-
Pikelo combines artificial intelligence and pedagogy to remove barriers to spoken English mastery.
-
Founded in 2024, the app targets learners facing time constraints, confidence issues, and lack of conversation partners.
-
Pikelo offers a 24/7 AI-powered virtual coach that corrects mistakes in real time.
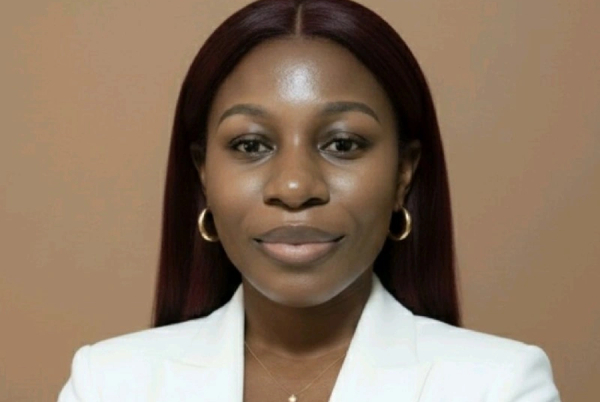
Miranda Anya is a Cameroonian technology entrepreneur. She co-founded and currently leads Pikelo as chief executive officer. She designed the application to improve spoken English efficiency through continuous interaction.
Founded in 2024, Pikelo targets users who want to improve their English but face recurring constraints. These constraints include the lack of conversation partners, fear of making mistakes, busy schedules, and low speaking confidence. The application addresses these challenges by offering continuous support and reducing learner isolation.
Consequently, Pikelo provides a simple, flexible, and always-available conversational environment. The platform allows users to practice without geographic or time limitations.
At the core of the platform, Pikelo deploys a virtual coach that remains available 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The coach allows users to practice English as often as needed, simulating interaction with a human conversational partner.
This repeated exposure integrates English into daily routines. As a result, users develop fluency through natural, constraint-free conversation practice.
Pikelo promotes a learning environment free from fear of mistakes. The virtual coach instantly corrects errors and guides users step by step through their learning journey.
This approach encourages consistent improvement while maintaining a supportive and confidence-building atmosphere that motivates users to speak more frequently.
Miranda Anya graduated from the University of Buea in 2015 with a bachelor’s degree in computer engineering. She later earned a master’s degree in artificial intelligence in 2024 from Nexford University.
She began her professional career in 2018 at Primeway Technologies in Dubai, where she worked as an IT sales engineer. In 2019, she joined World Attachments and assumed the role of business development manager.
Between 2020 and 2023, she worked as a UI/UX designer at Smartminds Studio. In parallel, she held the same position in 2021 at Peers Exchange Cameroon Agency.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
-
Genuka centralizes sales, inventory, and financial tracking for small businesses on a single platform.
-
Founded in 2024, Genuka targets merchants operating both online and offline, including social commerce.
-
Founder Wilfried Djopa combines entrepreneurship with his role as a software engineer at TheFork.
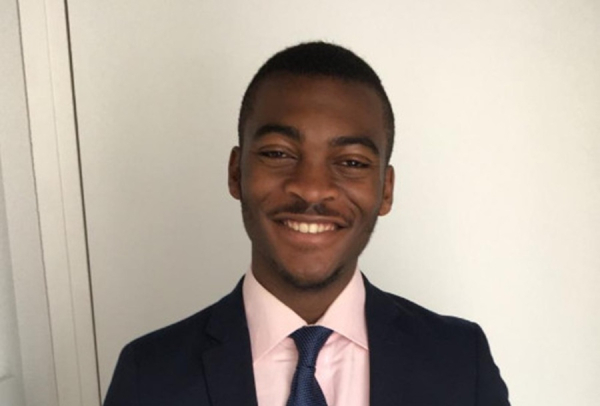
Wilfried Djopa is a Cameroonian software engineer and entrepreneur. He founded Genuka, an online platform that allows small businesses and merchants to monitor and manage their daily operations from a single interface.
Founded in 2024, Genuka targets entrepreneurs who sell products or services in physical stores, online shops, marketplaces, or through social media channels. The platform aims to help users, in Djopa’s words, “sell more, earn more, and manage less” by consolidating all operations into one system.
As a result, Genuka positions itself as an operational hub for fragmented and informal commercial activities.
The software provides daily tracking of sales and inventory levels. It triggers automatic alerts when stock levels decline to prevent shortages.
Genuka presents revenues, expenses, and margins through clear reports. These dashboards help users assess financial health and support faster and more informed decision-making.
Genuka allows businesses to list all products, including physical goods, digital items, and services. Users can assign prices, images, and descriptions to each product.
