press conference reported by the Algeria Press Service (APS). The upgrades will include facial recognition, body scanners, contactless travel, and smart gates. Mediouni said these technologies will optimize the use of airport spaces like halls, parking lots, and boarding areas while simplifying passenger entry and exit procedures.
This digitalization effort is part of a broader strategy to transform Algiers International Airport into a "regional hub". The goal is to leverage Algeria's strategic location near Europe, positioning the airport as a major transit point for global passenger and cargo traffic. The ambition is also to elevate the airport to a leading African hub, serving as a gateway for travelers from the continent to Asia, the Americas, and Europe while offering modern services.
Algiers International Airport is the country's main airport. Authorities projected it would handle around 10 million passengers in 2024, following 7.3 million in 2023 and 6.5 million in 2022. The airport is also central to the African and global expansion strategy of the national airline, Air Algérie.
In April 2025, the state-owned airline announced the launch of new direct routes to six destinations in Africa and Asia starting this winter. The new routes include Guangzhou (China), Kuala Lumpur (Malaysia), N'Djamena (Chad), Zanzibar (Tanzania), Libreville (Gabon), and Addis Ababa (Ethiopia). By the end of 2024, Air Algérie was already serving 25 African destinations with a passenger flow of 179,000 people.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
Janngo Capital has announced an investment in Jobzyn, a Moroccan startup that utilizes technology to simplify, clarify, and expedite the hiring process. The move is set to accelerate Jobzyn’s mission to deliver a next-generation hiring experience for both employers and job seekers across Africa and the MENA region.
With Janngo Capital’s backing, Jobzyn is now positioned to scale its solutions across the continent, offering a more transparent, data-driven, and inclusive model for employment that could play a critical role in addressing Africa’s growing demographic and economic challenges.
The investment also aligns with Janngo Capital’s broader mandate of building, growing, and financing pan-African digital champions that combine economic performance with inclusive social impact.
The National Communications Authority (NCA) of Ghana, in partnership with Togo’s Autorité de Régulation des Communications Électroniques et des Postes (ARCEP), held a three-day Border Coordination Meeting aimed at strengthening cross-border cooperation in the management of telecommunications services from September 9-11.
The meeting, held at the NCA Tower in Accra, brought together regulators and mobile network operators (MNOs) from both countries to address cross-border frequency interference and improve service quality for consumers living along the Ghana-Togo frontier.
The outcome is expected to not only reduce interference but also strengthen cross-border collaboration as the region pushes toward greater connectivity and digital inclusion.
More...
Bertin Nahum, a French entrepreneur of Beninese descent, is a co-founder and CEO of Quantum Surgical, a medical robotics company based in Montpellier.
Founded in 2017, Quantum Surgical designs and develops robotic systems for interventional surgery. The company's research focuses on improving cancer treatments, particularly for liver cancer, which continues to have a high mortality rate.
Quantum Surgical's flagship product is Epione, a robotic platform for image-guided percutaneous procedures. It enables targeted ablation of liver tumors with a high degree of precision. This technology is designed to improve success rates and broaden access to this form of treatment.
Epione incorporates artificial intelligence tools to optimize needle placement and surgical planning. It is marketed to specialized hospitals and interventional surgery practitioners, paving the way for wider use of robot-assisted surgery.
Quantum Surgical has received several awards, including the Prix Galien in 2022, a prestigious honor in the field of biopharmaceutical research. In 2023, the company was selected for the French Tech 2030 program, which supports emerging innovation leaders in France.
Nahum’s first company was Medtech SA, which developed and commercialized medical and surgical assistance technologies. Established in 2002, it was acquired by Zimmer Biomet in 2016.
An engineer who graduated from the National Institute of Applied Sciences in Lyon in 1994, Nahum also holds a master's degree in robotics from Coventry University in the United Kingdom.
Melchior Koba
After working for several years in financial institutions, she shifted her focus to entrepreneurship. Her goal is to make it easier for Kenyans to finance their projects.
Janet Kuteli, a Kenyan entrepreneur in the financial sector, is the founder and CEO of Fortune Credit, a Nairobi-based microfinance institution.
Founded in 2014, Fortune Credit aims to support marginalized populations and small business owners who are excluded from traditional banking. This includes those in the informal sector, such as motorcycle taxi drivers. The company offers credit and insurance services to promote economic empowerment for rural Kenyans.
