- MbiyoPay integrates mobile money, bank cards, crypto and digital tools into a single payment platform.
- The app is already operational in the DRC, Cameroon and Côte d’Ivoire after a 2023 launch.
- Founder Joel Mirimo previously created Maxuschain, a crypto-trading platform supporting 30+ cryptocurrencies.
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, entrepreneur Joel Mirimo has launched MbiyoPay, an application that consolidates digital payments by integrating mobile money, bank cards, cryptocurrencies and other digital solutions. The company aims to simplify and secure financial transactions for users across multiple African markets.
Mirimo, the founder and CEO of MbiyoPay, developed the platform to help consumers manage payments from a single smartphone. The app reflects his broader goal to streamline day-to-day transactions and expand access to digital financial tools.
MbiyoPay, founded in 2023, enables users to create virtual cards, receive money, pay bills and buy mobile credit without switching between multiple services. The platform centralizes transactions and reduces fragmentation by allowing users to collect payments from clients or receive transfers from individuals in one digital environment.
The app accepts several payment methods, including mobile money, bank cards, cryptocurrencies, QR codes, payment links and its own dedicated virtual card. MbiyoPay allows users to recharge the virtual card and make secure online payments on international platforms.
MbiyoPay has already rolled out services in several African countries, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, Cameroon and Côte d’Ivoire. Users can verify availability in each market directly through the app. The platform also lets users transfer funds to mobile money accounts, bank accounts or crypto wallets depending on their preferred channel.
Before launching MbiyoPay, Mirimo founded Maxuschain in 2022, a platform offering instant cryptocurrency trading via mobile money. Maxuschain supported more than 30 cryptocurrencies and integrated four blockchains.
Mirimo holds a bachelor’s degree in marketing and commercial and financial sciences obtained in August 2025. He worked as a payment agent and broker at Deriv, an international financial company, from 2021 to September 2025. He also served as business development director at Afgig, a 100% African marketplace connecting continental talent to global markets, from 2021 to 2024.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
-
Off-grid solar supplied 561 million people in 2023 and accounted for 55% of new electricity connections in Sub-Saharan Africa between 2020 and 2022.
-
Private operators like Sun King, Bboxx and Orange Energies expanded rapidly and secured major financing agreements in 2023–2024.
-
The sector needs $3.6 billion per year until 2030, including 40% in subsidies, to electrify the poorest and most remote households.
The lack of adequate grid infrastructure has turned Africa into a testbed for agile energy solutions. The rapid adoption of solar technologies is transforming millions of lives, although persistent constraints continue to slow progress.
Africa remains the global epicenter of energy poverty. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that most of the 730 million people without electricity live in Sub-Saharan Africa. The African Development Bank (AfDB) estimates that over 600 million Africans, nearly half the continent, still lack access to electricity.
AfDB states: “For these people, daily life is a struggle illuminated by the dim glow of kerosene lamps or the intermittent hum of diesel generators. These stopgap solutions are costly and polluting, perpetuating cycles of poverty and environmental degradation.” AfDB warns that the number of people without electricity will remain largely unchanged without “bold and immediate measures.”
Given the implications for productivity, education and health, the IEA considers decentralized solar a strategic priority for the continent.
The World Bank and AfDB partnered under the Mission 300 initiative to connect 300 million Africans by 2030. The World Bank states that off-grid solar represents the quickest and most cost-effective option to electrify 41% of the global population still without power by 2030.
Off-grid solar systems served 561 million people in 2023. Between 2020 and 2022, they provided 55% of new connections in Sub-Saharan Africa. The World Bank adds that off-grid solar remains cheaper and faster to deploy than grid or mini-grid connections for current levels of demand.
Growing network challenges—low coverage, limited capacity, aging infrastructure and expensive tariffs—continue to push households and firms toward off-grid solutions. The World Bank’s Off-Grid Solar Market Trends Report 2024 estimates that generators supply nearly 9% of the region’s electricity and cost households $28–50 billion per year in fuel, plus an additional 10–20% in maintenance.
Solar kits reduce energy costs, extend business hours, strengthen cold chains and boost small enterprise revenues. Electricity improves daily life by providing lighting, cooling, refrigeration, information access and nighttime security. Solar pumps help households adapt to drought and increase agricultural productivity, while refrigeration reduces post-harvest losses and preserves vaccines in health centers.
The Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP) reports rapid growth in “productive uses” of off-grid systems across agro-processing, crafts and services.