The platform groups products into collections based on seasons, promotions, or categories to simplify customer navigation. In addition, the tool supports the simultaneous management of multiple points of sale.
The platform also enables users to create a complete website to showcase their business and sell online. Users can customize design, layout, and content to reflect brand identity and target audiences.
Integrated marketing tools support customer acquisition and retention, strengthening sales performance beyond physical locations.
Alongside his entrepreneurial activity, Wilfried Djopa works as a software engineer at TheFork, a European online restaurant booking platform.
Before founding Genuka, he co-founded “La Mater” in 2019, a company providing services to individuals and businesses. He served as chief executive officer until 2024.
Djopa holds a master’s degree in digital systems engineering, obtained in 2020 from ESIGELEC, a generalist engineering school in France.
Djopa began his professional career in 2018 as a software development consultant at Junior Etudes ESIGELEC, a student association specializing in web and mobile development.
Between 2020 and 2022, he worked as a software development engineer at Ignifai, a French company specializing in artificial intelligence platforms.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
-
Uganda signed a public-private partnership to establish an ICT innovation hub in Mbale focused on skills and jobs.
-
The project includes blockchain-based digital certification to reduce credential fraud.
-
Authorities aim to align youth training with global digital labor demand.
The Ministry of ICT and National Guidance announced on February 19, the signing of a partnership with Spotlight on Africa and Algorithmic Partners.
The agreement provides for the creation of an ICT innovation hub in Mbale. The hub aims to strengthen digital skills among Ugandan youth and support local technology entrepreneurship.
According to authorities, the initiative marks a shift from policy intent to implementation in Uganda’s digital development agenda. The project relies on public-private collaboration to expand access to in-demand skills, stimulate local innovation, and promote economic empowerment, particularly for women.
The future center will offer training ranging from basic digital literacy to advanced competencies, including coding, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technologies.
The program also integrates a blockchain-based digital certification system. The system aims to secure qualification verification and reduce document fraud.
By strengthening trust between training institutions, employers, and graduates, the tool should improve transparency in the digital labor market and support the emergence of a structured, skills-driven innovation ecosystem.
Beyond training, the project seeks to expand access to digital public services in underserved areas and energize local innovation ecosystems.
The initiative aligns with Uganda’s national digital roadmap, which prioritizes digital infrastructure, skills development, cybersecurity, and data protection. The roadmap aims to build an inclusive, job-creating digital economy.
Programs such as the DigiTrack mobile computer lab have already trained more than 11,000 people nationwide over the past two quarters. These programs have included young people with special needs by delivering digital skills directly to communities.
The initiative also complements Uganda’s national business process outsourcing strategy, which aims to connect English-speaking young professionals to global markets.
The initiative also reflects broader continental trends. According to the World Bank and the International Finance Corporation, sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills for approximately 230 million jobs by 2030.
The fourth industrial revolution accelerates the digital transformation of labor markets and creates large-scale demand for qualified talent. As a result, centers such as the Mbale hub provide practical responses by training youth for future jobs and supporting economic and social inclusion at scale.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
- Dakar-based healthtech MedSen digitizes student medical records across Senegal.
- The platform claims coverage of more than 6 million students nationwide.
- Founder Ndeye-Talla Dioum launched the startup in 2020 to modernize school health systems.
Designed as a Senegalese medical monitoring platform for students, MedSen seeks to digitize the entire school health pathway, from prevention to individualized follow-up. The solution addresses a frequently overlooked challenge: coordination among schools, medical staff, parents and health authorities. Dakar-based entrepreneur Ndeye-Talla Dioum launched the startup in 2020.
“MedSen was born from our strong desire to leverage our local and international experience and expertise in service of a cause close to our hearts: improving the health of our populations in Senegal and Africa through innovative technological solutions,” the startup stated.
The platform operates through the creation of a unique digital health record for each student. The system centralizes essential information, including medical check-ups, vaccination history, consultations, screenings and referrals to healthcare facilities. The company aims to replace fragmented monitoring and paper-based records with a secure database accessible to authorized professionals.
MedSen also integrates operational tools for school medical teams. Medical inspectors can organize and monitor vaccination campaigns, visual and nutritional screenings, while accessing real-time statistical dashboards to guide public health policies at local and national levels.
In addition, a dedicated portal enables parents to monitor their children’s health, receive notifications, provide digital consent and communicate with medical teams. The feature strengthens continuity between school and family.
Through this approach, MedSen reflects a broader trend across Africa, where local digital solutions are supporting the modernization of health systems while addressing on-the-ground realities. The healthtech company reports that it covers more than 6 million students and operates in all regions of Senegal.
This article was initially published in French by Adoni Conrad Quenum
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
Plus Incubation Hub has launched the Plus Factor Grant Program to support high-potential African entrepreneurs from ideation to growth. The eight-week initiative offers equity-free grants of up to 1 million naira (about $740), alongside mentorship, training and market access support. Applications close online on March 15, 2026.