Fortune Credit leverages data from mobile payment platforms, such as M-Pesa, to assess borrowers' credit profiles and offer loans tailored to the needs of self-employed workers. This mechanism has enabled many moto-taxi drivers to secure financing to purchase their own vehicles, turning their work tools into a sustainable asset.
The institution also provides agricultural loans to smallholder farmers, entrepreneurs, and cooperatives. These financial solutions help with the purchase of inputs, equipment, and agricultural business development.
Fortune Credit was selected as one of the ten finalists for the 2025 Africa's Business Heroes competition. The company serves over 23,000 active clients, has disbursed more than 40,000 loans since its inception, and collaborates with over twenty international partners.
Kuteli earned a bachelor's degree in accounting in 2001 and a master's degree in business administration in 2012 from Kenyatta University. She began her career in 2007 at the Co-operative Bank of Kenya, where she served as Deputy Head of the Microcredit Department and later as Branch Manager for the Embakasi and Kawangware branches. From 2013 to 2014, she managed the Kenyatta branch of the National Bank of Kenya.
Melchior Koba
• Cameroon launches digitalization program to modernize local governance
• 240 of 374 municipalities signed on; key challenges remain
• Goal: boost transparency, online services, and investment appeal
The United Councils and Cities of Cameroon (UCCC) unveiled its "Program for the Digitalization of Councils and Cities" (PDCV) in Yaoundé on Thursday, September 11. The initiative aims to modernize local governance by providing municipalities with shared digital tools and online services for citizens.
The PDCV is structured around four main pillars: a shared digital platform for municipalities and the UCCC, the creation of an integrated suite of digital services, enhanced digital skills for municipal staff, and program coordination and monitoring. The stated goal is to make local governments more transparent, efficient, and better connected with their constituents.
The project is part of Cameroon’s broader digital transformation strategy, which includes the gradual dematerialization of administrative procedures and the interconnection of public services. As part of this effort, 374 municipal websites have already been developed. However, for these sites to become fully operational, each municipality must sign a memorandum of understanding with the UCCC. So far, 240 municipalities have taken this step, while 134 have not yet signed, according to the association.
Ultimately, the PDCV is expected to increase the visibility of local governments, facilitate citizens' access to online administrative services, and make regions more attractive to investors. However, several challenges remain, including inadequate ICT infrastructure, a limited internet penetration rate of 41.9% as per DataReportal, a lack of skilled personnel, energy instability, and insufficient municipal financial resources. The program's success also hinges on the effective implementation of the General Code of Decentralized Territorial Collectivities, which allocates 15% of state revenues to decentralization.
Cameroon faces significant challenges in digital governance. According to the 2024 United Nations E-Government Development Index, the country ranks 155th out of 193, with an index score of 0.4294, well below the global average of 0.6382. This program represents a strategic opportunity to bridge this gap and firmly establish Cameroonian administration in the era of smart digital governance.
Samira Njoya
The solution connects North African consumers with popular Turkish clothing and lifestyle brands. The Moroccan startup recently raised $1 million to support its growth and expand its reach in the region.
Justyol is a Moroccan online platform that provides North African consumers with access to Turkish clothing, lifestyle, and accessory brands. It was launched by a Casablanca-based startup, founded in 2022 by Ahmed Badran, Ahmed Rashed, and Anas Ahmed. In September 2025, the startup raised $1 million in September 2025 to support its growth.
"We are building more than just a platform; we are creating the infrastructure that will define the future of cross-border commerce in North Africa, serving hundreds of thousands of customers with unprecedented access to global products at competitive prices," said Ahmed Badran.
The company's mobile application is available on both iOS and Android and has been downloaded more than 100,000 times on the Play Store. The platform offers a wide selection of popular Turkish dresses, jackets, and pants. Justyol frequently provides significant discounts to make the items more accessible and also offers delivery services.
"Our platform is your gateway to premium Turkish fashion and an ever-expanding selection of lifestyle products. We are proud to provide superior quality products and exceptional service to our valued customers," the platform explains.
By positioning itself as a bridge between Turkey and North Africa, the startup is addressing a growing demand for international products and a need for greater diversity in local markets. Its business model could inspire other startups to explore similar niche markets.
Adoni Conrad Quenum