ESMAP states: “Off-grid solar systems allow households, businesses and farmers to use electricity productively and generate income. Among 79,000 surveyed off-grid customers in 31 countries, 86% of solar pump users increased productivity and 60% expanded cultivated areas, resulting in higher incomes for 88% of them.” ESMAP adds that 88% of refrigerators served productive uses, and 81% of users reported improved quality of life. In 2023, more than 3 million people operated a business using home solar systems.
The Pay-as-you-go (PAYGo) model accelerated sector growth by allowing customers to pay for equipment in installments using mobile money, scratch cards, airtime credit or cash.
Private Sector Drives Expansion
Startups strengthened their position between 2018 and 2024, even as financing dropped from $194 million to $192 million in 2024 after peaking at $425 million in 2023.
Sun King became a leading operator and supplies solar energy to 30% of Kenyan households. The company signed a $156 million securitization deal in July 2024 with ABSA, Citi, Co-operative Bank of Kenya, KCB Bank and Stanbic Bank Kenya. This deal follows a $130 million 2023 transaction aimed at distributing 3.7 million solar products in Kenya.
Bboxx expanded significantly over the past five years. The acquisition of PEG in 2022 extended its footprint into Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana and Mali. The company now operates in about ten countries and supplies over 2.5 million people with solar products.
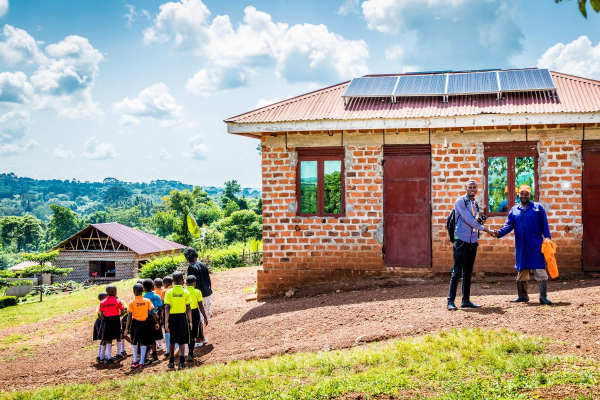
Telecom operator Orange also made off-grid energy a strategic priority. Through Orange Energies, the group connected over 600,000 households in 2024, giving nearly 4 million people access to electricity across 13 countries. The company developed the Orange Smart Energies IoT platform to support PAYGo and smart metering and now partners with vendors, utilities and mini-grid developers.
Orange Energies supplies solar panels, smart batteries, LED lamps, USB sockets and rural household appliances—including fans, freezers, TVs and radios—in partnership with Koolboks, Biolite, Sun King and Solar Run.
International institutions increasingly recognize Orange Energies’ expertise. In June 2024, the company won a €150,000 AFD tender to electrify more than 400 rural localities in Côte d’Ivoire under the EU-funded MAX project. In September 2024, the World Bank and GIZ awarded Orange Energies a $360,000 contract to equip 8,000 off-grid households in Liberia with autonomous solar solutions by June 2025.
Orange Energies also signed a public-private partnership in Guinea with the Rural Electrification Agency (AGER) and IPT PowerTech to build a mini-grid that will supply electricity to six localities.
Off-grid solar is no longer experimental. It has become an industrial, financial and social sector that electrifies communities, generates income and reshapes daily life. Yet several risks threaten long-term momentum.
Persistent Risks Threaten Scale
Market forces alone cannot electrify rural Africa. Reaching the poorest and most remote households requires public funding through subsidies, guarantees and concessional finance. The sector estimates that it needs $3.6 billion annually through 2030 to electrify those for whom off-grid solar is the lowest-cost solution. About 40% of this amount must come from targeted subsidies.
Extreme poverty limits the scale of PAYGo. Only a minority of rural households can afford monthly payments. Logistics challenges in remote or conflict-affected areas can raise final prices by 57%, pushing households back to candles, kerosene or shared generators. Only 22% of unelectrified households globally can afford PAYGo installments—a figure that drops to 16% in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Low household incomes directly weaken the financial health of solar companies. PAYGo repayment rates stagnate around 62%, and one in four customers faces payment difficulties. Most startups borrow in foreign currencies but collect revenue in local currencies, exposing them to FX risks.
Inflation and currency depreciation add further pressure. In Nigeria, the price of basic solar lanterns rose 91% to 300% in 2023 in local currency, erasing gains from lower global component prices.
Africa’s dependence on imports and the lack of local assembly also constrain scale. Without domestic assembly, reliable maintenance networks or affordable spare parts, systems break down frequently and leave households without electricity. Low-quality solar products—estimated at 70% of sales—undermine consumer trust. Shortages of skilled technicians in remote areas further hinder deployment.
