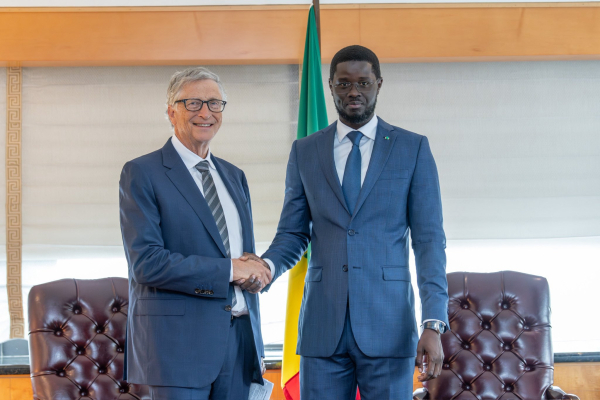
- The Gates Foundation pledged more than $10 million to support Senegal’s New Deal technologique, its national digital strategy launched in February 2025.
- The partnership will fund a universal digital ID, an AI hub for health and agriculture, and a Delivery Unit to oversee project transparency and efficiency.
- Senegal’s digital strategy requires $2 billion, of which $155 million still needs to be secured.
Senegal signed a $10 million-plus partnership with the Gates Foundation on September 24 to accelerate its national digital strategy, known as the New Deal technologique. The agreement was finalized on the sidelines of the 80th United Nations General Assembly in New York, the state broadcaster RTS reported.
Le Président a reçu en audience M. @BillGates, Président de la Gates Foundation.
— Présidence Sénégal (@PR_Senegal) September 24, 2025
Cette rencontre a permis de conclure un partenariat stratégique de plus de 10 millions de dollars pour accélérer le #NewDealTechnologique et faire du Sénégal un hub africain d’innovation numérique. pic.twitter.com/kBJk37Sigr
The program, launched in February 2025 by President Bassirou Diomaye Faye, aims to transform public services, strengthen digital sovereignty, and establish Senegal as a regional technology hub by 2034.
The deal provides for the rollout of a universal digital identity system, the creation of an artificial intelligence hub focused on health and agriculture, and the establishment of a Delivery Unit to ensure project transparency and efficiency.
The partnership follows an initial meeting between Bill Gates and President Faye during the 79th UN General Assembly, when both sides agreed to expand cooperation in areas including AI-assisted agriculture, sanitation, and digital innovation across strategic sectors.
Senegal budgeted CFA1,105 billion (about $2 billion) for the New Deal technologique. Authorities have already identified CFA950 billion, leaving CFA155 billion still to be mobilized.
Officials expect the Gates Foundation’s contribution to accelerate the implementation of priority projects, expand inclusive digital services for citizens, and attract additional private investment into Senegal’s tech ecosystem.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
Amid growing pressure for companies to balance performance and responsibility, she offers a technological approach to transform business practices and create tangible environmental impact.
Souha Bejaoui, a Tunisian engineer and entrepreneur, has won the top prize at the POESAM Tunisia 2025 (Orange Social Entrepreneur Prize in Africa and the Middle East). Bejaoui is the co-founder and CEO of ProVerdy, a startup specializing in climatetech.
Founded in 2024, ProVerdy develops technology solutions that enable companies to measure, manage, and reduce their environmental impact. Its platform provides precise tracking of carbon footprints and offers tailored recommendations to curb greenhouse gas emissions.
ProVerdy utilizes advanced artificial intelligence to simplify carbon accounting and deliver actionable data, helping businesses cut emissions and optimize costs. The platform also streamlines compliance with environmental regulations and simplifies reporting, allowing organizations to monitor their ecological transition progress.
The startup aims to "become the reference platform for measuring and managing the overall environmental impact of companies, while helping them mitigate and adapt to the effects of climate change."
Bejaoui holds a degree in scientific economics and management, earned in 2016 from the Polytechnic Institute of Tunisia. Following graduation, she joined LOGIDAS, a Tunisian industrial digitization firm, as a technical-functional consultant. In 2019, she moved to the French company Vneuron Risk & Compliance, where she served successively as a senior project manager and head of the quality and assurance department in Tunisia.