Morgan Stanley has launched the 2026 edition of its Inclusive Ventures Lab, a five-month accelerator offering mentorship and up to $250,000 in funding to early-stage startups and nonprofits. The program targets ventures delivering measurable impact in the environment, healthcare, economic empowerment or education. Applications, open to Seed through Series A companies, close on March 31, 2026.
The Connect NextGen Hackathon 2026, a joint initiative by Ericsson, the Nigerian government and Tech Revolution Africa, is now accepting applications from local startups and teams with a working prototype. The eight-week program offers intensive support, including mentorship and investor networking, and concludes with a final Demo Day. Applications are open until Tuesday, March 10, 2026, on the official platform.
-
GSMA will award grants of £100,000 to £200,000 ($135,000 to $270,000) over 15 to 18 months.
-
The fund targets Africa, Central and South America, and South and Southeast Asia.
-
Eligible startups must provide at least 25% co-financing of total project costs.
The Global Association of Mobile Network Operators (GSMA) announced on Sunday, February 23, the launch of an Innovation Fund to support small enterprises and startups that use mobile technologies to advance clean energy transition and digital inclusion. The initiative targets Africa, Central and South America, as well as South and Southeast Asia.
GSMA will provide grants ranging from £100,000 to £200,000 ($135,000 to $270,000) over a period of 15 to 18 months. The organization designed the fund to back commercially viable solutions that combine environmental impact with business sustainability.
“We invest in companies that use mobile technology to strengthen digital inclusion and support a sustainable energy transition, while offering circular solutions that extend device lifecycles and make connectivity more affordable for underserved communities,” said Philippe Bellordre, Acting Head of Mobile for Development at GSMA.
Eligible companies must register legally in one of the targeted regions, employ up to 250 people and demonstrate both revenue generation and an active user base. The fund requires beneficiaries to contribute at least 25% of total project costs through matching financing.
The program will support initiatives such as device repair, refurbishment and reuse, as well as trade-in programs and responsible collection and recycling of electronic waste. These solutions aim to extend device lifespans, reduce e-waste and improve connectivity affordability for underserved populations, thereby strengthening socio-economic inclusion.
In addition to financial support, selected startups will receive ongoing monitoring, evaluation and learning assistance, as well as increased visibility through GSMA publications and platforms.
Applications will remain open until April 6, 2026 at 23:59 UK time. Interested companies can submit applications through the dedicated online portal.
https://gsma-innovation.fluxx.io/user_sessions/new
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
- Madagascar converted CNTEMAD into a Public Virtual University backed by $3 million in financing.
- The university aims to enroll up to 49,000 students annually by 2029 and produce 10,000 additional graduates each year.
- The World Bank estimates that 230 million jobs in Sub-Saharan Africa will require digital skills by 2030.
The National Center for Tele-Education and Distance Learning (CNTEMAD) has transitioned into a Public Virtual University. Authorities officially launched the project on February 20 in Antananarivo. The World Bank is supporting the initiative through its DECIM program to expand access to higher education via digital tools and strengthen Madagascar’s human capital.
The new digital university operates on a platform developed in partnership with SAYNA. The platform manages the entire student journey remotely, from enrollment to examinations and thesis defenses. The project seeks to address growing demand for university education, particularly in remote areas, while reducing logistical costs and modernizing teaching methods.
The government allocated $3 million in financing to the project. The Public Virtual University plans to enroll up to 49,000 learners annually by 2029 and to generate 10,000 additional graduates each year.
The reform aligns with Madagascar’s national strategy for human capital development and digital transformation. Afrobarometer reported that more than 40% of young people aged 18 to 35 were unemployed in 2024. Policymakers view access to market-relevant training as a strategic lever to improve employability.
Survey data identified lack of training or preparation as the main barrier to employment at 30%, followed by lack of experience at 27% and mismatch between academic qualifications and employer needs at 16%. These constraints highlight the need for innovative and inclusive education solutions.
In parallel, the Public Virtual University project includes modernization of technical infrastructure and expansion to 16 regional centers equipped with autonomous solar solutions. The infrastructure will ensure operational continuity in areas with limited electricity access.
The initiative complements national digital training programs such as ASAN’AI and Skills4Job, which aim to equip young people with in-demand competencies, particularly in digital professions and customer relations.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
- Sonatel and Senelec signed a strategic agreement on February 20 in Dakar.
- Senegal counts 11.3 million Internet users, representing 60.6% penetration in early 2025.
- National electricity access exceeds 84%, with near-universal coverage in urban areas.