Muriel Edjo
-
Algeria launched a national digital platform on December 1 to report corruption in the social sector.
-
Transparency International ranks Algeria 107th globally in the 2024 Corruption Perceptions Index.
-
Nearly 9,500 civil servants have already been trained to use the new reporting tool.
Algeria launched a digital platform to help citizens and public officials report corruption in the social sector, strengthen transparency, and improve trust in public institutions.
The country continues to face systemic corruption that undermines public services and weakens citizen confidence. Consequently, authorities aim to modernize governance tools and reinforce accountability across the administration.
The Ministry of National Solidarity, Family and Women’s Affairs launched the national platform on December 1. The tool, available on both mobile and desktop, enables users to report suspicious practices, upload digital evidence, and track the status of their submissions.
Minister Soraya Mouloudji said the platform “forms part of the implementation of the national strategy to combat corruption and strengthen integrity, which is based on public ethics, the promotion of a culture of integrity within institutions, and improved transparency in the management of public funds.”
The platform centralizes all tools required for effective processing of corruption alerts: a structured reporting form, a secure space to upload supporting documents, an option for anonymous submissions, and a dashboard that informs users of the progress of their cases.
The ministry intends to improve administrative responsiveness, shorten processing times, and ensure strict traceability of all reports.
The launch comes as Algeria continues to struggle with governance issues. Transparency International’s Corruption Perceptions Index 2024 ranks Algeria 107th out of 180 countries, with a score of 34 out of 100, reflecting persistent public-sector corruption concerns.
According to the ministry, nearly 9,500 public agents have already received awareness and training sessions to ensure proper use of the platform and promote a culture of transparency in public services. The government considers these skills essential to guarantee the system’s reliability and the credibility of follow-up actions.
Although the platform could democratize reporting, improve the quality of evidence, and increase public pressure for stronger anti-corruption measures, its success depends on several key factors: serious investigations, effective whistleblower protection, and public visibility of enforcement outcomes.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
-
Mywagepay, founded in 2021, enables employees to access earned wages instantly through a digital platform.
-
The fintech integrates customizable credit products directly into SMEs’ services, helping firms boost revenues and customer acquisition.
-
CEO Beth Wambui Mwangi positions the platform as both a financial-wellbeing tool for employees and a growth accelerator for businesses.
Kenyan entrepreneur Beth Wambui Mwangi, founder and chief executive of Mywagepay, is reshaping how companies and employees access financial services. She is positioning her fintech as a tool that converts everyday financial challenges into opportunities for growth and inclusion.
Mwangi founded Mywagepay in 2021. The company develops a digital platform that creates or integrates credit products into business services. The system helps companies attract customers, increase revenues and accelerate growth.
The platform also gives workers quick access to wages already earned, allowing them to manage cash-flow needs without waiting for payday.
Mywagepay allows employees to receive a portion of their salary before the official payday through a secure mobile application. Users complete the process entirely online through a few simple steps, which ensures a smooth and fast experience.
Beyond wage advances, the company offers financial-wellbeing tools that help workers improve money management. These services include budgeting features, savings options and investment guidance. Mywagepay aims to encourage healthier and more sustainable financial habits across the workforce.
The fintech provides small and medium-sized enterprises with embedded credit solutions that integrate directly into their products or operations. Mywagepay designs these tools to help businesses offer financing to customers or employees without building their own financial infrastructure.
The company emphasizes personalized support to adapt each credit solution to the specific needs of individual SMEs.
Mwangi received a bachelor’s degree in education from Mount Kenya University in 2015. She also earned a master’s degree in business administration and management from the United States International University-Africa in 2022.
This article was initially published in French by Melchior Koba
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
The Egyptian startup Rology, an AI-assisted teleradiology platform, has closed a new funding round with investors including the Philips Foundation, Johnson & Johnson Impact Ventures, Sanofi Global Health’s impact fund and MIT Solve Innovation Future. The funding will be used to expand its network of radiologists and improve access to rapid diagnostics across 13 countries in Africa and the Middle East.
Mobile money integration specialist Tola Mobile is expanding its payment platform in Africa by adding card payment capabilities. Operating in 23 countries, Tola Mobile provides merchants with a single API that allows them to process deposits, withdrawals and real-time settlements through both mobile wallets and cards.