Melchior Koba
As both a scientific researcher and a digital innovator, Frédéric Ngaba explores artificial intelligence applications to design tools that solve real-world problems, especially in the education sector.
Frédéric Ngaba, a mathematician and artificial intelligence researcher, has won the top prize at the POESAM Cameroon 2025 (Orange Social Entrepreneur Prize in Africa and the Middle East). Ngaba is the co-founder and CEO of OSIA Technologies, a Cameroonian educational technology startup.
Founded in 2022 by Ngaba and Adidja Nezang Sale, OSIA Technologies developed a generative artificial intelligence solution dedicated to academic and career guidance. The platform allows users to submit their school results and receive a detailed analysis.
The OSIA solution integrates personalized psychotechnical tests to evaluate students' aptitudes and competencies. It also generates follow-up analytics to facilitate decision-making. Over 1,000 interconnected schools currently use OSIA's network to exchange exam materials and prepare students for year-end tests.
Full access to the platform costs 3,000 CFA francs (about $5) for users in Cameroon and 10 euros for international users. The startup already boasts over 13,500 active subscribers across 23 schools in Cameroon.
Ngaba holds a doctorate in analytical mathematics, which he earned in 2021 from the University of Yaoundé 1. Between 2020 and 2024, he worked as an affiliate manager for 1XBET in Cameroon while also serving as deputy manager for local cultural promoter Planet Saladin.
Melchior Koba
Designed to foster the emergence of software developers in remote or underserved areas, the solution aims to become a key player in technology-driven education across Africa.
Nigerian Startup Launches AI-Powered Mobile Coding Platform Efiwe for Underserved Youth
Efiwe is a mobile-first, artificial intelligence-powered platform designed to make coding accessible to everyone directly from a smartphone. The solution, which aims to become a key player in technology-driven education across Africa, was launched in August 2025 by founder Chidi Nwaogu.
"We believe coding education should be fun, accessible, and effective – and that's what Efiwe delivers," Nwaogu stated. "With over 33 languages available and a fully offline mode, we are breaking down barriers and giving people from all backgrounds the chance to learn how to code. Whether you’re a complete beginner or an aspiring developer, Efiwe is here to help you grow."
The initial modules cover HTML, with CSS and JavaScript lessons planned for release soon. The platform's curriculum is structured to guide users from scratch, enabling them to build a professional website without needing a computer or additional software. It also offers hundreds of structured, interactive challenges with real-time feedback.
In Nigeria, where many people rely solely on a smartphone and broadband access is uneven, Efiwe directly addresses the need for advanced digital skills among youth. By lowering financial and technical barriers, the platform provides access to high-demand skills without the investment in expensive hardware.
However, the startup faces several hurdles. These include ensuring the pedagogical content remains relevant, maintaining the quality of the AI experience, securing recognition for its certifications, and guaranteeing the offline access sufficiently covers more advanced technologies.
Efiwe has the potential to become a central figure in African edtech by fostering the emergence of developers in remote or underserved areas and boosting employability in the digital sector.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
Docotela which means "doctor" in the Zulu language connects patients and providers online.
South African telehealth platform Docotela is striving to make medical access simpler, faster, and more affordable through an intuitive online interface. Founded in 2023 by entrepreneur Dineo Lioma, the service allows patients to consult with physicians registered with the Health Professions Council of South Africa (HPCSA) from their phone or computer, eliminating the need for travel.
"With our cutting-edge platform, we bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers, delivering convenient and reliable medical services right to your fingertips," the startup stated. "We believe that by making healthcare more accessible and convenient, we can help people lead healthier, happier lives and ultimately extend their lifespan."
To use Docotela, a patient schedules a time slot, pays online, and receives a video link for the consultation. If medically necessary, the physician can then issue a prescription, a medical certificate, and a medication voucher. The platform offers various subscription plans, including individual and family options, alongside single-session consultations. It also provides mental health support, featuring online sessions with certified professional counselors for anxiety, depression, stress, and other emotional well-being issues.