Sonatel Group and Senelec announced on Friday, February 20, that they signed a strategic agreement in Dakar to accelerate the digital transformation of their operations and enhance the quality of energy and telecom services. Chief Executive Officers Brelotte Ba and Papa Toby Gueye formalized the partnership.
Un partenariat stratégique au service des usagers !
— Orange Business Sénégal (@obs_senegal) February 20, 2026
Hier, le @GroupeSonatel et la @Senelecofficiel
ont franchi une étape majeure avec la signature d’une convention pour un partenariat stratégique mené par Monsieur Brelotte Ba, Directeur Général du Groupe Sonatel, et Monsieur… pic.twitter.com/89fgO96dCq
The agreement provides for closer convergence between the operational capabilities of both groups to optimize performance and strengthen service quality. The partnership also includes the development of digital services for users, particularly through continuous improvement of customer relations and deployment of digital solutions to streamline access to essential services.
The two companies aim to reinforce synergies between energy infrastructure and communication networks to support Senegal’s national digital transformation ambitions.
A Convergence Driven by Infrastructure Expansion
The initiative aligns with Senegal’s broader strategy to accelerate digital transformation and modernize strategic infrastructure. Policymakers increasingly view convergence between energy and connectivity as a structural driver of economic performance.
According to DataReportal, Senegal counted approximately 11.3 million Internet users at the beginning of 2025, representing a penetration rate of 60.6% of the population. At the same time, electricity access exceeded 84% nationwide, with near-universal coverage in urban areas, according to the World Bank.
Against this backdrop of simultaneous expansion of energy and digital networks, cooperation between Sonatel and Senelec seeks to improve the quality and reliability of essential services for users. Rapid growth in digital usage, including mobile financial services, online administrative platforms and connected solutions, is increasing interdependence between reliable energy infrastructure and robust telecom networks.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
More...
- Daniel Bekele co-founded Ashewa Technology in 2020 to support SME digital transformation in Ethiopia.
- The company offers solutions including Nehabi, Smart ERP and the e-commerce platform Ashewa.com.
- Ashewa Technology targets private firms, large corporations and public institutions.
Ethiopian entrepreneur Daniel Bekele co-founded and leads Ashewa Technology as Chief Executive Officer. He supports small and medium-sized enterprises, large companies and public institutions in their digital transition.
Founded in 2020, Ashewa Technology positions itself as a strategic partner for professionals seeking to modernize operations, improve efficiency and access new markets through digital tools designed for the African context.
The company develops several technology solutions. Through Nehabi, it enables businesses to create showcase or professional websites without programming skills. It also offers Smart ERP, a management software solution that helps organizations of all sizes track activities, structure operations and support growth.
Through its e-commerce platform Ashewa.com, Ashewa Technology facilitates the buying and selling of products in Ethiopia. The platform aims to simplify trade and unlock new commercial opportunities. The company has also developed Hybrid Learning, a solution that modernizes education by combining digital tools with structured pedagogical approaches.
In addition, Ashewa Technology designs customized web and mobile applications tailored to the specific needs of private enterprises and public organizations. The company also provides domain name registration and hosting services to ensure stable and high-performance online deployment of websites and applications.
Daniel Bekele earned a diploma in software development and digital marketing in 2019 from Ubunifu College in Kenya. He also obtained an advanced national diploma in e-commerce and artificial intelligence in 2021 from Indian Technology College. In the same year, he earned a diploma in education with a specialization in business operations management and artificial intelligence from ASEAN Online Education.
He began his career in 2015 as a sales and digital marketing specialist at JTMM Africa, a trading company. In 2016, while studying in Kenya, he developed a lead generation tool called UBU. In 2018, he joined Kiyaye as a software developer, contributing to the development of its website and social networking application.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Adapted in English by Ange J.A de Berry Quenum
MarkHack 5.0 will be held in Lagos on 5 June 2026. The conference, themed “The Culture Algorithm: AI and the Human Experience,” will bring together marketers, content creators, startup founders and policymakers to explore how artificial intelligence is reshaping culture, media and everyday life. The programme includes keynote speeches, panel discussions, a hackathon and demonstrations of emerging AI-driven solutions.
The 2026 National Cleantech Innovation Challenge seeks local solutions to South Africa’s energy, climate-related and economic-development objectives. The competition comprises nine province-level challenges, spanning regenerative agriculture, sustainable transport and renewable energy. It is open to innovators, small and medium-sized enterprises and research teams. Apply via the NCIC website by 21 April 2026.
Kenyan entrepreneurs developing emission-reduction solutions can now apply to the Climate Finance Accelerator to make their projects investment-ready. Funded by the UK government, the program provides technical support, strengthens funding proposals, and connects projects with investors, with a particular focus on those seeking more than $3 million. Applications close on March 11, 2026.