Nigerian fintech company FairMoney, through its subsidiary MyCredit Investments Limited, has had its long-term rating upgraded to BBB+ and its short-term rating to A2 by Global Credit Ratings. The upgrade reflects the strength of its business model, well-managed credit-risk growth and 2024 revenue of more than 112 billion naira, equivalent to over 77 million dollars.
- Stokvel Academy provides online courses and tools to help South Africans create and manage stokvels.
- The platform, launched in 2017 in Soweto by Busisiwe Skenjana, aims to expand financial education and reduce youth unemployment.
- The initiative seeks to modernize traditional collective-saving groups and strengthen financial inclusion in underserved communities.
Stokvel Academy, an e-learning platform developed by the Soweto-based start-up of the same name, offers online courses, educational resources and practical tools designed to help individuals and communities create or join stokvels, the traditional collective-saving groups widespread in South Africa. The platform positions itself as a response to limited access to formal credit and low levels of financial literacy.
Busisiwe Skenjana launched the start-up in 2017. She said, “By training young agents, we do not only tackle unemployment, but we also give stokvels the means to become stronger and more resilient.” Her approach combines skills development with community-driven financial empowerment.
The platform hosts a structured catalogue of modules covering basic saving principles, financial planning, cash-flow management, governance of savings groups, risk assessment and investment strategy. Users access these tools through a web browser and learn at their own pace. Stokvel Academy aims to make financial education inclusive by lowering barriers to understanding collective-saving mechanisms.
The platform blends tradition with technology to update a well-established social model. Existing stokvels can use the training to strengthen internal governance, prevent conflicts and improve long-term sustainability. New members can rely on the tools to adopt structured saving practices from the outset.
Limited access to banking services continues to affect a large share of South Africans. Stokvel Academy positions its services as an alternative that supports financial inclusion, capacity building and community empowerment. By training informed and responsible savers, the platform seeks to reinforce household resilience, stimulate local investment and promote forms of solidarity-based economic activity adapted to African realities.
This article was initially published in French by Adoni Conrad Quenum
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
- Côte d’Ivoire launched Tradepost to digitalize postal logistics and ease cross-border trade in ECOWAS.
- Authorities expect the system to accelerate customs procedures, reduce logistics costs and provide full shipment traceability.
- The initiative targets improved access to African and international markets for Ivorian SMEs.
Côte d’Ivoire launched the Tradepost project on December 1 in Abidjan to modernize postal logistics and facilitate cross-border commerce within ECOWAS. The Universal Postal Union (UPU), La Poste de Côte d’Ivoire and the West African Postal Conference (CPEAO) jointly support the initiative. The project signals a new phase in regional economic integration and in the digitalization of postal services.
Assoua Raymond, chief of staff at the Ministry of Digital Transition and Digitalization, said Tradepost will “accelerate customs procedures through digitalization, reduce logistics costs and delivery times, while offering full shipment traceability.” He added that the platform represents “a strategic instrument to connect Ivorian SMEs to African and international markets.”
Tradepost aims to digitalize and harmonize procedures linked to trade flows, including parcel declaration, processing, tracking and customs formalities. It also seeks to connect users to regional and global e-commerce platforms. Authorities designed the system to remove long-standing barriers to cross-border trade in West Africa, such as fragmented regulations, high logistics costs, slow procedures and weak integration of digital ecosystems.
The launch aligns with the rapid rise of digital trade in West Africa. Improved connectivity, broader digital public services and the growth of online-commerce platforms drive this momentum. Côte d’Ivoire stands out in this trend. The country’s e-commerce market reached more than CFA280 billion ($495.5 million) in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 11.3% through 2027, according to Ivorian e-commerce industry stakeholders.
Authorities expect Tradepost to strengthen parcel traceability and harmonize procedures across borders. They said the system should reduce obstacles to regional commerce, improve market access for artisans, farmers and young entrepreneurs, and support a more transparent and efficient e-commerce ecosystem in ECOWAS. The data-driven approach will allow policymakers to identify bottlenecks, guide investment and sustain long-term digital and economic integration.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
Zazu, a digital banking platform designed for entrepreneurs and small businesses, recently raised $1 million in a pre-seed funding round from African and European investors.
The startup is currently active in South Africa and Morocco, where it integrates with key payment providers such as Paystack and Ozow. Zazu plans to accelerate its rollout now, ahead of a major pan-African expansion scheduled for 2026.
More...
British fintech company Wise has received conditional approval from the South African Reserve Bank to operate as an authorized foreign-exchange intermediary, allowing it to offer international transfers to consumers.