The healthtech firm seeks to provide accessible consultations even in rural areas, contingent upon internet connectivity. By offering monthly subscriptions with unlimited consultations, Docotela helps users better manage healthcare expenditures.
However, the startup faces several key challenges. These include ensuring the diagnostic reliability of telemedicine, particularly for complex cases, guaranteeing the protection of personal data, and securing adequate internet access in remote regions. Furthermore, Docotela must convince South African health authorities, medical aids, and insurers to formally recognize and cover online consultations.
Adoni Conrad Quenum
-
Kenya central bank launches cybersecurity center for banking sector
-
BS-SOC to handle threat intel, forensics, incident response
-
Move follows sharp rise in cyber fraud, $14.7M exposed in 2024
The Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) announced on Monday, September 22, 2025, the establishment of the Banking Sector Cybersecurity Operations Centre (BS-SOC) to strengthen the financial system's resilience against rapidly evolving cyber threats.
"The successful implementation of this initiative requires the full collaboration and cooperation of all stakeholders. This partnership is imperative to enhance the resilience of the banking sector against the significant and persistent challenges posed by sophisticated cyber threat actors," the Central Bank said in a statement.
The BS-SOC is integrated into the CBK’s Cyber Fusion Unit and will provide essential services, including threat intelligence, incident response, digital forensics, and cyber investigations.
All regulated financial institutions, encompassing commercial banks and payment service providers, must now report security incidents within prescribed timelines. They must also comply with existing directives and new 2024 requirements concurrently, pending the full harmonization of the regulatory framework.
The center aligns with the 2024 Critical Infrastructure and Cybercrime Regulation and the CBK’s 2024–2027 Strategic Plan. The move follows a sharp rise in cyberattacks targeting the country's financial ecosystem.
In its Financial Sector Stability Report published in August 2025, the Central Bank noted that reported bank fraud cases more than doubled in 2024, rising from 153 to 353. The value exposed reached 1.9 billion Kenyan shillings ($14.7 million), while actual losses nearly quadrupled, hitting 1.5 billion shillings.
By creating the dedicated operational center, the CBK aims to enhance the country’s ability to counter intrusions, limit financial losses, and restore public trust in the banking system. The BS-SOC is also expected to foster increased cooperation among banks, payment service providers, and regulatory authorities, contributing to the overall stability and security of Kenya's financial sector.
Samira Njoya
-
Algeria’s UFC hosts National Digital Education Week, Sept 23–30
-
University built 683 online courses, 68 platforms, trained 800 staff
-
Agreement with Arabic Language Council grants access to 12,000 e-books
Algeria’s University of Continuing Education (UFC) launched its National Digital Education Week on Tuesday, September 23, 2025, an event running until September 30 to showcase its advancements in digital transformation. The university regards digitalization as a "strategic choice for the Algerian university," according to the state-run Algérie Presse Service (APS).
In his address, UFC Rector Yahia Djaafri stated that the university has already trained more than 800 instructors in information and communication technologies (ICT). This year, the UFC also finalized the design of 683 online courses, including 120 in English, and now operates 68 digital platforms for its students.
The first day of the event was also marked by the signing of a cooperation agreement with the High Council of the Arabic Language (HCLA). The pact will grant UFC students access to the HCLA’s digital library, which contains over 12,000 literary works.
Djaafri emphasized that investing in digitalization "strengthens quality and innovation, and opens up broad prospects for partnership with economic and technological institutions, positioning the university as a fundamental player in building a knowledge-based society."
The UFC's push aligns with a broader national project to digitize higher education. In January, Minister of Higher Education and Scientific Research Kamel Baddari stated during a visit to the University of Oran 1 that the "digitalization of universities has become a reality and is beginning to yield results, realizing its general principle of simplification and efficiency," APS reported.
In April 2024, a report presented to the Council of Ministers highlighted notable progress in developing management methods for university institutions and modernizing student services. These developments are aimed at improving student living conditions and rationalizing public expenditure in the sector.
Isaac K. Kassouwi
-
Government to launch Morocco Digital for Sustainable Development at UNGA
-
Initiative backed by UNDP to strengthen digital governance and AI adoption
-
Morocco ranks 4th in Africa on UN e-government index, above global average
Morocco will officially launch an Arab-African center of excellence in artificial intelligence and data science during the 80th United Nations General Assembly, which begins on September 23. Backed by the UN Development Program (UNDP), the Morocco Digital for Sustainable Development (D4SD) hub aims to promote inclusive digital transformation across Arab states and African regions.
The initiative stems from a memorandum of understanding signed in July between Morocco and the UNDP, on the sidelines of the National AI Forum. According to the UN agency, the partnership will help countries improve digital public services, encourage responsible AI use, and build institutional and regulatory systems to support digital transformation and sustainable development.
UNDP highlighted Morocco’s leadership in digital governance, AI, and data science. The country ranks 90th worldwide and 4th in Africa in the 2024 UN E-Government Development Index (EGDI), with a score of 0.6841 out of 1, above both the African and global averages. In September 2023, Morocco also launched its “Digital Morocco 2030” strategy to consolidate its progress and accelerate socio-economic development through digital innovation.
The initiative comes as digital benefits remain unevenly distributed across Africa. According to UNDP, countries still face systemic barriers such as weak infrastructure, limited AI capacity, low investment in digital innovation, and uncoordinated regulatory frameworks.
• Botswana’s Lasiwe Boago Robert, founder of Afras Technology, wins POESAM 2025 prizes.
• Startup develops tech solutions in education, agriculture, AI and digital infrastructure.
• Her AI platform Letlotlo la rona links unemployed graduates to paid work programs.
Botswanan entrepreneur Lasiwe Boago Robert, founder and CEO of Afras Technology, has received the Women’s Prize and third prize at the 2025 Orange Social Venture Prize Africa & Middle East (POESAM) in Botswana.
Founded in 2023, Afras Technology develops technology solutions for education, agriculture, digital infrastructure and artificial intelligence. The company said it is working to build a future where technology is created in Africa for Africa, aimed at empowering communities, businesses, and governments through scalable, data-driven innovation.
At the POESAM competition, Robert presented Letlotlo la rona, an AI-powered platform that connects unemployed graduates with public and private initiatives considered strategic by stakeholders. The platform offers paid professional experience and certification to participants.
Alongside her entrepreneurial work, Robert is a research assistant at the Botswana International University of Science & Technology (BIUST), where she earned a degree in pure and applied mathematics in 2022. She also holds a professional certificate in data analysis obtained in 2023 from online learning platform DataCamp.
Before founding Afras Technology, she taught mathematics as a private tutor. In 2023, she joined the Orange Summer Challenge, a three-month internship program run by the Orange Digital Center, and took part in the Digital Makers Challenge, another initiative of the center.
• DeepLeaf, founded in 2023 by Aboulmanadel El Mahdi, wins Orange POESAM Morocco 2025 prize.
• Its AI platform detects over 1,000 plant diseases, pests and deficiencies across 80 crops.
• Startup offers mobile app, drones and API tools to support precision agriculture.
Moroccan entrepreneur and AI specialist Aboulmanadel El Mahdi, founder and CEO of DeepLeaf, has won the first prize of the Orange Social Venture Prize Africa & Middle East (POESAM) Morocco 2025. His startup develops agricultural technology solutions using artificial intelligence.
Created in 2023, DeepLeaf has built machine learning models capable of detecting plant diseases from a simple photo of a leaf or fruit. Its AI platform can identify more than 1,000 diseases, pests, and nutritional deficiencies affecting over 80 major crops.
The system has processed millions of diagnostics worldwide and keeps improving through real-time feedback loops. Its models are tailored to local conditions and updated every two months with new data from experimental sites and new partners.
DeepLeaf also provides drones for crop monitoring and a mobile app for instant detection. It has developed an application programming interface (API) for agritech platforms seeking to integrate crop diagnostics into their services.
Aboulmanadel El Mahdi graduated in computer engineering from the Polytechnic School of Agadir in 2023. That same year, he won first place in the PitchAgriHack competition. In April 2025, he also took the top prize at the GITEX Africa innovation contest.
More...
• Djibouti and Romania discuss cooperation on digital transformation and innovation.