The approval will enable South Africans to send money abroad at the mid-market exchange rate, with all fees disclosed upfront. The move comes amid rising demand for faster and cheaper cross-border payments in the region.
The D-Prize global competition is accepting applications from African and international entrepreneurs developing solutions to reduce extreme poverty.
Selected startups working in sectors such as health, water, agriculture, energy and education can receive up to $20,000 in seed funding to launch a pilot.
The application deadline is Jan. 4, 2026.
-
Togo integrates three new procedures online: renunciation of nationality, reinstatement of nationality, and modification of patronym or matronym.
-
The national portal now centralises 101 digital public services, including passports, residency cards and nationality certificates.
-
The UN’s 2024 EGDI report ranked Togo 161st out of 193, highlighting a major digitalisation gap the government actively seeks to close.
Togo aims to digitise all public services in the coming years to simplify administrative processes and improve access for all citizens. The addition of new online procedures confirms the progress of this nationwide transformation.
Togo continues to modernise its administration by adding three new services to the national portal service-public.gouv.tg. Citizens can now complete online the renunciation or reinstatement of Togolese nationality and the modification of their patronym or matronym.
The Ministry of Justice and Human Rights leads these digital procedures as part of a methodical modernisation effort. The platform now enables users to complete entire processes remotely: application submission, real-time tracking and receipt of decisions. Officials strengthened the national digital one-stop shop to centralise administrative services and improve accessibility.
This deployment comes as Togo accelerates the digitalisation of administrative services. In recent months, the national portal added major services, including applications for nationality certificates, passport renewals, residence permits, criminal records, construction permits and other formalities. With these additions, the platform now offers 101 online services.
The integration of the three new procedures addresses key priorities: reducing citizens’ travel, increasing procedural transparency, shortening processing times and improving administrative efficiency. The expansion also strengthens administrative inclusion by enabling citizens—especially those far from urban centres—to access essential services without geographic constraints.
This acceleration of digital transformation occurs as Togo works to close a significant gap in public-service digitalisation. The 2024 UN E-Government Development Index (EGDI) assigned Togo a score of 0.3920, ranking the country 161st out of 193, a result that underscores the scale of the challenges ahead. The progress achieved in recent months demonstrates the government’s determination to modernise public administration, improve accessibility and integrate Togo’s public sector into the digital era.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum
-
Enovation Factory and UNDP Cameroon launched Scale 32, a 14-month national programme to support 32 tech startups.
-
The programme provides intensive training, mentorship, workspace access and investor matchmaking, followed by 12 months of alumni support.
-
Cameroon seeks to strengthen its technology ecosystem amid low startup survival rates, weak governance and limited access to capital.
Cameroonian startups continue to struggle to attract investment as limited managerial expertise and weak ecosystem structuring hinder their growth. Observers argue that targeted support remains essential to improve competitiveness and unlock financing opportunities.
Enovation Factory, a Cameroon-based incubator and accelerator, launched in partnership with UNDP Cameroon a national 14-month initiative named Scale 32. The programme aims to support 32 technology startups by addressing their main barriers to growth, including access to capital, management skills and investor networks.
The programme unfolds in two phases. The first cohort will receive six months of intensive support from January to June 2026. The second cohort will benefit from a similar cycle from June to December 2026.
Enovation Factory will integrate selected startups into one of its two streams: Newbie, which targets early-stage or ideation-level projects, and Cracker, which targets operational startups seeking accelerated growth. The support package includes specialised training, mentorship, workspace access and connections with institutional partners and investors.
Enovation Factory will transition each startup into its Alumni programme after the six-month support phase. The incubator will provide an additional 12 months of follow-up, which includes access to its network, financing opportunities and major ecosystem events. The structure aims to ensure that each company consolidates the skills and gains achieved during the programme.
The initiative comes as Cameroon seeks to fortify its technology ecosystem and stimulate job creation. Policymakers attempt to complement existing sector-building efforts by addressing low startup survival rates and the weak governance that affects many early-stage companies.
However, challenges persist. The small volume of capital raised by local startups, the limited number of firms able to attract investors and the region’s low share of venture-capital flows underscore the need for deeper structural reforms. Analysts stress the need to strengthen corporate governance, improve investor appeal, reinforce institutional support and enhance the visibility of Cameroonian startups on the global stage.
Startups operating in technology, agritech, healthtech, fintech, edtech, green economy and other innovative sectors may apply before 18 December via the link provided by Enovation Factory: https://www.enovation-factory.com/postuler.
This article was initially published in French by Samira Njoya
Adapted in English by Ange Jason Quenum