• Talks highlight Romania’s expertise in e-government and strong IT talent pool.
• Partnership could strengthen Djibouti’s digital governance, skills and cybersecurity.
Djibouti’s Minister of Digital Transformation, Mariam Hamadou, met last week with Olivia Toderean, Romania’s new non-resident ambassador to Djibouti, to explore a potential partnership focused on digital development and innovation.
According to the ministry, discussions centered on Romania’s expertise in digital transformation, which could open the way to promising cooperation in supporting Djibouti’s digital growth. Romania ranks 72nd globally in the UN e-government development index, with a score of 0.7636. It also boasts a strong IT talent base, ranking sixth worldwide for certified information technology specialists per capita, ahead of the United States and Russia.
The initiative comes as Djibouti steps up efforts to structure its digital economy. Following the adoption of a digital code in May, the country is now preparing a national artificial intelligence strategy. While Djibouti has already built strong telecom infrastructure, advancing public sector digitalization and strengthening specialized skills remain key to fostering innovation and digital inclusion.
If finalized, the partnership could help Djibouti enhance cybersecurity, accelerate digital transformation of its administration, and develop a pool of local digital talent. For Romania, it offers an opportunity to extend its expertise in East Africa and deepen bilateral ties in technology and innovation.
This funding is intended to expand broadband infrastructure, strengthen digital public platforms, and develop employment-ready digital skills across Zambia.
Zambia has secured a $120 million grant from the World Bank to scale up its public digital infrastructure, a major step toward meeting national development goals under the Science, Technology, and Innovation Policy and Vision 2030. The announcement was made by Minister of Technology and Science Felix Mutati during the launch of the ABSA Mobi Tap mobile payment app in Lusaka on September 18.
The support comes through the Digital Zambia Acceleration Project (DZAP), part of Phase II of the Inclusive Digitalization in Eastern and Southern Africa Multiphase Programmatic Approach (IDEA MPA). The $2.48 billion regional program, approved by the World Bank Board on June 27, 2024, covers Angola, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Malawi, and COMESA as the coordinating regional bloc. Zambia is the fifth country to implement the program.
During a July 2024 visit to Lusaka, World Bank Managing Director and Chief Administration Officer Wengcai Zhang pledged $100 million in IDA financing for DZAP, alongside an additional $20 million in unguaranteed commercial financing. He said the project would expand broadband and last-mile infrastructure, strengthen digital public infrastructure, and support high-impact sectors including health, education, and agriculture.
Zhang explained that DZAP would nurture employment-ready digital skills and increase access to digitally enabled services across Zambia. He noted the project is aligned with government priorities under Vision 2030 and would improve efficiency in both the public and private sectors.
Ahead of full approval, expected from the World Bank Board in March 2025, a $6 million Project Preparation Advance was signed in October 2024. This enabled the Smart Zambia Institute to begin stakeholder consultations on the project’s Environmental and Social Management Framework, drawing participation from all ten provinces.
DZAP has four core components aligned with IDEA’s pillars. These include extending backbone and regional networks, supplying last-mile connectivity, and strengthening the enabling environment. Other priorities include developing digital ID and trust services, enhancing digital government, supporting regional trade facilitation, and fostering digitalization in key sectors while nurturing employment-ready skills.
The program is expected to have far-reaching implications. Improved connectivity will reduce the urban-rural digital divide, opening access to e-government services, digital health, and online education for millions. Recent statistics highlight the need for these investments. As of early 2025, Zambia had approximately 19.9 million mobile connections, accounting for 92.1% of the population. However, internet penetration stood at only 33%, meaning roughly two-thirds of Zambians remained offline. Broadband-capable mobile access was high, but many users still lacked reliable, affordable internet.
The program will also invest in digital skills, preparing Zambian youth for jobs in fintech, agritech, and other emerging sectors. By doing so, it aims to position Zambia not only as a consumer of digital services but as a regional hub for innovation and investment.
The project aligns with Zambia’s wider push to digitize services, modernize governance, and enhance financial inclusion.
Hikmatu Bilali
-
Government unveils e-mining cadastre to digitalize permits and authorizations.
-
Mining share of GDP rose from less than 1% in 2014 to nearly 4% in 2025.
-
Platform aims to cut delays, boost transparency and attract investors.
Côte d’Ivoire has officially launched the e-mining cadastre portal, a digital platform designed to modernize the management of mining permits and authorizations. The system was inaugurated on September 22 in Abidjan by Prime Minister Robert Beugré Mambé.
“The launch of the e-mining cadastre is a decisive step for the development of our mining sector, which has recorded strong growth over the past decade,” the prime minister said, stressing the government’s push for modern and transparent governance. Between 2012 and 2025, national gold output quadrupled, while manganese production increased tenfold, underscoring the sector’s momentum.
The new system covers the full cycle of mining titles, from applications and processing to delivery, monitoring and archiving. It is powered by Landfolio and hosted on a secure cloud infrastructure. More than 200 mining administration officials have been trained to operate it. Authorities say the tool will speed up procedures, align with international standards such as EITI, and help curb illegal mining.
The launch comes as the mining sector’s contribution to GDP has climbed from less than 1% before 2014 to nearly 4% today. The government aims to reach 6% by year-end, supported by promising deposits of gold, manganese, nickel and lithium, alongside reforms to attract investors.
Officials expect the portal to improve transparency, competitiveness and revenue collection, while ensuring more responsible resource management. Mines, Petroleum and Energy Minister Mamadou Sangafowa-Coulibaly said the ambition is to make Côte d’Ivoire a benchmark in Africa for responsible management of extractive resources within the next decade.
The launch signals a wider digital shift: African governments and companies are no longer just consumers of foreign AI systems, but are beginning to shape the technology around local realities, identities, and needs.
On September 20, 2025, on the sidelines of the 80th United Nations General Assembly (UNGA80), Nigeria’s Minister of Communications, Innovation, and Digital Economy, Dr. Bosun Tijani, officially launched the Nigerian Atlas for Languages & AI at Scale (N-ATLAS). The Atlas is an open-source facility designed to map the country’s rich linguistic diversity of country with artificial intelligence (AI) and power-inclusive chat solutions.
The first version of the project, N-ATLAS v1, is a multilingual and multimodal large language model that supports Yoruba, Hausa, Igbo, and Nigerian-accented English. Built on Meta’s Llama-3 8B architecture and fine-tuned with over 400 million tokens of multilingual instruction data, it is Nigeria’s most ambitious step yet toward embedding African voices in AI development. “This is the first step in a broader journey to make Africa a contributor and leader in shaping AI’s future,” said Tijani.
The project is powered by Awarri Technologies in partnership with the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA) and the National Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics (NCAIR). For Nigerians, the launch could transform how people interact with technology in their daily lives.
Language models like N-ATLAS make it possible to use apps, chatbots, and government services in local languages, not just English — helping millions who are more comfortable in Hausa, Igbo, or Yoruba. By making digital tools work in local tongues, the model breaks down barriers for communities left behind by the English-dominated internet.
With more than 500 native languages, Nigeria faces the risk of cultural erosion in the digital age. N-ATLAS helps preserve and digitize this linguistic heritage for future generations. Governments, schools, and businesses can deploy AI-powered platforms that communicate directly in people’s languages — from healthcare advice to education and customer support. This ensures more people can participate in the digital economy.
By investing in tools like N-ATLAS, Nigeria is positioning itself as a leader in African-led AI innovation. The model will enable researchers, entrepreneurs, and startups across the continent to develop culturally relevant AI solutions, while reducing their dependence on Western-trained systems that often fail to function effectively in African languages.
This movement is echoed across the continent, with similar initiatives gaining momentum. In South Africa, Lelapa AI’s InkubaLM supports languages such as Hausa, Swahili, Zulu, Yoruba, and Xhosa. Ethiopia’s Artificial Intelligence Institute is also advancing language technologies for Amharic, Afaan Oromo, Aff-Somali, and Tigrigna, integrating them into public services like the Smart Court system. These efforts reflect a continental awakening — one where African nations are reclaiming their linguistic space in the digital world and actively contributing to the global AI landscape.
Hikmatu Bilali